import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, Point, LineString
import random
from datetime import datetime
import os
# 字体设置
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 确保中文显示
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 12
plt.rcParams['font.weight'] = 'heavy'
# 船舶参数设置
SHIP_SPEEDS = [20, 24, 26, 30] # 节
SHIP_START_POINTS = [(187, 175), (169, 112), (50, 88), (73, 214)] # 起始点
# 任务清单参数
TASK_LOCATIONS = [(53, 119), (207, 143), (35, 100), (120, 110), (80, 190)]
TASK_TYPES = ['S1', 'S2', 'S3', 'S4', 'S4']
TASK_DURATIONS = [2, 0, 0, 2, 4] # 小时
TASK_TRACKING_DIST = [0, 3, 1, 0, 0] # 海里
MOVING_TASKS = [False, True, True, False, False]
MOVING_SPEEDS = [0, 15, 15, 0, 0] # 节
MOVING_COURSES = [0, 309, 86.08, 0, 0] # 度
# 任务区线
EXIT_POLYGON = Polygon([(194.0, 177.6), (173.4, 106.9), (42.5, 81.2),
(68.1, 220.7), (144.6, 211.5)])
# 巡航线:5个点围成的闭合线圈
Cruise_line = [(187.05, 175.1), (168.65, 112.1), (50, 88.75), (73, 214.05), (142.45, 205.75)]
cruise_polygon = Polygon(Cruise_line)
cruise_boundary = LineString(cruise_polygon.exterior.coords) # 闭合边界线
# 遗传算法参数设置
POP_SIZE = 4
MAX_GEN = 50
CX_PROB = 0.85
MUT_PROB = 0.15
ELITE_RATIO = 0.1
KNOTS_TO_KMH = 1
NAUTICAL_TO_KM = 1
# == == == == == 辅助函数(无修改) == == == == ==
def calc_course(from_pos, to_pos):
"""计算两点航向(0°正北,顺时针递增)"""
dx = to_pos[0] - from_pos[0]
dy = to_pos[1] - from_pos[1]
if dx == 0 and dy == 0:
return 0.0
math_angle = np.arctan2(dy, dx)
course = (90 - np.degrees(math_angle)) % 360
return round(course, 6)
def get_closest_cruise_point(end_pos):
"""计算任务结束点到巡航线边界的最短距离点"""
end_point = Point(end_pos)
proj_dist = cruise_boundary.project(end_point)
closest_point = cruise_boundary.interpolate(proj_dist)
closest_pos = (round(closest_point.x, 6), round(closest_point.y, 6))
boundary_vertices = list(cruise_boundary.coords)[:-1]
min_x, max_x = min(v[0] for v in boundary_vertices), max(v[0] for v in boundary_vertices)
min_y, max_y = min(v[1] for v in boundary_vertices), max(v[1] for v in boundary_vertices)
cx, cy = closest_pos
if not (min_x - 1e-6 <= cx <= max_x + 1e-6 and min_y - 1e-6 <= cy <= max_y + 1e-6):
vertex_dists = [euclidean(end_pos, v) for v in boundary_vertices]
closest_idx = np.argmin(vertex_dists)
closest_pos = boundary_vertices[closest_idx]
return closest_pos
def calc_end_course_to_cruise(end_pos):
"""计算指向巡航线的航向"""
closest_pos = get_closest_cruise_point(end_pos)
return calc_course(end_pos, closest_pos)
def get_target_position(task_id, t):
"""计算任务在t时刻的位置(移动任务动态计算)"""
if not MOVING_TASKS[task_id]:
return TASK_LOCATIONS[task_id]
x0, y0 = TASK_LOCATIONS[task_id]
speed_kmh = MOVING_SPEEDS[task_id] * KNOTS_TO_KMH
course_rad = np.deg2rad(MOVING_COURSES[task_id])
dx = speed_kmh * t * np.sin(course_rad)
dy = speed_kmh * t * np.cos(course_rad)
return (round(x0 + dx, 6), round(y0 + dy, 6))
def is_target_exited(task_id, t):
"""判断移动任务是否超出任务区"""
if not MOVING_TASKS[task_id]:
return False
pos = get_target_position(task_id, t)
return not EXIT_POLYGON.contains(Point(pos))
def calc_distance(pos1, pos2):
"""计算两点距离"""
return round(euclidean(pos1, pos2), 6)
def calc_travel_time(ship_speed, distance):
"""计算航行时间"""
if distance == 0:
return 0.0
speed_kmh = ship_speed * KNOTS_TO_KMH
return round(distance / speed_kmh, 6)
# 添加新函数:计算目标移动到任务区外所需的时间
def calc_exit_time(task_id, start_time):
"""计算目标从start_time开始移动到任务区外所需的时间"""
current_time = start_time
while not is_target_exited(task_id, current_time):
current_time += 0.1 # 每次增加0.1小时
return current_time - start_time
# == == == == == 遗传算法核心(无修改) == == == == ==
class GAOptimizer:
def __init__(self, num_ships=4, num_tasks=5):
self.num_ships = num_ships
self.num_tasks = num_tasks
self.forced_tasks = [0, 1, 2] # 强制出发时刻为0的任务
self.normal_tasks = [3, 4] # 普通任务
def init_population(self):
"""初始化种群(无修改)"""
population = []
for _ in range(POP_SIZE):
forced_shuffled = random.sample(self.forced_tasks, len(self.forced_tasks))
normal_shuffled = random.sample(self.normal_tasks, len(self.normal_tasks))
chrom = forced_shuffled + normal_shuffled
population.append(chrom)
return population
def evaluate_individual(self, individual):
"""评估个体适应度 - 修正S2/S3任务处理逻辑"""
ship_times = [0.0] * self.num_ships
ship_positions = [pos for pos in SHIP_START_POINTS]
used_ships_for_forced = set()
def evaluate_individual(self, individual):
"""评估个体适应度 - 修正航向时间和追踪时间计算"""
ship_times = [0.0] * self.num_ships
ship_positions = [pos for pos in SHIP_START_POINTS]
used_ships_for_forced = set()
for task_id in individual:
if task_id in self.forced_tasks:
for ship_idx in range(self.num_ships):
if ship_idx not in used_ships_for_forced:
target_ship_idx = ship_idx
used_ships_for_forced.add(ship_idx)
break
current_time = 0.0
else:
target_ship_idx = np.argmin(ship_times)
current_time = ship_times[target_ship_idx]
ship_speed = SHIP_SPEEDS[target_ship_idx]
current_pos = ship_positions[target_ship_idx]
# 获取任务初始位置
initial_target_pos = TASK_LOCATIONS[task_id]
if TASK_TYPES[task_id] in ['S2', 'S3']:
# 修正:计算航向时间(舰艇到达与目标距离为跟踪距离时的时间)
# 这是一个追击问题:舰艇以速度v_ship追击目标,目标以速度v_target移动
# 我们需要找到舰艇到达与目标距离为跟踪距离的时间
# 1. 计算初始距离
initial_dist = calc_distance(current_pos, initial_target_pos)
# 2. 计算追击时间(使用向量方法)
target_speed = MOVING_SPEEDS[task_id]
course_rad = np.deg2rad(MOVING_COURSES[task_id])
target_direction = (np.sin(course_rad), np.cos(course_rad))
# 舰艇到目标的向量
dx = initial_target_pos[0] - current_pos[0]
dy = initial_target_pos[1] - current_pos[1]
# 相对速度向量
rel_vx = target_speed * target_direction[0] - ship_speed * dx / initial_dist
rel_vy = target_speed * target_direction[1] - ship_speed * dy / initial_dist
# 相对速度大小
rel_speed = np.sqrt(rel_vx ** 2 + rel_vy ** 2)
# 航向时间(舰艇到达跟踪距离的时间)
if rel_speed > 1e-6: # 避免除以零
travel_time = (initial_dist - TASK_TRACKING_DIST[task_id]) / rel_speed
travel_time = max(0.0, travel_time) # 确保非负
else:
travel_time = 0.0
# 修正:计算追踪时间(目标移动到任务区外所需的时间)
tracking_time = calc_exit_time(task_id, current_time + travel_time)
# 总任务时间 = 航向时间 + 追踪时间
task_time = travel_time + tracking_time
# 任务结束位置
end_pos = get_target_position(task_id, current_time + task_time)
# 更新舰艇状态
ship_times[target_ship_idx] = current_time + task_time
ship_positions[target_ship_idx] = end_pos
else:# 非S2/S3任务保持不变
if MOVING_TASKS[task_id]:
target_pos = get_target_position(task_id, current_time)
else:
target_pos = initial_target_pos
distance = calc_distance(current_pos, target_pos)
travel_time = calc_travel_time(ship_speed, distance)
# 普通任务时间 = 航行时间 + 任务持续时间
task_time = travel_time + TASK_DURATIONS[task_id]
# 更新舰艇状态
ship_times[target_ship_idx] = current_time + task_time
ship_positions[target_ship_idx] = get_target_position(task_id, current_time + task_time)
total_time = max(ship_times)
return 1 / (total_time + 1e-6), total_time
def evaluate_population(self, population):
"""评估种群(无修改)"""
fitness_list = []
total_time_list = []
for ind in population:
fit, total_time = self.evaluate_individual(ind)
fitness_list.append(fit)
total_time_list.append(total_time)
return fitness_list, total_time_list
def select_parents(self, population, fitness):
"""选择父代(无修改)"""
parents = []
for _ in range(POP_SIZE):
candidates = random.sample(range(POP_SIZE), 3)
winner = max(candidates, key=lambda i: fitness[i])
parents.append(population[winner])
return parents
def crossover(self, parent1, parent2):
"""交叉操作(无修改)"""
size = len(parent1)
forced_size = len(self.forced_tasks)
start_forced, end_forced = sorted(random.sample(range(forced_size), 2))
start_normal = forced_size
end_normal = size - 1
start_normal_rand, end_normal_rand = sorted(random.sample(range(start_normal, end_normal + 1), 2))
child1 = [-1] * size
child1[start_forced:end_forced + 1] = parent1[start_forced:end_forced + 1]
child1[start_normal_rand:end_normal_rand + 1] = parent1[start_normal_rand:end_normal_rand + 1]
idx = 0
for gene in parent2[:forced_size]:
if gene not in child1[:forced_size] and idx < forced_size:
while child1[idx] != -1:
idx += 1
child1[idx] = gene
idx = start_normal
for gene in parent2[start_normal:]:
if gene not in child1[start_normal:] and idx <= end_normal:
while child1[idx] != -1:
idx += 1
child1[idx] = gene
child2 = [-1] * size
child2[start_forced:end_forced + 1] = parent2[start_forced:end_forced + 1]
child2[start_normal_rand:end_normal_rand + 1] = parent2[start_normal_rand:end_normal_rand + 1]
idx = 0
for gene in parent1[:forced_size]:
if gene not in child2[:forced_size] and idx < forced_size:
while child2[idx] != -1:
idx += 1
child2[idx] = gene
idx = start_normal
for gene in parent1[start_normal:]:
if gene not in child2[start_normal:] and idx <= end_normal:
while child2[idx] != -1:
idx += 1
child2[idx] = gene
return child1, child2
def mutate(self, individual):
"""变异操作(无修改)"""
forced_size = len(self.forced_tasks)
if random.random() < 0.5:
idx1, idx2 = random.sample(range(forced_size), 2)
else:
idx1, idx2 = random.sample(range(forced_size, len(individual)), 2)
individual[idx1], individual[idx2] = individual[idx2], individual[idx1]
return individual
def optimize(self):
"""优化主逻辑(无修改)"""
population = self.init_population()
best_fitness_history = []
avg_fitness_history = []
current_gen_best_time_history = []
current_gen_avg_time_history = []
best_solution = None
best_fitness = 0
best_total_time = float('inf')
for gen in range(MAX_GEN):
fitness_list, total_time_list = self.evaluate_population(population)
current_best_fit = max(fitness_list)
current_avg_fit = sum(fitness_list) / POP_SIZE
current_best_time = min(total_time_list)
current_avg_time = sum(total_time_list) / POP_SIZE
best_fitness_history.append(current_best_fit)
avg_fitness_history.append(current_avg_fit)
current_gen_best_time_history.append(current_best_time)
current_gen_avg_time_history.append(current_avg_time)
if current_best_fit > best_fitness:
best_fitness = current_best_fit
best_total_time = current_best_time
best_solution = population[np.argmax(fitness_list)].copy()
parents = self.select_parents(population, fitness_list)
offspring = []
for i in range(0, POP_SIZE, 2):
if i + 1 < POP_SIZE:
p1, p2 = parents[i], parents[i + 1]
if random.random() < CX_PROB:
c1, c2 = self.crossover(p1, p2)
else:
c1, c2 = p1.copy(), p2.copy()
offspring.append(c1)
offspring.append(c2)
offspring = [self.mutate(ind) for ind in offspring]
elite_size = int(ELITE_RATIO * POP_SIZE)
elite_indices = np.argsort(fitness_list)[-elite_size:]
for i in range(elite_size):
offspring[i] = population[elite_indices[i]].copy()
population = offspring
if gen % 10 == 0:
print(f"Generation {gen}: "
f"Best Time = {current_best_time:.2f}h, "
f"Avg Time = {current_avg_time:.2f}h, "
f"Best Fitness = {current_best_fit:.4f}")
return (best_solution, best_fitness, best_total_time,
best_fitness_history, avg_fitness_history,
current_gen_best_time_history, current_gen_avg_time_history)
def decode_solution(self, solution):
"""任务解码(无修改,保持原有航向逻辑)"""
ship_times = [0.0] * self.num_ships # 舰艇当前可用时间
ship_positions = [pos for pos in SHIP_START_POINTS] # 舰艇当前位置
ship_tasks = [[] for _ in range(self.num_ships)] # 存储各舰艇的任务详情
used_ships_for_forced = set() # 已分配强制任务的舰艇
# 第一步:先将所有任务分配到对应舰艇,暂不计算“任务结束后航向”
for task_id in solution:
# 1. 确定任务分配的舰艇
if task_id in self.forced_tasks:
# 强制任务:分配给未使用的舰艇
for ship_idx in range(self.num_ships):
if ship_idx not in used_ships_for_forced:
target_ship_idx = ship_idx
used_ships_for_forced.add(ship_idx)
break
depart_time = 0.0 # 强制任务0时刻出发
else:
# 普通任务:分配给最早空闲的舰艇
target_ship_idx = np.argmin(ship_times)
depart_time = ship_times[target_ship_idx]
# 2. 计算当前任务的核心参数
ship_speed = SHIP_SPEEDS[target_ship_idx]
depart_pos = ship_positions[target_ship_idx]
initial_target_pos = TASK_LOCATIONS[task_id]
# 任务起始位置(移动任务需按出发时间计算)
task_start_pos = get_target_position(task_id, depart_time)
# 航行时间与任务开始时间
travel_dist = calc_distance(depart_pos, task_start_pos)
travel_time = calc_travel_time(ship_speed, travel_dist)
task_start_time = depart_time + travel_time
# 出发航向(指向当前任务的起始位置)
depart_course = calc_course(depart_pos, task_start_pos)
# 任务结束时间与结束位置
if TASK_TYPES[task_id] in ['S2', 'S3']:
# 修正:计算航向时间(舰艇到达跟踪距离的时间)
# 计算初始距离
initial_dist = calc_distance(depart_pos, initial_target_pos)
# 计算追击时间
target_speed = MOVING_SPEEDS[task_id]
course_rad = np.deg2rad(MOVING_COURSES[task_id])
target_direction = (np.sin(course_rad), np.cos(course_rad))
# 舰艇到目标的向量
dx = initial_target_pos[0] - depart_pos[0]
dy = initial_target_pos[1] - depart_pos[1]
# 相对速度向量
rel_vx = target_speed * target_direction[0] - ship_speed * dx / initial_dist
rel_vy = target_speed * target_direction[1] - ship_speed * dy / initial_dist
# 相对速度大小
rel_speed = np.sqrt(rel_vx ** 2 + rel_vy ** 2)
# 航向时间(舰艇到达跟踪距离的时间)
if rel_speed > 1e-6:
travel_time = (initial_dist - TASK_TRACKING_DIST[task_id]) / rel_speed
travel_time = max(0.0, travel_time)
else:
travel_time = 0.0
# 计算追踪时间(目标移动到任务区外所需的时间)
tracking_time = calc_exit_time(task_id, depart_time + travel_time)
# 任务开始时间 = 出发时间 + 航向时间
task_start_time = depart_time + travel_time
# 任务结束时间 = 开始时间 + 追踪时间
task_end_time = task_start_time + tracking_time
# 任务结束位置
task_end_pos = get_target_position(task_id, task_end_time)
# 任务总耗时
task_duration = travel_time + tracking_time
else:
# 普通任务:固定时长
task_duration = TASK_DURATIONS[task_id]
task_end_time = task_start_time + task_duration
task_end_pos = get_target_position(task_id, task_end_time)
# 3. 生成任务详情(“任务结束后航向”暂设为None,后续统一计算)
task_detail = {
"舰艇编号": target_ship_idx + 1,
"任务编号": task_id,
"任务类型": TASK_TYPES[task_id],
"舰艇速度(节)": ship_speed,
"舰艇出发时刻(小时)": round(depart_time, 6),
"舰艇出发坐标(x,y)": depart_pos,
"舰艇出发航向(°)": depart_course,
"处置任务开始时刻(小时)": round(task_start_time, 6),
"处置任务开始坐标(x,y)": task_start_pos,
"处置任务结束时刻(小时)": round(task_end_time, 6),
"处置任务结束坐标(x,y)": task_end_pos,
"任务结束后航向(°)": None, # 占位符,后续计算
"任务耗时(小时)": round(task_duration, 6)
}
# 将任务详情添加到对应舰艇的任务列表
ship_tasks[target_ship_idx].append(task_detail)
# 4. 更新舰艇的当前状态(为下一个任务做准备)
ship_times[target_ship_idx] = task_end_time
ship_positions[target_ship_idx] = task_end_pos
# 第二步:遍历每个舰艇的任务列表,计算“任务结束后航向”
for ship_idx in range(self.num_ships):
tasks = ship_tasks[ship_idx]
num_tasks = len(tasks)
# 逐个处理舰艇的每个任务
for i in range(num_tasks):
current_task = tasks[i]
current_end_pos = current_task["处置任务结束坐标(x,y)"]
if i == num_tasks - 1:
# 情况1:当前任务是舰艇的最后一个任务→航向指向巡航线
end_course = calc_end_course_to_cruise(current_end_pos)
else:
# 情况2:当前任务有后续任务→航向指向下一个任务的起始位置
next_task = tasks[i + 1] # 下一个任务的详情
next_task_id = next_task["任务编号"] # 下一个任务的ID
# 下一个任务的出发时间 = 当前任务的结束时间(舰艇完成即出发)
next_depart_time = current_task["处置任务结束时刻(小时)"]
# 下一个任务的起始位置(按出发时间计算)
next_task_start_pos = get_target_position(next_task_id, next_depart_time)
# 计算当前任务结束后,指向下一步任务的航向
end_course = calc_course(current_end_pos, next_task_start_pos)
# 更新当前任务的“任务结束后航向”
current_task["任务结束后航向(°)"] = end_course
return ship_tasks
# == == == == == 主程序(核心修改:可视化图表标注) == == == == ==
if __name__ == "__main__":
optimizer = GAOptimizer(num_ships=4, num_tasks=5)
(best_sol, best_fit, best_total_time,
best_fit_hist, avg_fit_hist,
gen_best_time_hist, gen_avg_time_hist) = optimizer.optimize()
# 输出结果
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("优化完成!基础结果如下:")
print(f"最佳任务序列: {best_sol}")
print(f"历史最佳总完成时间: {best_total_time:.2f} 小时")
print(f"历史最佳适应度: {best_fit:.4f}")
print(f"巡航线闭合线圈顶点: {Cruise_line}")
print("=" * 60)
# 导出Excel
ship_tasks = optimizer.decode_solution(best_sol)
all_tasks = []
for ship in ship_tasks:
all_tasks.extend(ship)
df = pd.DataFrame(all_tasks)
column_order = [
"舰艇编号", "任务编号", "任务类型", "舰艇速度(节)",
"舰艇出发时刻(小时)", "舰艇出发坐标(x,y)", "舰艇出发航向(°)",
"处置任务开始时刻(小时)", "处置任务开始坐标(x,y)",
"处置任务结束时刻(小时)", "处置任务结束坐标(x,y)",
"任务结束后航向(°)", "任务耗时(小时)"
]
df = df[column_order]
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
excel_filename = f"第一问舰艇任务分配详情_{timestamp}.xlsx"
try:
df.to_excel(excel_filename, index=False, engine="openpyxl")
print(f"\nExcel表格已生成:{excel_filename}")
print(f"文件路径:{os.path.abspath(excel_filename)}")
print("提示:“任务结束后航向(°)”已按规则计算(有后续任务指向下一任务,无则指向巡航线)")
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n导出Excel失败:{str(e)}")
print("请确保已安装依赖库:pip install pandas openpyxl shapely")
# 1. 适应度变化图(无修改)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.plot(best_fit_hist, label="最佳适应度", color="#1f77b4", linewidth=2.5)
plt.plot(avg_fit_hist, label="平均适应度", color="#ff7f0e", linewidth=2.5)
plt.xlabel("迭代次数", fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel("适应度(总完成时间倒数)", fontsize=20)
plt.title("遗传算法迭代过程中适应度变化", fontsize=24, pad=20)
plt.legend(fontsize=18, loc="upper right")
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, linestyle="--")
plt.xticks(fontsize=16)
plt.yticks(fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 2. 总完成时间图(无修改)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.plot(gen_best_time_hist, label="每代最佳总完成时间", color="#2ca02c", linewidth=2.5)
plt.plot(gen_avg_time_hist, label="每代平均总完成时间", color="#d62728", linewidth=2.5, linestyle="--")
plt.axhline(y=best_total_time, color="#2ca02c", linestyle=":", linewidth=2,
label=f"历史最佳总时间:{best_total_time:.2f}h")
plt.xlabel("迭代次数", fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel("总完成时间(小时)", fontsize=20)
plt.title("遗传算法每代任务总完成时间变化", fontsize=24, pad=20)
plt.legend(fontsize=18, loc="upper right")
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, linestyle="--")
plt.xticks(fontsize=16)
plt.yticks(fontsize=16)
last_gen = MAX_GEN - 1
plt.annotate(
f'历史最佳:{best_total_time:.2f}h',
xy=(last_gen, best_total_time),
xytext=(last_gen - 80, best_total_time + 2),
fontsize=16,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", color="#2ca02c", lw=2)
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# -------------------------- 3. 可视化图表(核心修改:新增编号标注) --------------------------
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
# 绘制巡航线闭合线圈(无修改)
cruise_x = [p[0] for p in Cruise_line] + [Cruise_line[0][0]]
cruise_y = [p[1] for p in Cruise_line] + [Cruise_line[0][1]]
plt.plot(cruise_x, cruise_y, color="#1f77b4", linewidth=3, label="巡航线闭合线圈")
plt.fill(cruise_x, cruise_y, color="#1f77b4", alpha=0.1)
# 绘制所有任务结束点、航向及编号标注(核心修改)
for task in all_tasks:
end_x, end_y = task["处置任务结束坐标(x,y)"]
end_course = task["任务结束后航向(°)"]
ship_num = task["舰艇编号"] # 舰艇编号
task_id = task["任务编号"] # 任务编号
# 1. 绘制任务结束点(红色圆点)
plt.scatter(end_x, end_y, color="#d62728", s=150, zorder=5)
# 2. 绘制航向箭头(无修改)
arrow_len = 15 # 箭头长度(可调整)
angle_rad = np.deg2rad(90 - end_course) # 航向转数学角度
dx = arrow_len * np.cos(angle_rad)
dy = arrow_len * np.sin(angle_rad)
plt.arrow(end_x, end_y, dx, dy, color="#d62728", width=0.8,
head_width=3, head_length=3, zorder=6)
# 3. 标注舰艇编号(蓝色,16号字体,位于点上方,避免遮挡)
plt.text(
x=end_x, y=end_y + 8, # 位置:点上方8个单位
s=f"舰艇{ship_num}",
color="#d62728", # 舰艇编号用蓝色(与巡航线同色,区分度高)
fontsize=17, # 舰艇编号字体更大
fontweight="bold",
ha="center", va="center",
zorder=7 # 层级高于点和箭头,避免被覆盖
)
# 4. 标注任务编号(黑色,12号字体,位于点下方,与舰艇编号错开)
plt.text(
x=end_x, y=end_y - 8, # 位置:点下方8个单位
s=f"任务{task_id}",
color="black", # 任务编号用黑色
fontsize=14, # 任务编号字体更小
fontweight="normal",
ha="center", va="center",
zorder=7
)
# 5. 标注航向值(红色,14号字体,位于箭头延长线,避免与编号重叠)
plt.text(
x=end_x + dx + 3, y=end_y + dy + 3, # 位置:箭头末端外侧3个单位
s=f"{end_course}°",
color="#483D8B",
fontsize=18,
ha="center", va="center",
zorder=7
)
# 图表设置(调整标题,明确标注信息)
plt.xlabel("X坐标", fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel("Y坐标", fontsize=20)
plt.title("任务结束后航向可视化(标注:舰艇编号/任务编号/航向)", fontsize=24, pad=20)
plt.legend(fontsize=16, loc="upper left")
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, linestyle="--")
plt.axis("equal") # 等比例显示,避免方向失真
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()上述输出适应度变化图和总完成时间图的代码有些错误请纠正
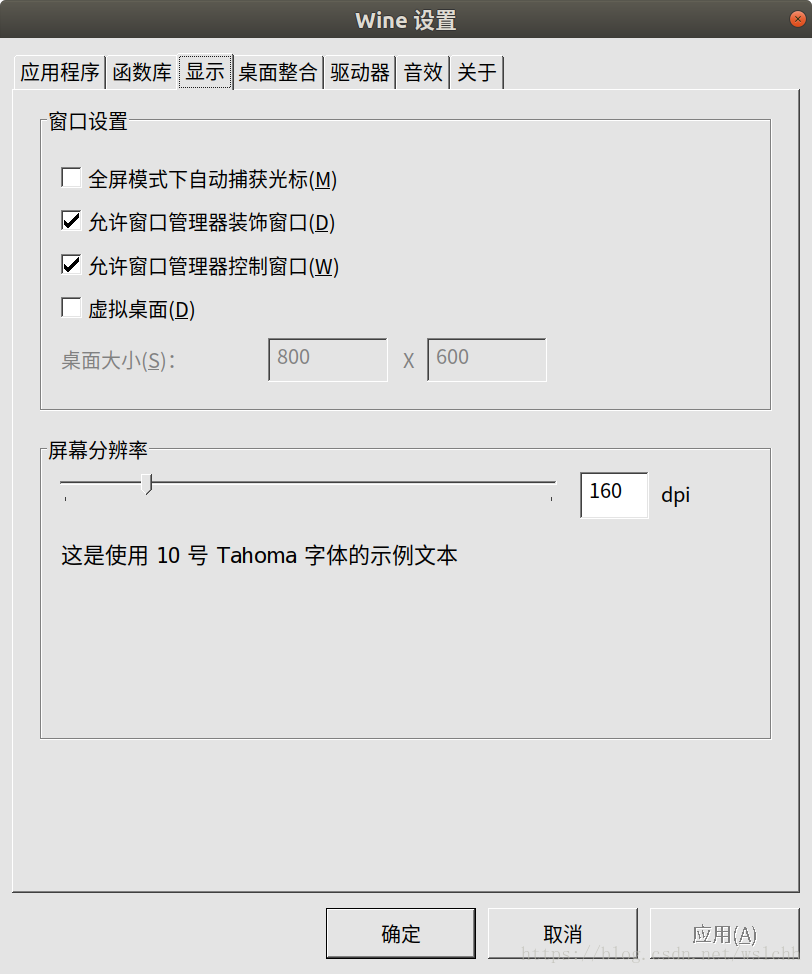

 本文介绍如何解决刚安装的Crossover默认字体过小的问题。通过打开Crossover中的wine配置,进入显示设置更改屏幕分辨率,即可调整字体大小。
本文介绍如何解决刚安装的Crossover默认字体过小的问题。通过打开Crossover中的wine配置,进入显示设置更改屏幕分辨率,即可调整字体大小。





 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?


