490. The Maze
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won’t stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball’s start position, the destination and the maze, determine whether the ball could stop at the destination.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)
Output: true
Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
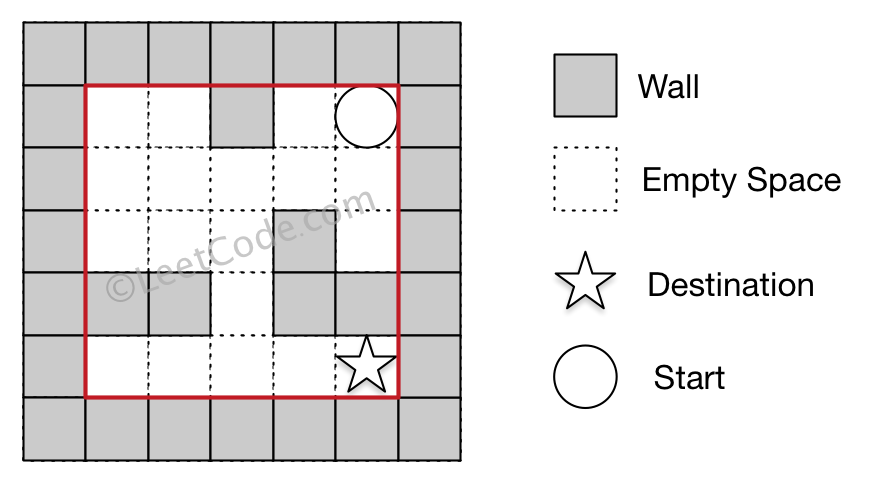
Example 2:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2)
Output: false
Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
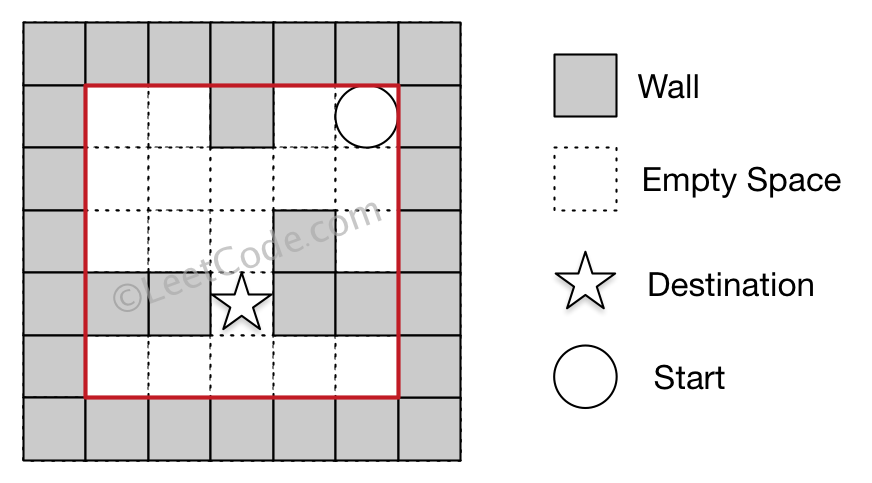
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won’t exceed 100.
方法1: recursion
思路:
这道题目和常规dfs/bfs不一样在于,在遍历中只能通过墙/边界来改变方向,dfs向一个方向前进必须到底。这也导致了需要对visited这个集合重新定义:滚过的地方可以以不同方向滚过第二次,不能mark。我们需要标记的visited是那些已经到过的start,在这些位置再发起dfs一定会产生重复。另外,用一个go2End函数来将球直接移动到四个方向的尽头,而不是只挪动一步,在这个newstart上再发起dfs。函数终止是某一次滚动的尽头,也就是newstart和destination一致。
易错点:
- unordered_set好像不支持vector<\int>。
Complexity
Time complexity : O(mn). Complete traversal of maze will be done in the worst case. Here, mm and n refers to the number of rows and columns of the maze.
Space complexity : O(mn). visited array of size m*n is used.
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPath(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
set<vector<int>> visited_start;
return pathHelper(maze, start, destination, visited_start);
}
bool pathHelper(vector<vector<int>> & maze, vector<int> & start, vector<int> & destination, set<vector<int>> & visited_start) {
if (start == destination) return true;
visited_start.insert(start);
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
vector<int> newStart = go2End(maze, start, dirs[i]);
if (!visited_start.count(newStart) && pathHelper(maze, newStart, destination, visited_start)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
vector<int> go2End(vector<vector<int>> & maze, vector<int> start, vector<int> & dir) {
int newStartX = start[0] + dir[0], newStartY = start[1] + dir[1];
if (newStartX < 0 || newStartX >= maze.size() || newStartY < 0 || newStartY >= maze[0].size() || maze[newStartX][newStartY]) return start;
return go2End(maze, {newStartX, newStartY}, dir);
}
};
方法2: bfs
思路:
和正常bfs区别在于用go2End的结果来代替一步移动,用visited_start来代替visited。
Complexity
Time complexity : O(mn). Complete traversal of maze will be done in the worst case. Here, mm and n refers to the number of rows and columns of the maze.
Space complexity : O(mn). visited array of size m*n is used.
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPath(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
set<vector<int>> visited_start;
queue<vector<int>> q;
q.push(start);
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
while (!q.empty()) {
vector<int> pos = q.front();
q.pop();
if (pos == destination) {
return true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
vector<int> newStart = go2End(maze, pos, dirs[i]);
if (!visited_start.count(newStart)){
q.push(newStart);
visited_start.insert(newStart);
}
}
}
return false;
}
vector<int> go2End(vector<vector<int>> & maze, vector<int> & start, vector<int> & dir) {
int newStartX = start[0] + dir[0], newStartY = start[1] + dir[1];
if (newStartX < 0 || newStartX >= maze.size() || newStartY < 0 || newStartY >= maze[0].size() || maze[newStartX][newStartY]) return start;
vector<int> newStart ={newStartX, newStartY};
return go2End(maze, newStart, dir);
}
};







 博客围绕判断迷宫中球能否到达目的地展开,给出递归(DFS)和BFS两种方法。递归方法需重新定义visited集合,用go2End函数将球移到尽头;BFS用go2End结果代替一步移动,用visited_start代替visited。两种方法时间和空间复杂度均为O(mn)。
博客围绕判断迷宫中球能否到达目的地展开,给出递归(DFS)和BFS两种方法。递归方法需重新定义visited集合,用go2End函数将球移到尽头;BFS用go2End结果代替一步移动,用visited_start代替visited。两种方法时间和空间复杂度均为O(mn)。
















 5500
5500

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








