作者:【吴业亮】
博客:https://wuyeliang.blog.youkuaiyun.com/
一、存储模型
1、如果将存储系统比作一个排队模型
1)、去前台取单号
2)、等待排在你之前的人办完业务
3)、轮到你去某个柜台
4)、柜台职员帮你办完手续1
5)、柜台职员帮你办完手续2
6)、柜台职员帮你办完手续3
7)、办完业务,从柜台离开
2、如何评估银行的效率呢:
服务时间 = 手续1 + 手续2 + 手续3
响应时间 = 服务时间 + 等待时间
性能 = 单位时间内处理业务数量
3、那银行如何提高效率呢:
增加柜台数
降低服务时间
4、排队系统或存储系统的优化方法是
增加并行度
降低服务时间
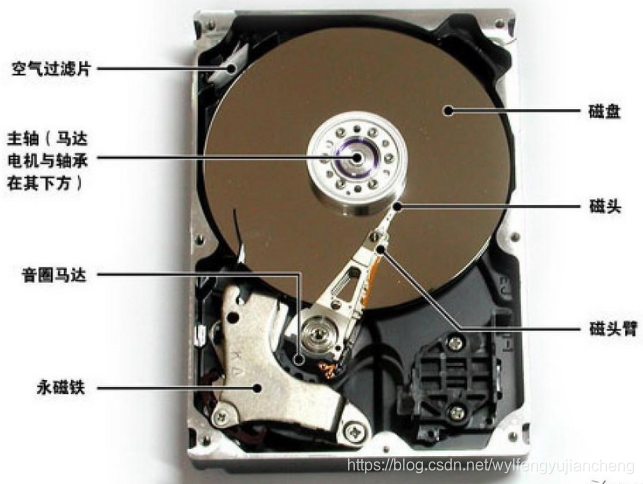
二、机械盘存储原理
每个硬盘都有一个磁头(相当于银行的柜台),硬盘的工作方式是:
1)、收到IO请求,得到地址和数据大小
2)、移动磁头(寻址)
3)、找到相应的磁道(寻址)
4)、读取数据
5)、传输数据
则磁盘的随机IO服务时间: 服务时间 = 寻道时间 + 旋转时间 + 传输时间
对于10000转速的SATA硬盘来说,一般寻道时间是7 ms,旋转时间是3 ms, 64KB的传输时间是 0.8 ms, 则SATA硬盘每秒可以进行随机IO操作是 1000/(7 + 3 + 0.8) = 93,所以我们估算SATA硬盘64KB随机写的IOPS是93。一般的硬盘厂商都会标明顺序读写的MBPS。
三、使用fio性能测试
1、安装fio测试工具
# yum install fio -y
2、创建配置文件fio.conf并执行测试
# fio fio.conf -output=fio-all.log
配置文件如下:
[global]
ioengine=libaio
time_based
direct=1
thread
group_reporting
randrepeat=0
norandommap
numjobs=1
ramp_time=60
runtime=1200
size=500G
filename=/dev/rbd0
[randread-4k-io32]
bs=4k
iodepth=32
rw=randread
stonewall
[randwrite-4k-io32]
bs=4k
iodepth=32
rw=randwrite
stonewall
[randread-8k-io32]
bs=8k
iodepth=32
rw=randread
stonewall
[randwrite-8k-io32]
bs=8k
iodepth=32
rw=randwrite
stonewall
[read-64k-io32]
bs=64k
iodepth=32
rw=read
stonewall
[write-64k-io32]
bs=64k
iodepth=32
rw=write
stonewall
[rw-64k-io32]
bs=64k
iodepth=32
rw=rw
rwmixread=70
stonewall
3、io的参数说明
1)、ioengine: 负载引擎,我们一般使用libaio,发起异步IO请求。
2)、bs: IO大小
3)、direct: 直写,绕过操作系统Cache。因为我们测试的是硬盘,而不是操作系统的Cache,所以设置为1。
4)、rw: 读写模式,有顺序写write、顺序读read、随机写randwrite、随机读randread等。
5)、size: 寻址空间,IO会落在 [0, size)这个区间的硬盘空间上。这是一个可以影响IOPS的参数。一般设置为硬盘的大小。
6)、filename: 测试对象
7)、iodepth: 队列深度,只有使用libaio时才有意义。这是一个可以影响IOPS的参数。
8)、runtime: 测试时长
9)、–output TestResult.log:日志输出到TestResult.log。
其中8k读执行结果如下:
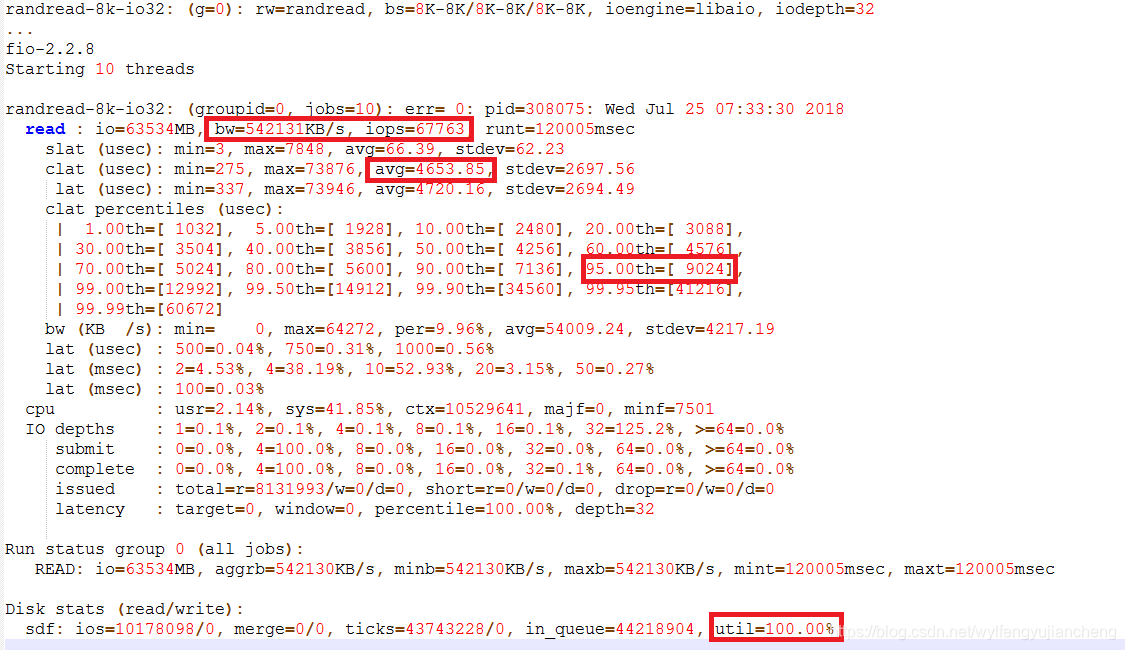
关注参数
1)、IOPS 67763,
2)、每个IO请求的平均响应时间,大约是2.6ms。
3)、95%的IO请求的响应时间是小于等于 9.024 ms。
4)、该硬盘的利用率已经达到了100%。
5)、lat是总延迟,slat是提交io到内核的延迟,clat是内核到磁盘完成之间的延迟,因此lat=slat+clat
四、Rados性能测试工具
1、创建pool
# ceph osd pool create testbench 100 100
2、清除缓存
# echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
# sync
3、4M写入测试
rados bench -p testbench 180 write -t 32 --no-cleanup
Total time run: 31.364848
Total writes made: 1397
Write size: 4194304
Object size: 4194304
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 178.161
Stddev Bandwidth: 112.269
Max bandwidth (MB/sec): 424
Min bandwidth (MB/sec): 0
Average IOPS: 44
Stddev IOPS: 28
Max IOPS: 106
Min IOPS: 0
Average Latency(s): 0.717869
Stddev Latency(s): 0.716959
Max latency(s): 3.66663
Min latency(s): 0.0918219
4、4k写入测试
rados bench -p testbench 180 write -t 32 -b 4096 --no-cleanup
Total time run: 30.050254
Total writes made: 16240
Write size: 4096
Object size: 4096
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 2.11105
Stddev Bandwidth: 0.65485
Max bandwidth (MB/sec): 3.66797
Min bandwidth (MB/sec): 0.898438
Average IOPS: 540
Stddev IOPS: 167
Max IOPS: 939
Min IOPS: 230
Average Latency(s): 0.0591956
Stddev Latency(s): 0.0758244
Max latency(s): 0.860732
Min latency(s): 0.00115017
5、4M顺序读
rados bench -p testbench 180 seq -t 32 --no-cleanup
Total time run: 19.473191
Total reads made: 7310
Read size: 4194304
Object size: 4194304
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 1501.55
Average IOPS 375
Stddev IOPS: 14
Max IOPS: 398
Min IOPS: 347
Average Latency(s): 0.0845073
Max latency(s): 0.375913
Min latency(s): 0.0127095
6、4M随机读
rados bench -p testbench 180 rand -t 32 --no-cleanup
Total time run: 180.101422
Total reads made: 67529
Read size: 4194304
Object size: 4194304
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 1499.8
Average IOPS: 374
Stddev IOPS: 13
Max IOPS: 407
Min IOPS: 282
Average Latency(s): 0.0846821
Max latency(s): 0.506308
Min latency(s): 0.0106904
7、清除数据
rados -p testbench cleanup
8、参数说明
格式:rados bench -p <pool-name> <seconds> <mode> -b <block size> -t --no-cleanup
pool-name:测试存储池名称
seconds:测试时间,单位秒
mode:操作模式,write:写,seq:顺序读;rand:随机读
-b:block size,块大小,默认为 4M,单位字节,只有在写的时候有效。
-t:读/写并行数,默认为 16
–no-cleanup 表示测试完成后不删除测试用数据。
注意:在测试之前要执行一次命令加–no-cleanup产生数据
通过man rados bench 命令得到如下帮助。
bench seconds mode [ -b objsize ] [ -t threads ]
Benchmark for seconds. The mode can be write, seq, or rand. seq and rand are read benchmarks, either sequential or random.
Before running one of the reading benchmarks, run a write benchmark with the --no-cleanup option. The default object size
is 4 MB, and the default number of simulated threads (parallel writes) is 16. The --run-name <label> option is useful for
benchmarking a workload test from multiple clients. The <label> is an arbitrary object name. It is "benchmark_last_meta‐
data" by default, and is used as the underlying object name for "read" and "write" ops. Note: -b objsize option is valid
only in write mode. Note: write and seq must be run on the same host otherwise the objects created by write will have
names that will fail seq.
cleanup [ --run-name run_name ] [ --prefix prefix ]
Clean up a previous benchmark operation. Note: the default run-name is "benchmark_last_metadata"
























 732
732

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








