一、简介
数据结构+算法 = 程序
为什么要学习数据结构和算法呢
- 代码化繁为简
- 提高代码性能
- 提高面试通过率
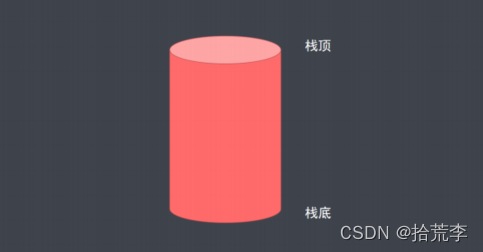
二、栈的概念
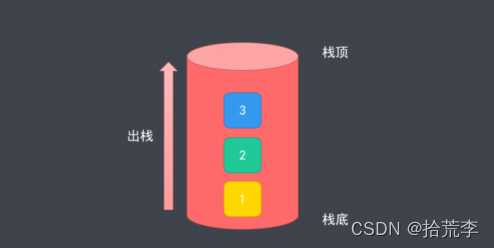
- 栈是一种遵从后进先出原则的有序集合
- 添加新元素的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底
- 操作栈的元素时,只能从栈顶操作(添加、移除或者取值)
图示:
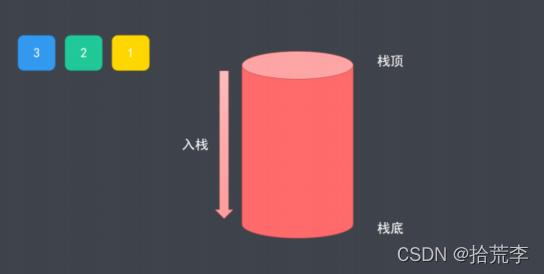
后进先出
三、栈的实现
class Stack {
constructor () {
// 存储栈的数据
this.data = []
// 记录栈的数据个数(相当于数组的 length)
this.count = 0
}
// push() 入栈方法
push (item) {
// 方式1:数组方法 push 添加
// this.data.push(item)
// 方式2:利用数组长度
// this.data[this.data.length] = item
// 方式3:计数方式
this.data[this.count] = item
// 入栈后,count 自增
this.count++
}
// pop() 出栈方法
pop () {
// 出栈的前提是栈中存在元素,应先行检测
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('栈为空!')
return
}
// 移除栈顶数据
// 方式1:数组方法 pop 移除
// return this.data.pop()
// 方式2:计数方式
const temp = this.data[this.count - 1]
delete this.data[--this.count]
return temp
}
// isEmpty() 检测栈是否为空
isEmpty () {
return this.count === 0
}
// top() 用于获取栈顶值
top () {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('栈为空!')
return
}
return this.data[this.count - 1]
}
// size() 获取元素个数
size () {
return this.count
}
// clear() 清空栈
clear () {
this.data = []
this.count = 0
}
}
const s = new Stack()
s.push('a')
s.push('b')
s.push('c')
四、包含min函数的栈
**题目:**定义栈的数据结构,清在该类型中实现一个能够得到该栈最小元素的min函数,在该栈中调用min、push及pop的时间复杂度都是O(1)
我们建立两个栈 一个存储数据,一个存储最小值
[4,2,3,5,6,7,8,1,1]
[4,2,1,1] 永远把最小值放在前面
// 在存储数据的栈外,再新建一个栈,用于存储最小值
class MinStack {
constructor () {
// stackA 用于存储数据
this.stackA = []
this.countA = 0
// stackB 用于将数据降序存储(栈顶值为最小值)
this.stackB = []
this.countB = 0
}
// 入栈
push (item) {
// stackA 正常入栈
this.stackA[this.countA++] = item
// stackB 如果没有数据,直接入栈
// 如果 item 的值 <= stackB 的最小值,入栈
if (this.countB === 0 || item <= this.min()) {
this.stackB[this.countB++] = item
}
}
// 最小值函数
min () {
return this.stackB[this.countB - 1]
}
// 获取栈顶值
top () {
return this.stackA[this.countA - 1]
}
// 出栈
pop () {
// 先进行 stackB 的检测
// 如果 stackA 的栈顶值 === stackB 的栈顶值,stackB 出栈
if (this.top() === this.min()) {
delete this.stackB[--this.countB]
}
// stackA 出栈
delete this.stackA[--this.countA]
}
}
const m = new MinStack()
五、包含 min 函数的栈-使用数组方法
class MinStack {
constructor () {
this.stack = []
}
// 入栈
push (item) {
this.stack.push(item)
}
// 查看栈顶值
top () {
return this.stack[this.stack.length - 1]
}
// 实现最小值功能
min () {
return Math.min.apply(null, this.stack)
}
// 出栈方法
pop () {
return this.stack.pop()
}
}
const m = new MinStack()
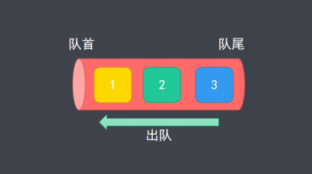
六、队列的概念
- 队列是一种遵从先进先出原则的有序集合
- 添加新元素的一端称为队尾,另一端称为队首


七、队列的实现-基于数组
class Queue {
constructor () {
// 用于存储队列数据
this.queue = []
this.count = 0
}
// 入队方法
enQueue (item) {
this.queue[this.count++] = item
}
// 出队方法
deQueue () {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return
}
// 删除 queue 的第一个元素
// delete this.queue[0]
// 利用 shift() 移除数组的第一个元素
this.count--
return this.queue.shift()
}
isEmpty () {
return this.count === 0
}
// 获取队首元素值
top () {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return
}
return this.queue[0]
}
size () {
return this.count
}
clear () {
// this.queue = []
this.length = 0
this.count = 0
}
}
const q = new Queue()
八、双端队列
双端队列(double-ended queue) 指的是允许同时从队尾与队首两端进行存取操作的队列,操作更加灵活。
双端队列与 JavaScript 中的数组操作十分相似,只是不允许在数组两端以外的位置进行存取操作。
我们实现以下功能:
- addFront/addBack
- removeFront/removeBack
- frontTop/backTop
九、链表
概念:链表是有序的数据结构
可以从首、尾、中间进行数据存取。
为什么不直接用数组?
1.数组在内存中占用一段连续的空间
2.添加、移除会导致后续元素位移,性能开销大。
- 链表是有序的数据结构,链表中的每个部分称为节点。
- 链表可以从首、尾、中间进行数据存取。
- 链表的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间。
- 优点:添加与删除不会导致其余元素位移。
- 缺点:无法根据索引快速定位元素。
const arr = []
console.time('perfTest')
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
// arr.push(i)
arr.unshift(i) // 比push方法耗时更长百倍
}
console.timeEnd('perfTest')
小结:
- 获取、修改元素时,数组效率高。
- 添加、删除元素时,链表效率高。
十、链表的实现
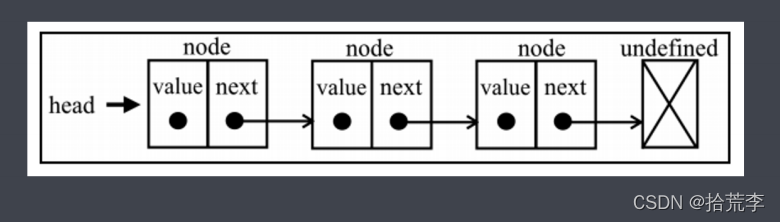
- 我们实现一下功能
- 节点类:value、next
- 链表类:
- addAtTail尾部添加节点
- addAtHead头部添加节点
- addAtIndex指定位置添加节点
- get获取节点
- removeAtIndex删除指定节点
// 节点类
class LinkedNode {
constructor (value) {
this.value = value
// 用于存储下一个节点的引用
this.next = null
}
}
// 链表类
class LinkedList {
constructor () {
this.count = 0
this.head = null
}
// 添加节点 (尾)
addAtTail (value) {
// 创建新节点
const node = new LinkedNode(value)
// 检测链表是否存在数据
if (this.count === 0) {
this.head = node
} else {
// 有数据的时候
// 找到链表尾部节点,将最后一个节点的 next 设置为 node
let cur = this.head
while (cur.next != null) { // while循环找到最后一个节点 设置 cur.next
cur = cur.next
}
cur.next = node
}
this.count++
}
// 添加节点(首)
addAtHead (value) {
const node = new LinkedNode(value)
if (this.count === 0) {
//无数据
this.head = node
} else {
// 有数据
// 将 node 添加到 head 的前面
node.next = this.head
this.head = node
}
this.count++
}
// 获取节点(根据索引)
get (index) { // 从0位置到index找到最后一个就行
if (this.count === 0 || index < 0 || index >= this.count) {
return
}
// 迭代链表,找到对应节点
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next
}
return current
}
// 添加节点(根据索引)
addAtIndex (value, index) {
if (this.count === 0 || index >= this.count) {
return
}
// 如果 index <= 0,都添加到头部即可
if (index <= 0) {
return this.addAtHead(value)
}
// 要先切断链表再添加
// 后面为正常区间处理
const prev = this.get(index - 1)
const next = prev.next
const node = new LinkedNode(value)
prev.next = node
node.next = next
this.count++
}
// 删除(根据索引)
removeAtIndex (index) {
if (this.count === 0 || index < 0 || index >= this.count) {
return
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next
} else {
const prev = this.get(index - 1)
prev.next = prev.next.next
}
this.count--
}
}
// 测试代码
const l = new LinkedList()
l.addAtTail('a')
l.addAtTail('b')
l.addAtTail('c')
十一、链表的多种形式
常见的链表形式有:
- 双向链表
- 循环链表
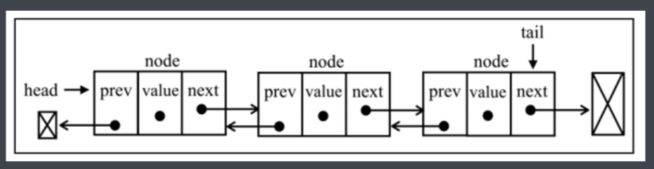
双向链表
- 双向链表是指在普通链表的基础上,增加一个用于记录上一个节点的属性prev,可用于双向访问。
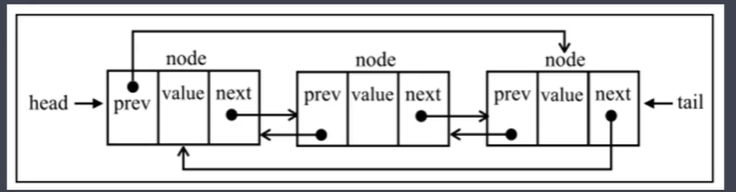
循环链表
- 循环链表又称为环形链表,指的是链表最后一个节点的next指向第一个节点,形成首尾相连的循环结构,称为循环列表。
- 在实际使用中,环的结束点可以为链表的任意点。
判断循环链表
在JavaScript中,判断一个链表是否为环形链表可以通过使用快慢指针(Floyd Cycle Detection Algorithm)的方法来实现。快指针会每次移动两个节点,慢指针会每次移动一个节点。如果链表中存在环,那么快慢指针最终会在环中相遇。
以下是实现这一算法的示例代码:
class ListNode {
constructor(value) {
this.val = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
function hasCycle(head) {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return false;
}
let slow = head;
let fast = head.next;
while (slow !== fast) {
if (!fast || !fast.next) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
// 示例使用
const node1 = new ListNode(1);
const node2 = new ListNode(2);
const node3 = new ListNode(3);
const node4 = new ListNode(4);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node2; // 形成环形链表
console.log(hasCycle(node1)); // 输出: true
十二、树与二叉树
树
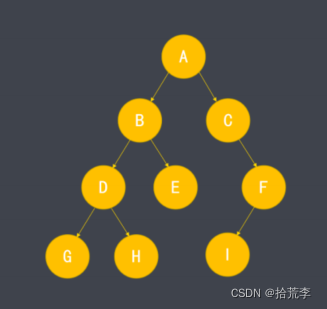
- 树形结构是一种非线性数据结构
- 树中的每一部分称为节点,节点间存在分支结构与层次关系
- 每个树形结构都具有一个根节点
- 根据节点之间的关系,也存在父节点、子节点、兄弟节点的概念。
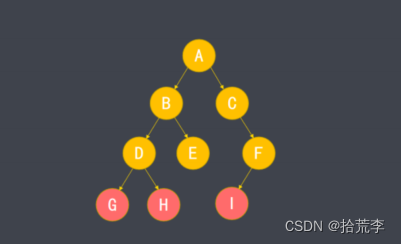
- 不含子节点的节点称为叶节点
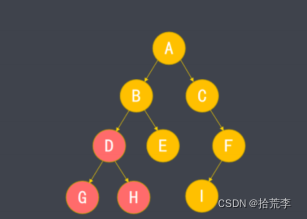
- 子树:对某个节点与其后代节点的整体称呼。
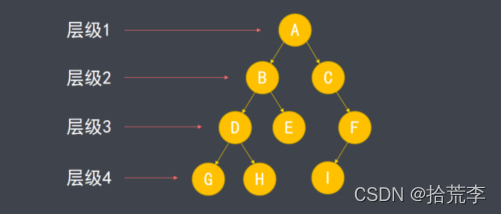
- 由于存在父子关系,树中的节点形成多级结构,称为层级。
- 根节点层级为1,向下依次递增
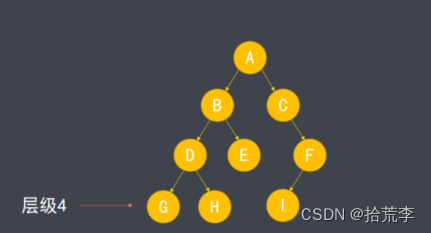
- 树中最深节点的层级称为树的高度。
二叉树
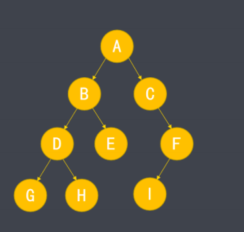
- 二叉树是树形结构中的一种,二叉树中的每个结点最多只能存在2个子结点。
- 左子节点,右子节点
- 左子树,右子树
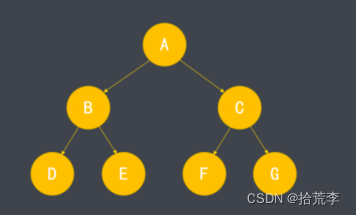
- 除普通二叉树外,还存在一些特殊形式的二叉树。
- 如上图,二叉树的每层结点都达到最大值,称为满二叉树。
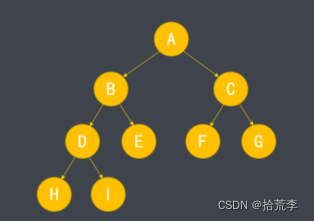
- 二叉树的除最后一层外,每层节点都达到最大值,且最后一层节点都位于左侧,这种形式称为完全二叉树。
- 满二叉树也属于完全二叉树。
二叉树的存储形式
- 由于完全二叉树的结构连续,有迹可循,可采用顺序存储方式。
- 如按照从左往右,从上到下的顺序将节点存储在数组中。
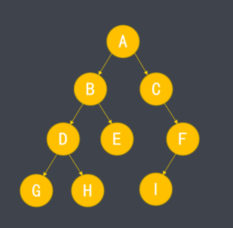
- 普通二叉树由于结构不规则,不适合使用顺序存储,为了记录节点的关系,可使用链式存储方式。
- 每个节点通过value表示值,left、right表示左右子节点。
二叉树的遍历
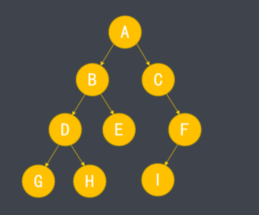
- 二叉树的遍历从根节点开始,根据数据访问顺序不同存在三种遍历形式:前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历。
- 这里的序表示树节点的访问顺序
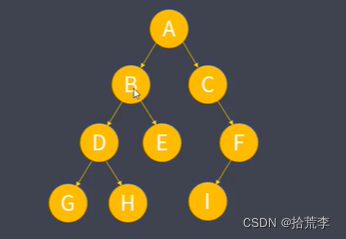
前序遍历
- 前序遍历:按 根节点-》左子树-》右子树顺序进行遍历
- 上述二叉树前序遍历结果为:ABDGHECFI
中序遍历
- 中序遍历:按 左子树-》根节点-》右子树 顺序进行遍历
- 上述二叉树中序遍历结果为:GDHBECIF
后序遍历
- 后续遍历:按 左子树-》右子树-》根节点 顺序进行遍历。
- 上述二叉树后续遍历结果为:GHDEBIFCA
递归实现前序遍历:(深度遍历)
// 定义二叉树节点类
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.val = value; // 当前节点值
this.left = null; // 左子节点指针
this.right = null; // 右子节点指针
}
}
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
// 用于存储遍历的结果
const res = []
// 设置函数用于进行递归遍历
const preorder = (root) => {
// 当前结点为空时,无需进行递归
if (!root) {
return
}
// 记录根节点值
res.push(root.val)
// 前序遍历左子树
preorder(root.left)
// 前序遍历右子树
preorder(root.right)
}
preorder(root)
return res
};
// 创建一个测试二叉树
const root = new TreeNode('A');
const b = new TreeNode('B');
const c = new TreeNode('C');
const d = new TreeNode('D');
const e = new TreeNode('E');
const f = new TreeNode('F');
b.left = d;
c.right = e;
d.left = f;
e.right = f;
root.left = b;
root.right = c;
console.log(preorderTraversal(root));
迭代实现前序遍历:(广度遍历)
// 定义二叉树节点类
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.val = value; // 当前节点值
this.left = null; // 左子节点指针
this.right = null; // 右子节点指针
}
}
// 广度优先遍历函数
function breadthFirstTraversal(root) {
if (!root) return []; // 如果根节点为空则返回空数组
let result = []; // 存放结果的数组
let queue = [root]; // 辅助队列,初始时只包含根节点
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift(); // 取出队首元素并移除
result.push(node.val); // 将该节点值添加到结果数组中
if (node.left) {
queue.push(node.left); // 若有左子节点,则入队
}
if (node.right) {
queue.push(node.right); // 若有右子节点,则入队
}
}
return result;
}
// 创建一个测试二叉树
const root = new TreeNode('A');
const b = new TreeNode('B');
const c = new TreeNode('C');
const d = new TreeNode('D');
const e = new TreeNode('E');
const f = new TreeNode('F');
b.left = d;
c.right = e;
d.left = f;
e.right = f;
root.left = b;
root.right = c;
console.log(preorderTraversal(root));
实现二叉树的最大深度
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (!root) {
return 0
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
};
十三、二叉搜索树
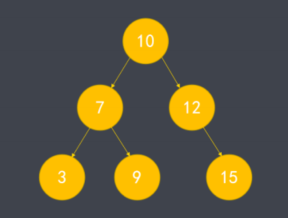
- 二叉搜索树是一种特殊的二叉树,简称 BST。
- 左子树的节点小于根节点,右子树的节点大于根节点。
- 子树也为二叉搜索树。
验证搜索二叉树
var isValidBST = function(root) {
// 通过一个辅助函数来统一设置左右子树的比较
return helper(root, -Infinity, Infinity);
};
const helper = (root, lower, upper) => {
if (root === null) {
return true
}
// 当前节点值超出边界,说明二叉树为非 BST
if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
// 否则,递归处理左右子节点,并更新大小范围
// 同时根据左右子节点的返回值进行返回,只有全部递归结果均为 true, 才说明二叉树为 BST
return helper(root.left, lower, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, upper);
}
原题:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
二叉树 常见考点有深度优先遍历、广度优先遍历。其中,深度优先遍历又分为前序、中序、后序遍历。
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Celine921/article/details/123554335
十四、空间复杂度和时间复杂度概念
算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度是衡量算法效率的两个重要指标。
-
时间复杂度(Time Complexity)是用来描述算法执行所需时间随输入规模增长的变化关系。它通常使用大O符号来表示,例如O(n)、O(n^2)等。时间复杂度描述的是算法在最坏情况下执行所需的时间,即算法的最大运行时间。 -
空间复杂度(Space Complexity)是用来描述算法执行所需空间随输入规模增长的变化关系。它也通常使用大O符号来表示,例如O(n)、O(n^2)等。空间复杂度描述的是算法在最坏情况下所需的额外内存空间,包括算法中使用的辅助数据结构和临时变量等。
算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是用来衡量算法的效率和资源消耗的。通常情况下,我们希望算法的时间复杂度尽可能低,即执行速度快;同时,空间复杂度也要尽可能低,即占用的内存空间少。不过,在实际应用中,时间复杂度和空间复杂度可能会有一定的权衡。
需要注意的是,时间复杂度和空间复杂度只是对算法的一种理论分析,实际执行时间和空间占用也受到计算机硬件、编程语言和优化等方面的影响。因此,在选择和评估算法时,需要综合考虑时间复杂度、空间复杂度以及实际环境等因素。
其他算法
https://u19tul1sz9g.feishu.cn/docx/A53kdaTlCocjTBx8eV2cETC8ncN








 本文介绍了数据结构和算法在编程中的重要性,涵盖栈、队列、链表、二叉树等核心概念,并演示了如何通过实现min函数优化栈和队列操作。深入讲解了栈的后进先出原则,以及如何用代码实现栈和队列,包括使用数组和链表的方法。同时探讨了二叉搜索树、排序算法和基本的数据结构和算法复杂度概念。
本文介绍了数据结构和算法在编程中的重要性,涵盖栈、队列、链表、二叉树等核心概念,并演示了如何通过实现min函数优化栈和队列操作。深入讲解了栈的后进先出原则,以及如何用代码实现栈和队列,包括使用数组和链表的方法。同时探讨了二叉搜索树、排序算法和基本的数据结构和算法复杂度概念。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








