二叉树找值找为x的结点
找值不简单吗?轻轻松松拿捏,大部分同学都会写出这样的代码
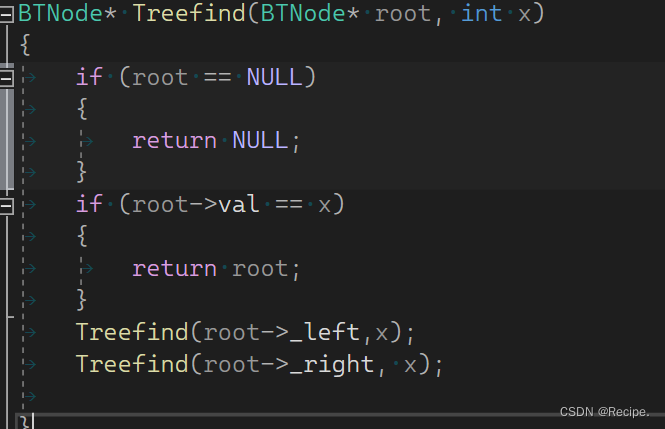
但这种代码有问题,因为没有把查找结果返回给上一层,没有用返回值接收。
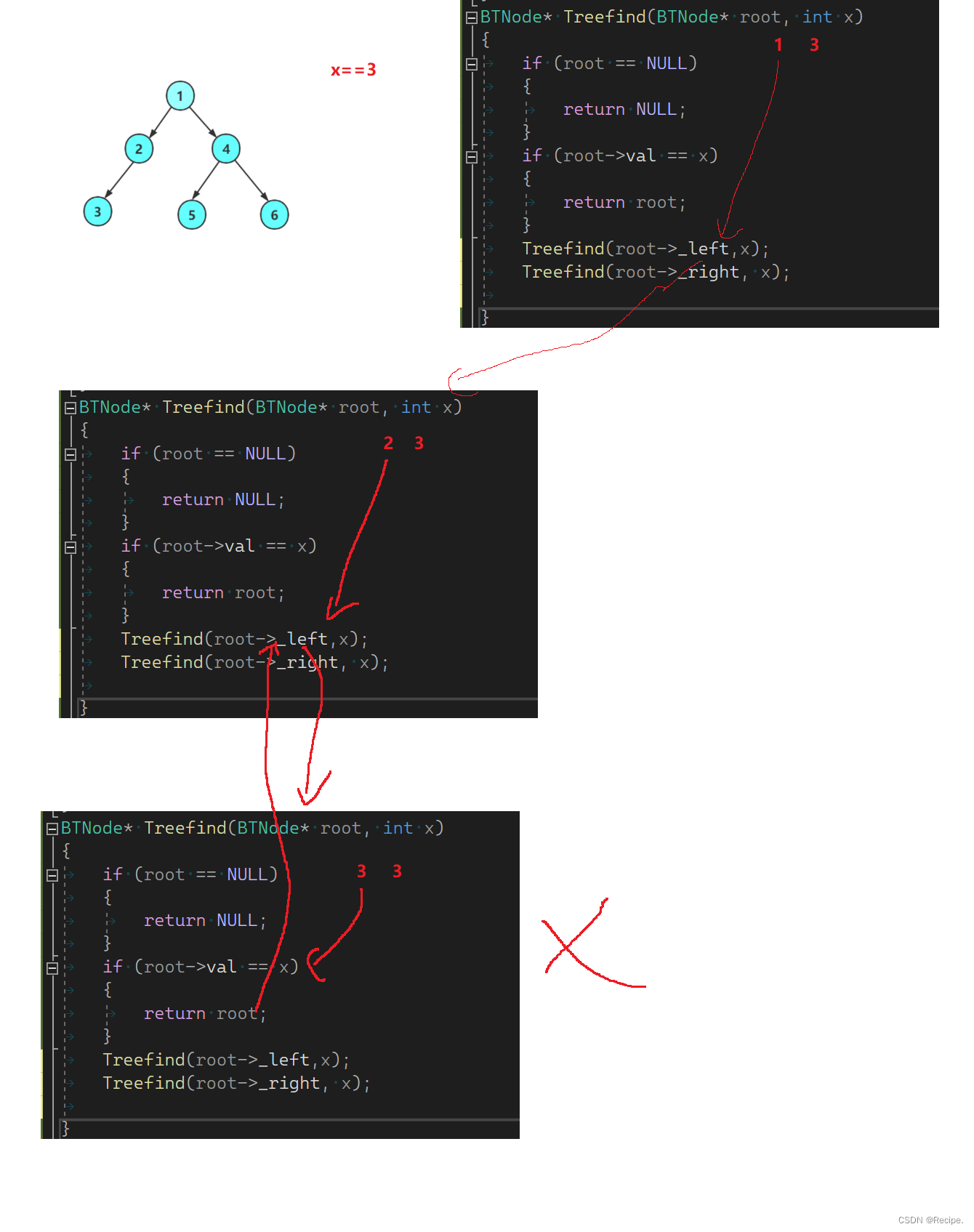
当找到3时返回给了上一层,但并没有用返回值接收,那么结果就会丢失,理论上如果左树找到了,就不会去右树去寻找,因此用返回值判断左树是否存在且返回结果是很重要的。
那么就有同学突发奇想了,那么我把&&改成||不就行了,这样在左树找到就不用去右树找了。
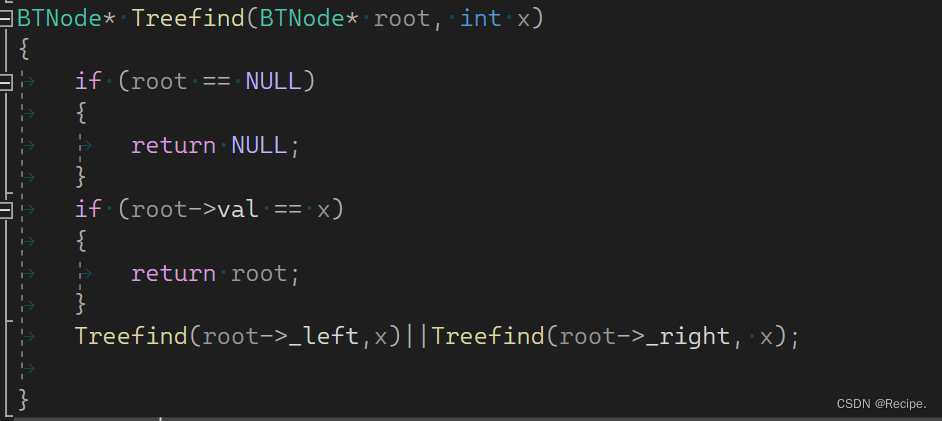
首先||只能返回值1和0,也就真(true)和假(false),只有当返回值是bool布尔值时才能用||,况且返回值是BTNode*,所以这种方法是错误的。
那么我们用接收返回值写一下。
这个代码有什么问题吗?
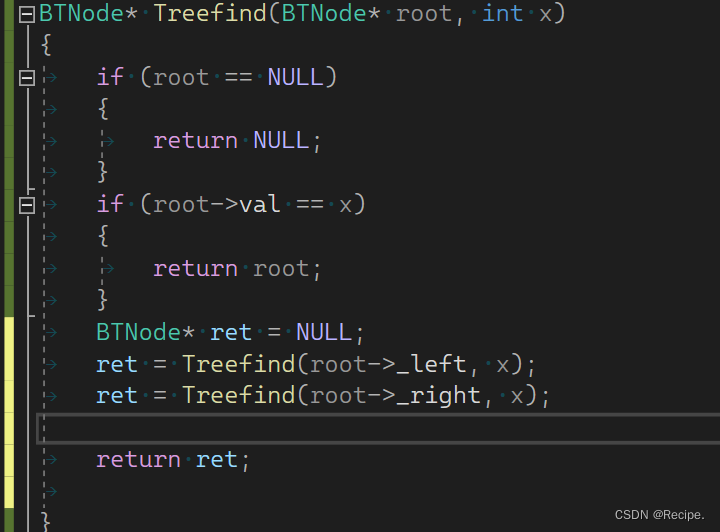
这个代码有两个问题,第一,理论上左树找到结果就不用去右树去查找,但这个代码不管左树有没有找到结果,都会去右树查找,第二,如果左树找到结果永远会被右树的空值覆盖。
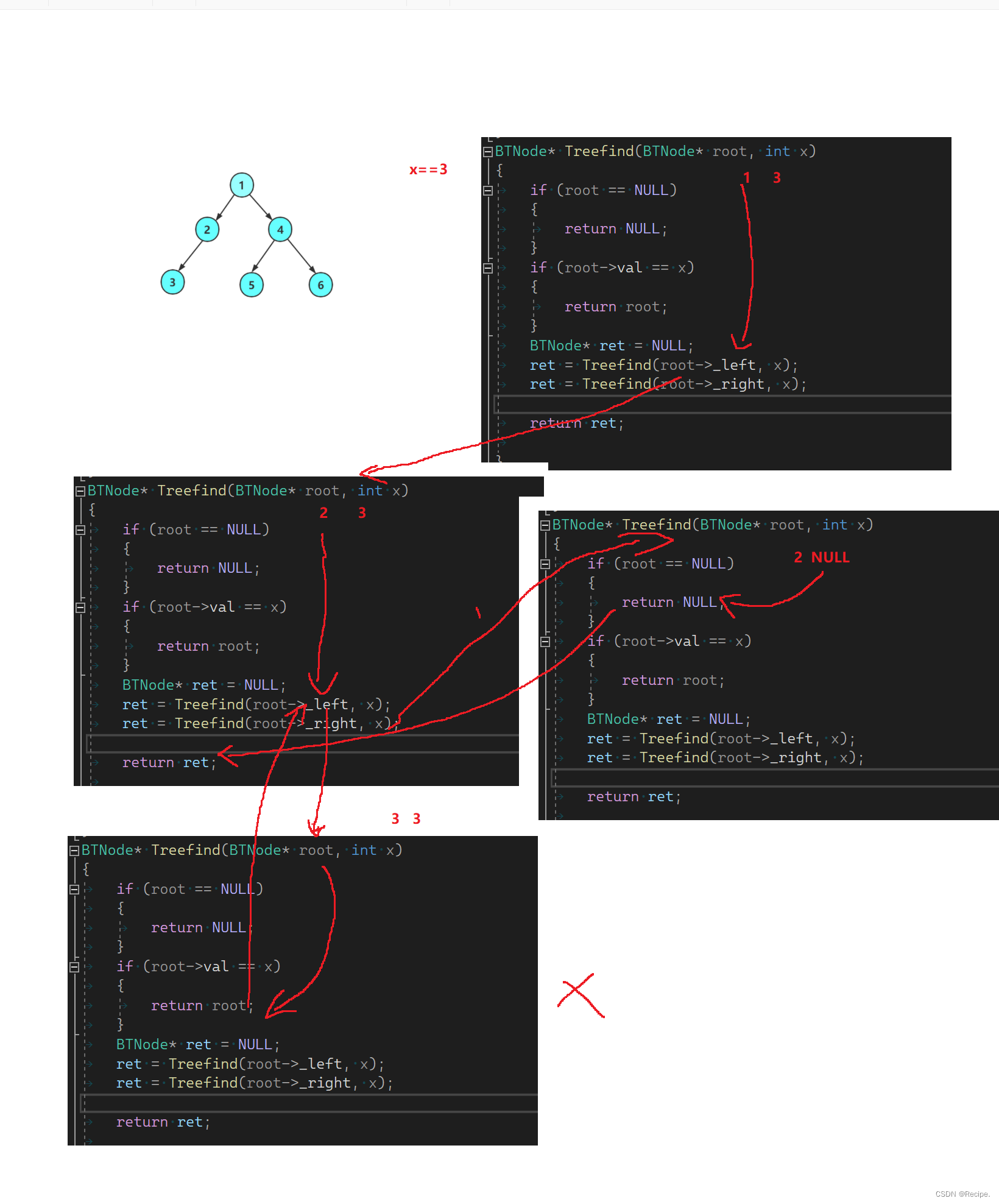
正确写法
逻辑最顺的写法
BTNode* Treefind(BTNode* root, int x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->val == x)
{
return root;
}
BTNode* ret = NULL;
ret = Treefind(root->_left, x);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = Treefind(root->_right, x);
if (ret)
return ret;
return NULL;
}
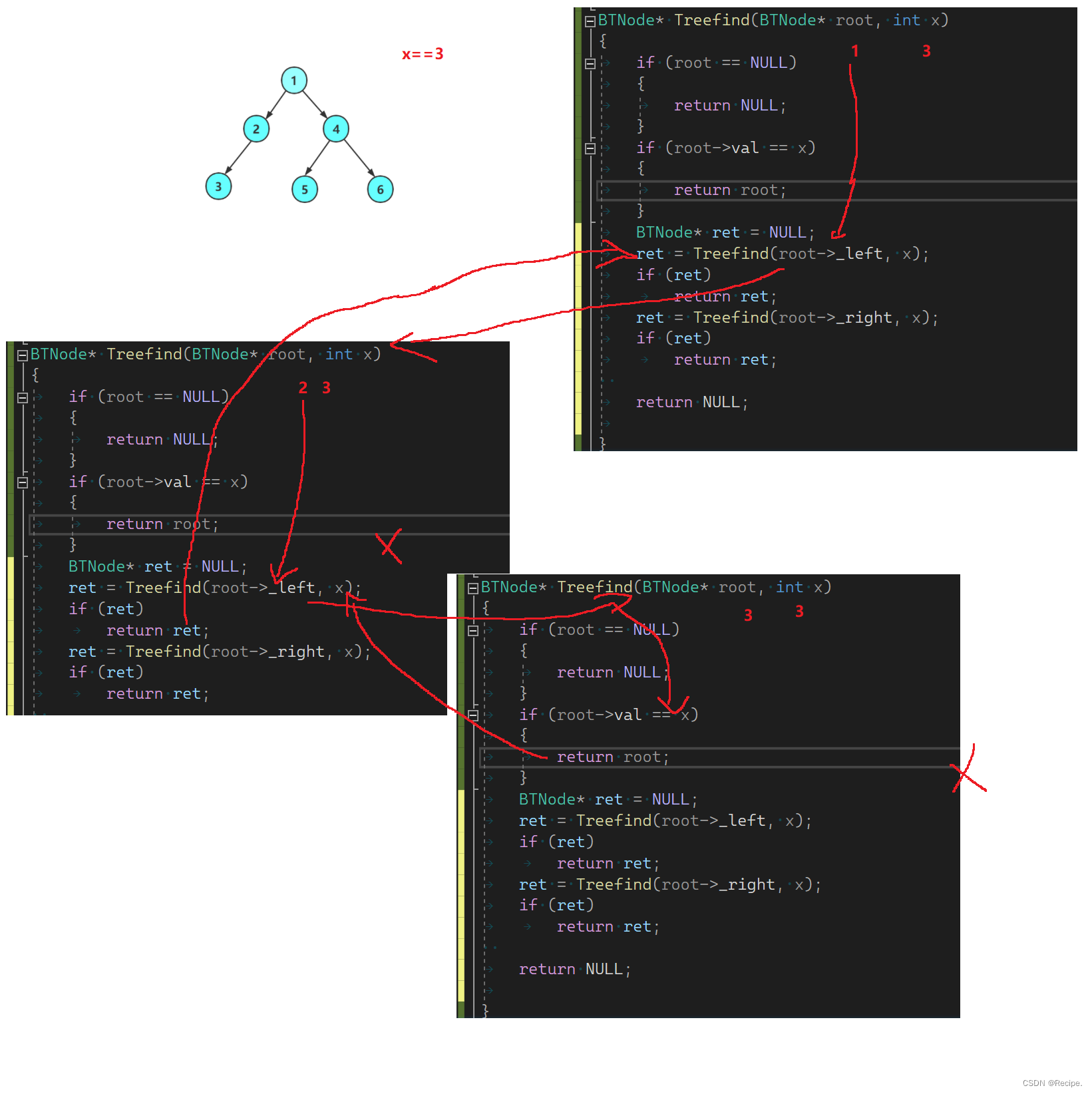 找x==4时
找x==4时
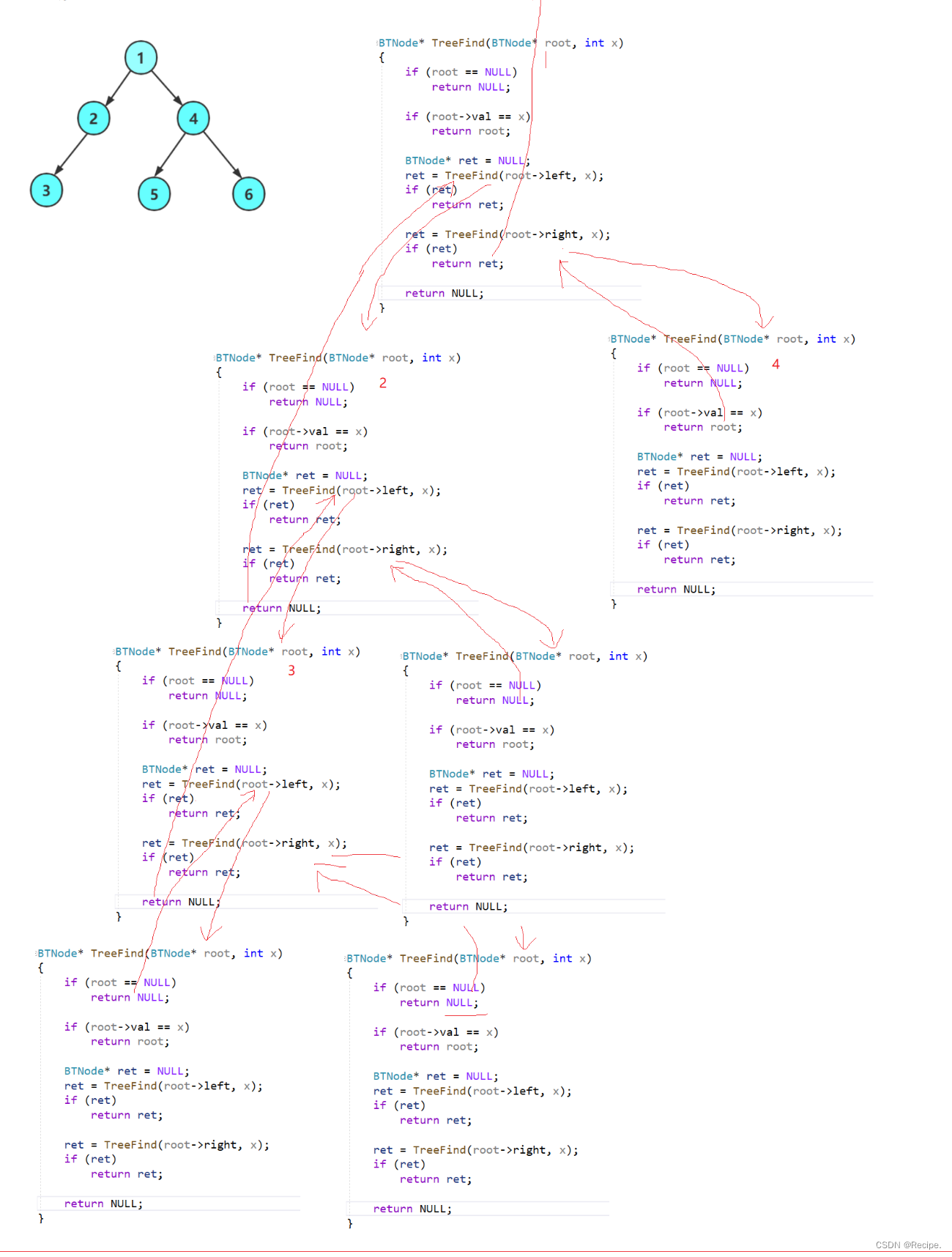
二叉树的销毁
二叉树销毁采用后序比较方便 前序也可以 不过很麻烦,推荐用后序
void TreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestroy(root->_left);
TreeDestroy(root->_right);
free(root);
}
这里root不用置空 因为置不置空都不影响root,因为root形参是局部变量,如果要置空,可以在外部置空。
二叉树的层序遍历
二叉树的层序遍历最好的办法就是队列结构,因为队列是先进先出的。
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueInit(&q);
if (root)
QuePush(&q,root);
while (Empty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", Front->val);
if (Front->_left)
QuePush(&q, Front->_left);
if (Front->_right)
QuePush(&q, Front->_right);
QuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueDestroy(&q);
}

1带2 4 2带3 N 4带5 6 层序遍历使用队列遍历是最好办法!
判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
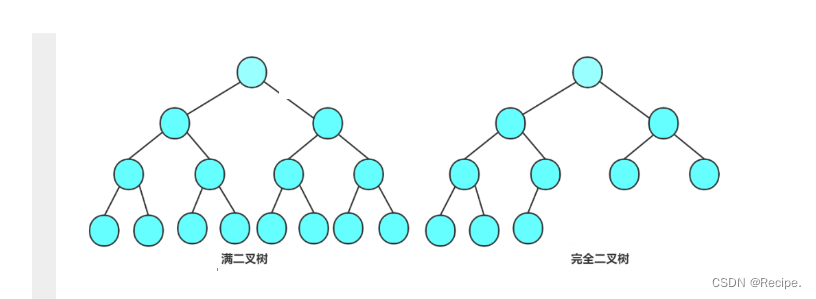
假设有k层高度,满二叉树的每一层结点都是满的 从左到右是连续
假设有k层高度,完全二叉树的k-1层都是满的,k层不完全满 且从左到右是连续。
那么使用层序遍历是最好的。
完全二叉树:如果非空节点是连续的,是完全二叉树。
不是完全二叉树:如果非空节点不是连续的,中间有空节点,就不是完全二叉树。
int Treecomplete(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueInit(&q);
if (root)
QuePush(&q, root);
while (!Empty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueFront(&q);
if (Front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QuePush(&q, Front->_left);
QuePush(&q, Front->_right);
QuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
//已经遇到空节点,如果队列中后面的节点还有非空,就不是完全二叉树
while (!Empty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueFront(&q);
QuePop(&q);//这里pop的队列的节点 不会影响二叉树取Front的节点。
if (Front != NULL)
{
QueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
![]()
求二叉树的高度
二叉树高度不就是左子树或者右子树的深度最长的那一个,加上根节点自己。
一般大家求高度的时候,都会这样去写代码,但这样写是有问题的,使用三目运算符使虽然让代码行数减少了,但造成了空间栈的浪费,因为在算左子树深度和右子树深度时,求出来的结果值只用在了判断它们俩谁大谁小的问题上面并没有保存返回值,当判断完左还是右大以后,后面运行的代码它还要再次去计算左子树或者右子树深度再+1,造成了重复计算(栈浪费),如果是数据量大会造成栈溢出。
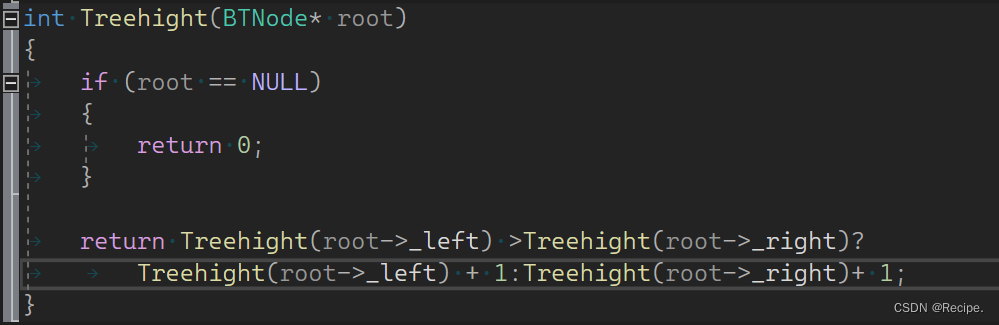
解决办法就是创建变量接收左子树或者右子树的深度,再进行比较,这样就不会造成栈溢出的问题,也节省了空间和提高了效率。
int Treehight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lefthight = Treehight(root->_left);
int righthight = Treehight(root->_right);
return lefthight > righthight ? lefthight + 1 : righthight + 1;
}
![]()
完整代码
Queue.h
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct BinaryTree* Queuetype;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
Queuetype data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queque
{
QNode* tail;
QNode* head;
int size;
}Que;
void QueInit(Que* p);
void QueDestroy(Que* p);
void QuePush(Que* p,Queuetype x);
void QuePop(Que* p);
Queuetype QueFront(Que* p);
Queuetype QueBack(Que* p);
bool Empty(Que* p);
Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueInit(Que* p)
{
assert(p);
p->head = p->tail =NULL;
p->size = 0;
}
void QueDestroy(Que* p)
{
QNode* cur = p->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
p->head = p->tail = NULL;
p->size = 0;
}
void QuePush(Que* p, Queuetype x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (p->tail == NULL)
{
p->head = p->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
p->tail->next = newnode;
p->tail = newnode;
}
p->size++;
}
void QuePop(Que* p)
{
assert(p);
assert(!Empty(p));
if (p->head->next == NULL)
{
free(p->head);
p->head = p->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = p->head->next;
free(p->head);
p->head = next;
}
p->size--;
}
Queuetype QueFront(Que* p)
{
assert(p);
assert(!Empty(p));
return p->head->data;
}
Queuetype QueBack(Que* p)
{
assert(p);
assert(!Empty(p));
return p->tail->data;
}
bool Empty(Que* p)
{
assert(p);
return p->head == NULL;
}
test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
struct BinaryTree* _left;
struct BinaryTree* _right;
int val;
}BTNode;
#include"Queue.h"
BTNode* buynode(int x)
{
BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->_left = NULL;
newnode->_right = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
return newnode;
}
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf(" NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->val);
PreOrder(root->_left);
PreOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf(" NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->_left);
printf("%d ", root->val);
InOrder(root->_right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf(" NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->_left);
PostOrder(root->_right);
printf("%d ", root->val);
}
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueInit(&q);
if (root)
QuePush(&q,root);
while (!Empty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", Front->val);
if (Front->_left)
QuePush(&q, Front->_left);
if (Front->_right)
QuePush(&q, Front->_right);
QuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueDestroy(&q);
}
int Treecomplete(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueInit(&q);
if (root)
QuePush(&q, root);
while (!Empty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueFront(&q);
if (Front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QuePush(&q, Front->_left);
QuePush(&q, Front->_right);
QuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
//已经遇到空节点,如果队列中后面的节点还有非空,就不是完全二叉树
while (!Empty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueFront(&q);
QuePop(&q);
if (Front != NULL)
{
QueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
int Treesize(BTNode*root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : Treesize(root->_left) + Treesize(root->_right)+1;
}
int Treeleafsize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return Treeleafsize(root->_left) + Treeleafsize(root->_right);
}
int TreeKlevel(BTNode* root,int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return TreeKlevel(root->_left, k - 1) + TreeKlevel(root->_right, k - 1);
}
int Treehight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return Treehight(root->_left) >Treehight(root->_right)?
Treehight(root->_left) + 1:Treehight(root->_right)+ 1;
}
void TreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestroy(root->_left);
TreeDestroy(root->_right);
free(root);
}
BTNode* Treefind(BTNode* root, int x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->val == x)
{
return root;
}
BTNode* ret = NULL;
ret = Treefind(root->_left, x);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = Treefind(root->_right, x);
if (ret)
return ret;
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* node1 = buynode(1);
BTNode* node2 = buynode(2);
BTNode* node3 = buynode(3);
BTNode* node4 = buynode(4);
BTNode* node5 = buynode(5);
BTNode* node6 = buynode(6);
node1->_left = node2;
node1->_right = node4;
node2->_left = node3;
node4->_left = node5;
node4->_right = node6;
PreOrder(node1);
printf("\n");
InOrder(node1);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(node1);
printf("\n");
printf("Treesize:%d\n", Treesize(node1));
printf("Treeleafsize:%d\n", Treeleafsize(node1));
printf(" TreeKlevel:%d\n", TreeKlevel(node1, 2));
printf("Treehight:%d\n", Treehight(node1));
LevelOrder(node1);
printf("Treecomplete:%d\n", Treecomplete(node1));
TreeDestroy(node1);
node1 = NULL;
}




 文章讲述了如何改进二叉树查找算法,强调返回值的使用以避免结果丢失,同时讨论了完全二叉树的判断方法以及避免栈溢出的求树高技巧。涉及层次遍历、队列操作和结构分析。
文章讲述了如何改进二叉树查找算法,强调返回值的使用以避免结果丢失,同时讨论了完全二叉树的判断方法以及避免栈溢出的求树高技巧。涉及层次遍历、队列操作和结构分析。
















 2188
2188

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








