#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 5
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode{
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList{
NodePtr nodes;
int* used;
} *ListPtr;
//初始化
ListPtr initLinkedList(){
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
tempPtr->used[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}
return tempPtr;
}
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr){
int p = paraListPtr->nodes[0].next;;
while (p != -1) {
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
int p, q, i;
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i ++) {
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1) {
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
for (i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0){
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}
}
if (i == DEFAULT_SIZE){
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar){
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar)){
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1) {
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;
}
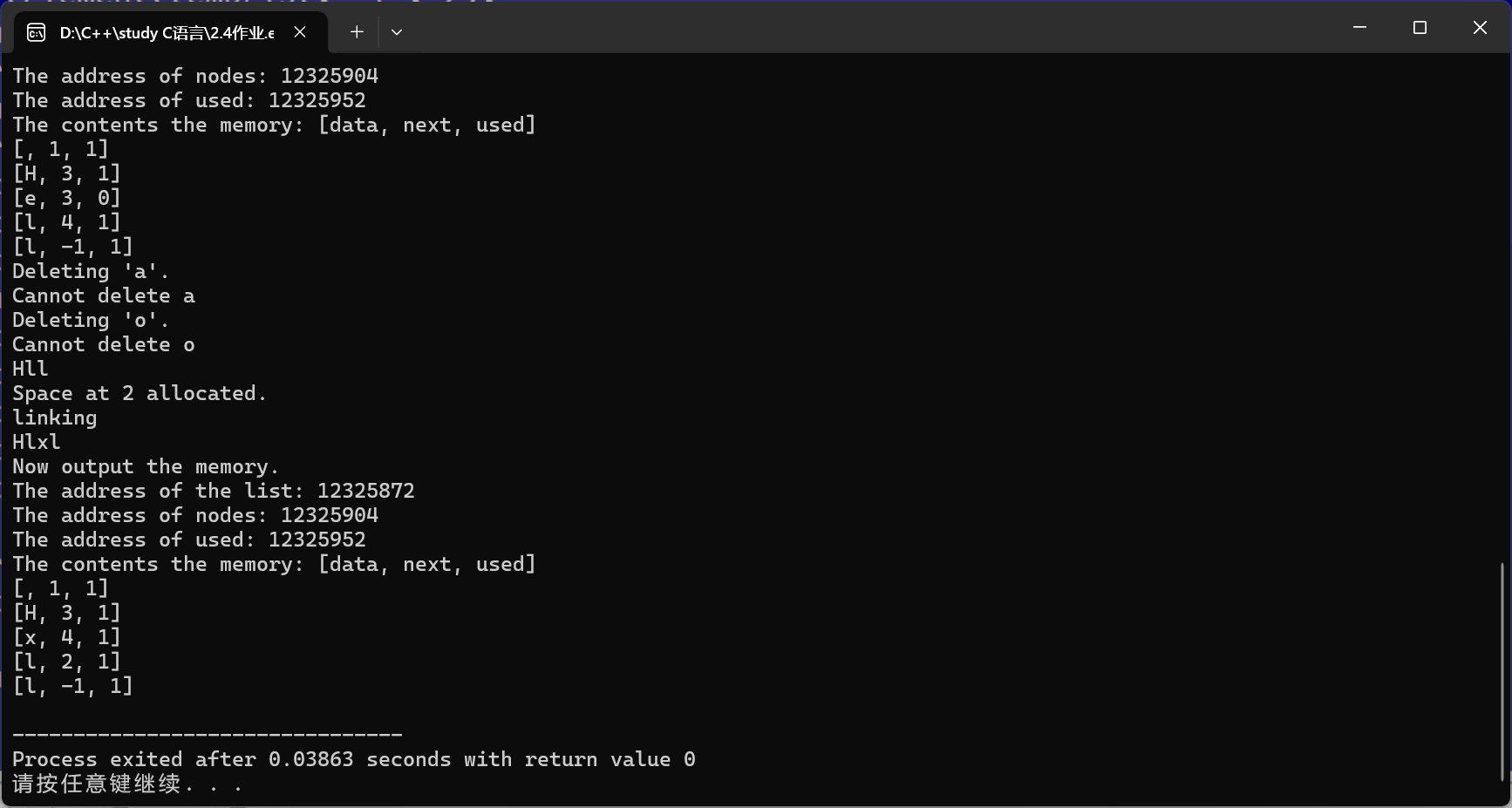
void outputMemory(ListPtr paraListPtr) {
int i;
printf("Now output the memory.\r\n");
printf("The address of the list: %ld\r\n", paraListPtr);
printf("The address of nodes: %ld\r\n", paraListPtr->nodes);
printf("The address of used: %ld\r\n", paraListPtr->used);
printf("The contents the memory: [data, next, used]\r\n");
for (i = 0; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++) {
printf("[%c, %d, %d]\r\n", paraListPtr->nodes[i].data, paraListPtr->nodes[i].next, paraListPtr->used[i]);
}
}
void appendInsertDeleteTest(){
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
outputMemory(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
outputMemory(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
outputMemory(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
outputMemory(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
outputMemory(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
outputMemory(tempList);
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 2);
printList(tempList);
outputMemory(tempList);
}
int main(){
appendInsertDeleteTest();
return 0;
}
 1.静态链表是一种使用数组来模拟链表结构的数据结构。它通过数组中的每个元素包含数据域和游标域来实现链表的功能。
1.静态链表是一种使用数组来模拟链表结构的数据结构。它通过数组中的每个元素包含数据域和游标域来实现链表的功能。
2.静态链表结合了顺序表和链表的优点;实现方式使他更有效地利用空间;适用于没有指针的语言环境。
3.数组中的下标代表的是元素在数组中的位置。而地址是数据在存储器中的位置(地址)。




















 3578
3578

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








