Linux权限的概念
su 切换用户
Linux下有两种用户:超级用户(root)、普通用户。
超级用户:可以再linux系统下做任何事情,不受限制
普通用户:在linux下做有限的事情。
超级用户的命令提示符是“#”,普通用户的命令提示符是“$”。
命令:su [用户名]
功能:切换用户。
例如,要从root用户切换到普通用户user,则使用 su user。 要从普通用户user切换到root用户则使用 su root(root可以省略),此时系统会提示输入root用户的口令。
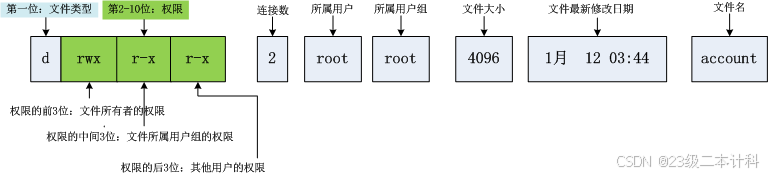
01.文件访问者的分类(人)
文件和文件目录的所有者:u---User(中国平民 法律问题)
文件和文件目录的所有者所在的组的用户:g---Group(不多说)
其它用户:o---Others (外国人)
所有人:a --all
02.文件类型和访问权限
a)字符表示方法
d:文件夹
-:普通文件
l:软链接(类似Windows的快捷方式)
b:块设备文件(例如硬盘、光驱等)
p:管道文件
c:字符设备文件(例如屏幕等串口设备)
s:套接口文件文件类型
b)基本权限
i.读(r/4):Read对文件而言,具有读取文件内容的权限;对目录来说,具有浏览该目录信息的权限 没有对应权限用 - 表示
ii.写(w/2):Write对文件而言,具有修改文件内容的权限;对目录来说具有删除移动目录内文件的权限
iii.执行(x/1):execute对文件而言,具有执行文件的权限;对目录来说,具有进入目录的权限
chmod 修改文件权限
03.修改文件权限
a)chmod
功能:设置文件的访问权限
格式:chmod [参数] 权限 文件名
常用选项:
R -> 递归修改目录文件的权限
说明:只有文件的拥有者和root才可以改变文件的权限[root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 12 drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz //对u(拥有者)去除对dir1文件的写w 程序运行x [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chmod u-wx dir1 [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 12 dr--r-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz也可以用二进制表示,763 7:让u有rwx权限 6:让g有rw-权限 3:让o有-wx权限
421 以此类推
[root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chmod 763 dir1 [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 12 drwxrw--wx 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chmod 421 dir1 [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 12 dr---w---x 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chmod 000 dir1 [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 12 d--------- 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz
如果u g都是同一个人,那么它的身份就是u,能用的权限也是u的权限。
(如果是root可以无视权限)
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz ---------- 1 root root 4 Aug 14 09:51 test.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# echo "eeee" >> test.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# cat test.txt ccc eeee
04.修改文件的所有者u
chown 修改文件的所有者
[root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chown wws test.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 16 d-wxrwxr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz ---------- 1 wws root 9 Aug 14 11:32 test.txtsudo useradd -m username 创建新用户
su username 登录用户
Ctrl+d 退出登录
cat /etc/passwd root账号下查看所用用户
sudo userdel username 删除用户 删除用户的家目录和相关文件,可以使用 -r 选项.
05.修改文件的所属组g
chgrp 修改文件的所属组
[root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chgrp wws test.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 16 d-wxrwxr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz ---------- 1 wws wws 9 Aug 14 11:32 test.txtchown username:username test.txt 同时修改拥有者 所属组
---------- 1 wws wws 9 Aug 14 11:32 test.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chown root:root test.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 16 d-wxrwxr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz ---------- 1 root root 9 Aug 14 11:32 test.txt
注意:root把test.txt拥有者 所属组给wws后,wws可以改文件的权限,但不能改拥有者 所属组。
1.可以登录root再改
2.以wws身份 sudo 并输入密码 (前提有sudo权限)
06.目录的访问权限
进入目录要有 x 可执行权限
查看目录里面内容 r 可读权限
修改目录文件名 删除/创建文件 w 可写权限
07.最终权限=起始权限&(~权限掩码)
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 14 20:09 newdir -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 14 20:10 newtest.txt为什么新建目录和新建文件的权限不一样呢?
起始权限:
目录 777文件 666
umask 获取掩码权限 umask+八进制 修改掩码
[root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# umask 0022 //看后三位022 八进制 18 对应二进制 000 010 010目录最终权限计算过程:
目录起始权限 111 111 111~权限掩码: 111 101 101
起始权限&(~权限掩码)= 111 101 101
最终权限:7 5 5 rwx r-x r-x
08目录的权限
root用户创建的目录/文件放到wws用户中,wws用户不是目录/文件的拥有者,没有rwx权限,但是可以删除对应目录/文件。
[wws@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]$ ll total 8 d--------- 2 root root 4096 Aug 15 10:31 dir1 ---------- 1 wws wws 9 Aug 14 11:32 test.txt [wws@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]$ rm -r dir1 rm: descend into write-protected directory ‘dir1’? y rm: remove write-protected directory ‘dir1’? y [wws@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]$ ll total 4 ---------- 1 wws wws 9 Aug 14 11:32 test.txt[wws@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]$ ls -ld drwx------ 2 wws wws 4096 Aug 15 10:35 .所有只要wws具有目录的写权限, wws就可以删除目录中的文件。
09.粘滞位
如果root创建了o+rwx权限的目录,A用户和B用户都可以在里面创建文件/目录,A用户可能访问不了B创建的文件,但可以删除B创建的文件。因此我们引出了粘滞位的概念。
chmod +t 将目录设置为粘滞位
[root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chmod 777 dir1 [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 16 drwxrwxrwx 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 13 21:54 dir2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 141 Aug 13 22:16 dir2.tgz drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 14 20:09 newdir -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 14 20:10 newtest.txt [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# chmod +t dir1 [root@hcss-ecs-d531 ~]# ll total 16 drwxrwxrwt 4 root root 4096 Aug 13 22:38 dir1 //后面有 t 说明该目录设置为粘滞位当一个目录被设置为"粘滞位"(用chmod +t),则该目录下的文件只能由
一、超级管理员删除
二、该目录的所有者删除
三、该文件的所有者删除
























 689
689

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








