参考自任玉刚先生的《Android开发艺术探索》
一、View的位置参数
在Android中,x轴和y轴的正方向分别为右和下。其中View的位置主要由它的四个顶点来决定,分别对应View的四个属性left、top、right和bottom,分别为左上角横坐标,左上角纵坐标,右下角横坐标和右下角纵坐标。这些坐标都是相对于View的父容器来说的,是相对坐标。如图所示
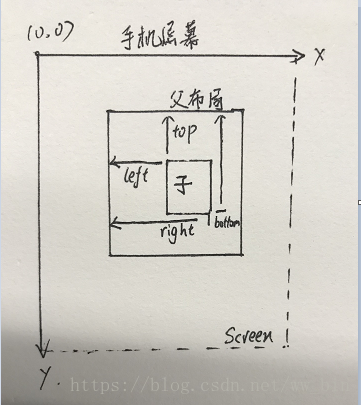
view的宽width = right - left;
view的高height = bottom - top;在view的源码中,这四个属性分别对应着mLeft、mTop、mRight和mBottom这四个成员变量,获取方法如下:
Left = getLeft();
Right = getRight();
Top = getTop();
Bottom = getBottom();从Android3.0开始,View增加了如下参数:x、y、translationX和translationY。其中x和y是view的左上角坐标(初始的时候x和y应该等于left和top的值),translationX和translationY是View左上角相对于父布局容器的偏移量,这四个参数全部都是相对于父布局的坐标,translationX和translationY的默认值为0。它们之间的关系为:
x = left + translationX;
y = top + translationY;注意:
1、View在平移过程中,top和left表示是原始左上角的位置信息,也就是初始值,因此两个值无论是否有平移都是不会改变的。在移动过程中,发生改变的是translationX和translationY,因此x,y和跟着发生变化。
当需要获取view当前的x,y坐标时,通过View对象本身的api可以用getX(),getY(),来获取。此时返回的是当前view相对于其父布局而言左上角的x,y坐标。
2、当需要获取当前view相对于手机屏幕左上角的x,y坐标时,可以用这两个api:
getLocationOnScreen(int[2]) ,计算该视图在全局坐标系中的x,y值(绝对坐标)(注意这个值是要从屏幕顶端算起,也就是说包括了通知栏的高度)。
这里注意,还有这个方法:
getLocationInWindow(int[2]) ,计算该视图在它所在的父布局中的的坐标x,y值。
借用网上的一幅图:
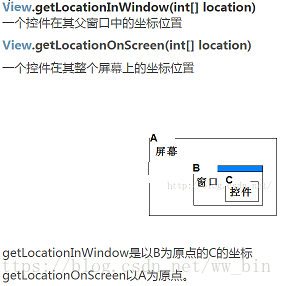
我们看看这两个api的源码:
/**
* <p>Computes the coordinates of this view on the screen. The argument
* must be an array of two integers. After the method returns, the array
* contains the x and y location in that order.</p>
*
* @param outLocation an array of two integers in which to hold the coordinates
*/
public void getLocationOnScreen(@Size(2) int[] outLocation) {
getLocationInWindow(outLocation);
final AttachInfo info = mAttachInfo;
if (info != null) {
outLocation[0] += info.mWindowLeft;
outLocation[1] += info.mWindowTop;
}
}
/**
* <p>Computes the coordinates of this view in its window. The argument
* must be an array of two integers. After the method returns, the array
* contains the x and y location in that order.</p>
*
* @param outLocation an array of two integers in which to hold the coordinates
*/
public void getLocationInWindow(@Size(2) int[] outLocation) {
if (outLocation == null || outLocation.length < 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("outLocation must be an array of two integers");
}
outLocation[0] = 0;
outLocation[1] = 0;
transformFromViewToWindowSpace(outLocation);
}二、MotionEvent
在手指接触屏幕后产生的一系列事件,典型的有这几种:
ACTION_DOWN : 手指刚接触屏幕
ACTION_MOVE : 手指在屏幕上移动
ACTION_UP : 手指从屏幕上松开的瞬间
正常情况下,一次手指触摸屏幕的行为会引发一系列点击事件,比如:
1、点击屏幕后松开,事件顺序为DOWN -> UP;
2、点击屏幕滑动一会儿再松开,事件顺序为DOWN->MOVE->……->MOVE->UP;
当需要获取view当前的x,y坐标时,通过MotionEvent对象可以用getX(),getY(),来获取。此时返回的是当前view相对于其父布局而言左上角的x,y坐标。
当需要获取当前view相对于手机屏幕左上角的x,y坐标时,通过MotionEvent对象可以使用getRawX(),getRawY()。
综合上面的一、二两大点,这里我写了个综合了两点知识的一个demo,如下图:
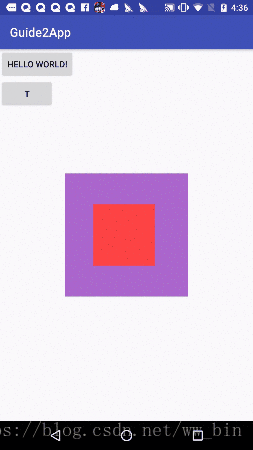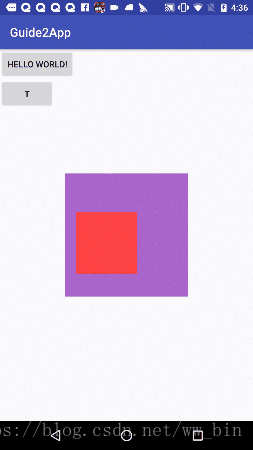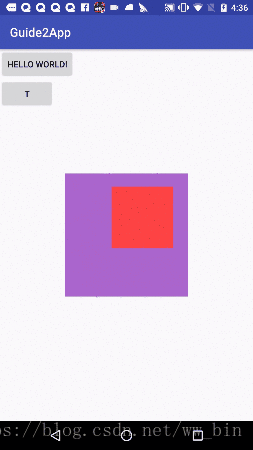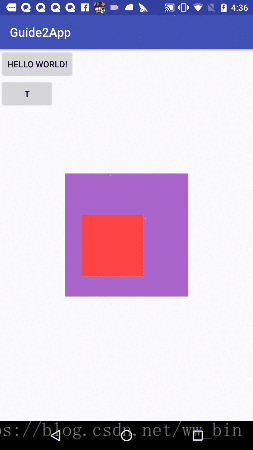
红色的正方形的父布局是紫色的正方形,此时手机触摸并移动红色的正方形,红色正方形跟着手指移动。实现方式:
首先实现紫色的父view:
package com.example.huehn.guide2app.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.ViewTreeObserver;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
public class ParentLayout extends RelativeLayout {
private Context context;
private int[] screenLocation = new int[2];
private int mLastX = 0;
private int mLastY = 0;
public ParentLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context);
}
public ParentLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context);
}
public ParentLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
}
private void init(Context context){
this.context = context;
this.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
ParentLayout.this.getLocationOnScreen(screenLocation);
mLastX = screenLocation[0];
mLastY = screenLocation[1];
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int) event.getRawX();
int y = (int) event.getRawY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int deltaX = x - mLastX;
int deltaY = y - mLastY;
int translationX = (int) (this.getTranslationX() + deltaX);
int translationY = (int) (this.getTranslationY() + deltaY);
this.setTranslationX(translationX);
this.setTranslationY(translationY);
break;
}
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
return true;
}
}





 本文详细介绍了Android中视图(View)的位置参数及其变化原理,并深入探讨了MotionEvent的相关概念及其实现方式。通过一个具体示例展示了如何利用这些知识实现视图的拖拽效果。
本文详细介绍了Android中视图(View)的位置参数及其变化原理,并深入探讨了MotionEvent的相关概念及其实现方式。通过一个具体示例展示了如何利用这些知识实现视图的拖拽效果。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








