Java多线程中使用JDK自带工具类实现计数器

前言
在实际开发过程中,经常遇到需要多线程并行的业务,最后需要进行将各个线程完成的任务进行汇总,但主线程一般会早于子线程结束,如果要想等各个子线程完成后再继续运行主线程,这时就需要对各个线程是否执行完成进行标识,JDK并发包中就给开发者提供了几个不错的使用工具类。
接下来将通过Thread#join方法以及CountDownLatch,CyclicBarrier类进行上述案例方案的分析。
线程#join方法
使用join()方法的子线程对象正常执行run()方法,但当前线程会被无超时中断,等待执行join()方法的线程销毁后,继续执行被分开的当前线程。join()方法原理是该方法内使用wait()方法多个,原始文件如下所示:
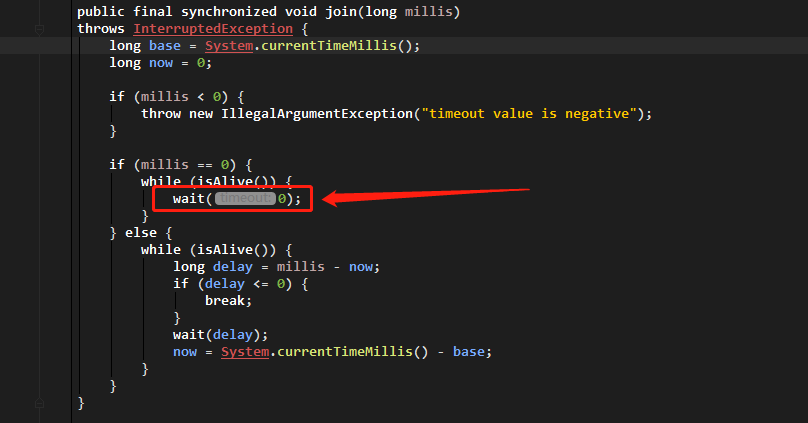
子线程join()完成时会调用notifyAll()来通知当前线程继续执行接下来的代码。
假如现在有两个线程产生数据结果,最后将两个线程结果进行相加,如果直接将两个线程执行并进行进行汇总,如下实现代码:
package top.ytao.demo.thread.count;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* htpps://ytao.top
*
* Created by YangTao on 2020/5/17 0017.
*/
public class JoinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Map<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
map.put("thread1", 1);
System.out.println("run thread1");
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
map.put("thread2", 2);
System.out.println("run thread2");
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
System.out.println(map.get("thread1") + map.get("thread2"));
System.out.println("end....");
}
}





 本文介绍了Java多线程中如何利用JDK自带的`Thread.join()`, `CountDownLatch`和`CyclicBarrier`实现计数器。通过示例展示了它们在等待子线程完成后再执行主线程任务的应用,强调了它们在多线程协作中的重要性。"
112495374,10552356,Power BI 数据建模指南:关系管理与分析,"['BI工具', '数据管理', '数据分析', 'Power BI教程', '数据建模']
本文介绍了Java多线程中如何利用JDK自带的`Thread.join()`, `CountDownLatch`和`CyclicBarrier`实现计数器。通过示例展示了它们在等待子线程完成后再执行主线程任务的应用,强调了它们在多线程协作中的重要性。"
112495374,10552356,Power BI 数据建模指南:关系管理与分析,"['BI工具', '数据管理', '数据分析', 'Power BI教程', '数据建模']
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1316
1316

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








