JSON:JavaScript Object Notation(JavaScript 对象表示法),是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
JSON 一般都会放在一个专门的以 .json 结尾的文件中。不允许注释。字符串必须用双引号括起来。不支持 undefined 类型。
JSON 的格式:
JSON 有三种格式,每种格式的写法都和 JS 中的数据类型很像,可以很轻松地和 JS 中的数据类型互相转换。
- 简单值格式:对应着 JS 中的基础数据类型,字符串、数字、布尔值、null。
”Lee“ - 对象格式:对应着 JS 中的对象。在大括号中书写,键值对之间以冒号分割,不同的键值对之间以逗号分割。key 值必须是用双引号括起来的字符串,value 值可以是用双引号括起来的字符串、数字、布尔值、null、对象、数组。
{ "username": "Lee", "age": 18, "hobby": ["足球", "篮球"], "family": { "father": "Tom", "mather": "Mary" } } - 数组格式:对应着 JS 中的数组。在中括号中书写,值之间使用逗号分割。
["Lee", 18, null]
JSON 的方法:
-
JSON.stringify():将 JS 中的对应值转换为 JSON 字符串。const obj = { id: 0, name: '张三', age: 12 } const objToStr = JSON.stringify(obj); console.log(obj) console.log(objToStr)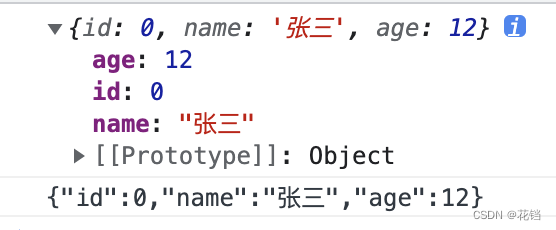
当对象的属性值为 undefined 时,JS 对象转换为 JSON 字符串时会忽略该属性。
const obj = { name: undefined, age: 12 } console.log(JSON.stringify(obj))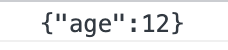
-
JSON.parse():将 JSON 字符串转换为 JS 中的对应值。const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest() xhr.addEventListener('readystatechange', () => { if (xhr.readyState !== 4) return const str = xhr.responseText const strToArr = JSON.parse(str); console.log(str); console.log(strToArr); }) xhr.open('get', './index.json', true) xhr.send(null)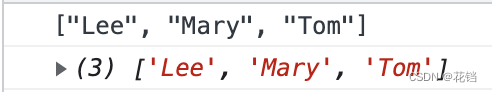





 本文深入讲解了JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)数据格式的基本概念、格式规范及其在Ajax前后端交互中的应用。介绍了JSON的三种主要格式:简单值、对象和数组,并详细说明了JSON与JavaScript数据类型之间的转换方法。
本文深入讲解了JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)数据格式的基本概念、格式规范及其在Ajax前后端交互中的应用。介绍了JSON的三种主要格式:简单值、对象和数组,并详细说明了JSON与JavaScript数据类型之间的转换方法。
















 545
545

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








