1、打开该网址:http://tool.chinaz.com/dns/?type=1&host=aka.ms&ip=
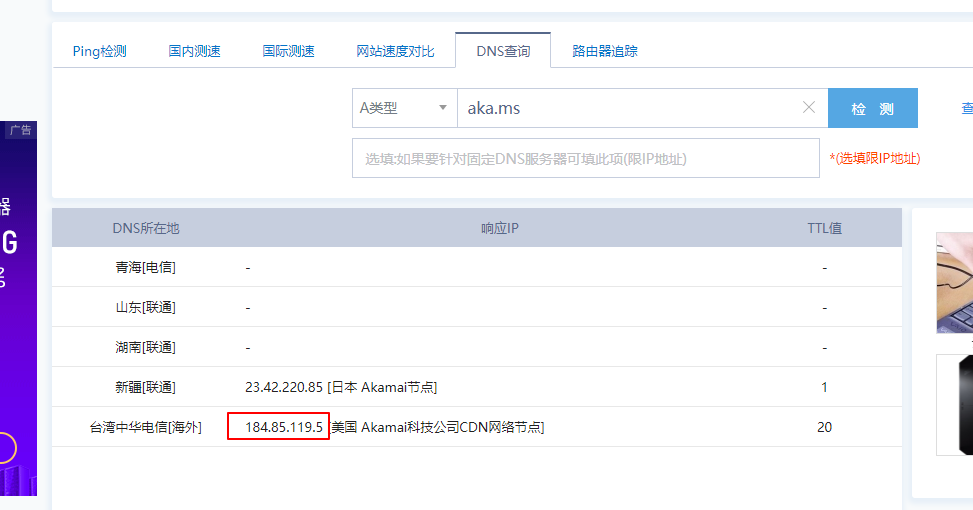
查看这个ip,在C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 文件中配置aka.ms响应,如 23.42.220.85 aka.ms
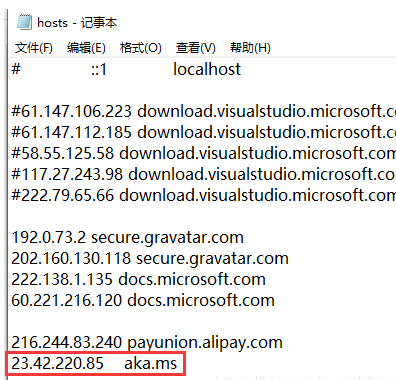
配置好了,再次点开安装文件,就可以下载了
参考地址:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/shanxing200/article/details/118157465
 文章介绍了如何通过打开特定网址检查IP,然后在Windows系统的hosts文件中配置aka.ms对应的IP地址,以此解决下载安装文件时遇到的问题。按照提供的步骤操作后,可以成功进行下载。
文章介绍了如何通过打开特定网址检查IP,然后在Windows系统的hosts文件中配置aka.ms对应的IP地址,以此解决下载安装文件时遇到的问题。按照提供的步骤操作后,可以成功进行下载。
1、打开该网址:http://tool.chinaz.com/dns/?type=1&host=aka.ms&ip=

查看这个ip,在C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 文件中配置aka.ms响应,如 23.42.220.85 aka.ms

配置好了,再次点开安装文件,就可以下载了
参考地址:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/shanxing200/article/details/118157465
您可能感兴趣的与本文相关的镜像

LobeChat
LobeChat 是一个开源、高性能的聊天机器人框架。支持语音合成、多模态和可扩展插件系统。支持一键式免费部署私人ChatGPT/LLM 网络应用程序。
 2万+
2万+
 1036
1036
 3328
3328

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?


