java -version :jdk 1.8.0_191
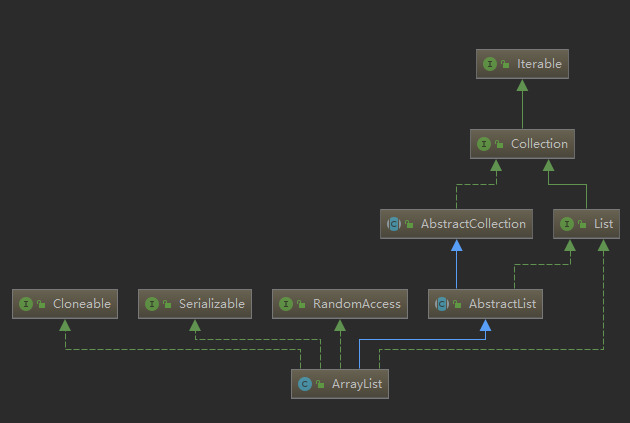
ArrayList
构造
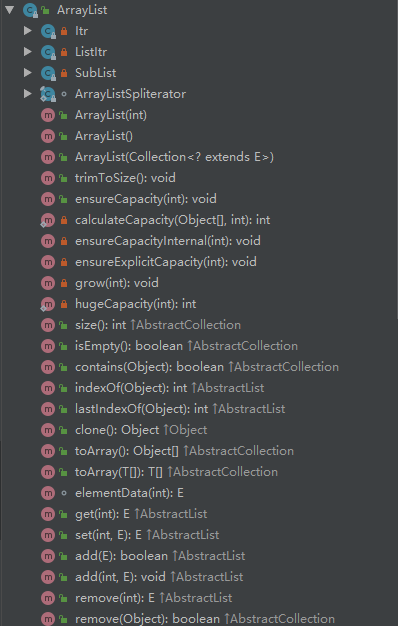
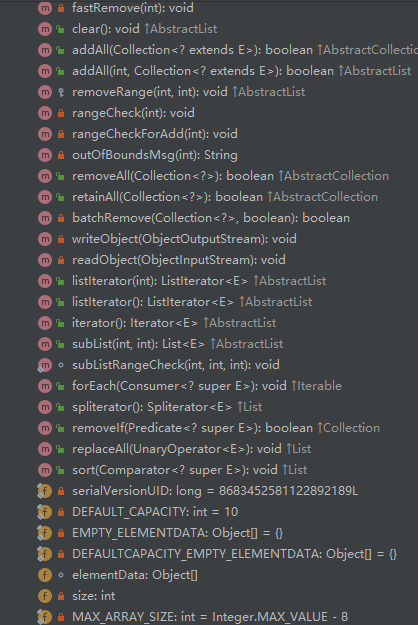
类内参数,方法
实现
基于数组实现。
插入时间复杂度 O(1)
查找时间复杂度 O(1)
删除时间复杂度 O(n)
修改时间复杂度 O(n)
静态参数
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
默认的数组大小为10
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
默认的空数组
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
存储ArrayList元素的数组。不能被序列化
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
存放的对象的数量
add方法
add(E e);
默认是向数组当前数量 +1 的下标位置存储。
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
判断新增加后的对象个数是否超过数组设置的数量限制,
如果超过了,则增加 >> 1。
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
add(int i, E e);
向指定下标位置存储对象,原本所有后续对象往后移动一个下标位置。
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
System.arraycopy():JVM 提供的数组拷贝实现,从汇编的角度出发,性能很好。
可以看出,ArrayList是可以存储null。
get方法
get(int index)
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
//判断是否数组越界
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
get方法只能通过下标直接获取,所以时间复杂度为 O(1)。
set方法
set(int index, E element)
将对应下标对象直接修改。
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
remove方法
remove(int index)
删除对应下标的对象。时间复杂度 O(1)
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//该下标如果不是在list末尾,则负责
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
删除的操作,即使删除了许多个,但是也不会发生反向扩容,也就是缩小数组的长度。
remove(Object o)
删除对象,时间复杂度 O(n)
通过for循环遍历查找删除。
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
//快速删除,其实原理和remove(int index)一样,因为已经找到下标了。
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
grow方法
当list中数组不够存储对象时,扩容操作,增加原来的一半
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
Arrays.copyOf()的底层还是调用 System.arraycopy()
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
>>1 等价于 /2
可以看出,ArrayList的主要消耗基本都是在扩容或者复制这些操作中,所以我们一般声明ArrayList的时候,最好给个初始值。更要减少在指定位置的插入操作。
序列化
ArrayList的 elementData 用 transient 修饰,表明不能被序列化。
但是提供了序列化和反序列化的方法。
序列化writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
/**
* Save the state of the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to a stream (that
* is, serialize it).
*
* @serialData The length of the array backing the <tt>ArrayList</tt>
* instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements
* (each an <tt>Object</tt>) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
反序列化readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
/**
* Reconstitute the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance from a stream (that is,
* deserialize it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in capacity
s.readInt(); // ignored
if (size > 0) {
// be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size);
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity);
ensureCapacityInternal(size);
Object[] a = elementData;
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
a[i] = s.readObject();
}
}
}
可以看出,ArrayList只序列化了数组中已经存储的数据。
Vector
实现的接口和继承的类和ArrayList一致,里面的方法,变量的定义也是基本一致的。
只是在操作数组的时候,在所有的方法上都添加 synchronized 关键字。
例如 add方法 :
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this Vector
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
所以基本上对数组的操作都是同步操作,但是由于性能不佳,所以不适合当高并发的数据结构。
如果想要用于高并发,可以使用java.util包里面类Collections的方法。
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
其实现的原理也是使用关键字 synchronized ,但是他不是使用在方法上,而是在方法内,即同步块。
例如:
public boolean add(E e) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.add(e);}
}
其中 mutex 是一个内部的Object,在初始化的时候:mutex = this;
但是 Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()) 在操作的时候,还是会锁整个数组。。。。
可以考虑使用 CopyOnWriteArrayList ,他在读的时候没有加锁,但是写的时候加锁,使用的锁机制是 ReentrantLock重入锁 。
总而言之,ArrayList 和 Vector 都不适合用于高并发。


























 1476
1476

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








