设计一个模拟进程状态转换的程序。单处理机系统中有n个进程,进程的状态有就绪、执行和阻塞,写一程序模拟进程的执行情况,并给出提示。
定义一个PCB进程控制块,如下:
struct PCB
{
string name; // 进程名
int arrivalTime; // 到达时间
int burstTime; // 需要运行的时间
int remainingTime; // 剩余时间
int startTime; // 开始时间
int finishTime; // 完成时间
int turnAroundTime; // 周转时间
double weightedTAT; // 带权周转时间
string state; // 进程状态
};其中进程的状态只有两种取值,正在执行和执行完成,当一个进程在执行时其他未执行完毕的进程默认处于阻塞状态。
定义时间片大小为10。
// 时间片大小
const int TIME_QUANTUM = 10;定义就绪队列。
queue<int> readyQueue; // 就绪队列定义总周转时间和总带权周转时间。
double totalTAT = 0; // 总周转时间
double totalWeightedTAT = 0; // 总带权周转时间将所有到达时间为0的进程加入到阻塞队列中,由于题目说明进程到达时间默认都为0,所以这一步的判断语句可以去掉。
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (processes[i].arrivalTime == 0)
{
readyQueue.push(i);
}
}采用时间片轮转处理机调度算法对进程进行调度。
while (completed < n)
{
if (!readyQueue.empty())
{
int index = readyQueue.front();
readyQueue.pop();
// 如果进程是第一次执行,记录开始时间
if (processes[index].remainingTime == processes[index].burstTime)
{
processes[index].startTime = currentTime;
}
// 执行当前进程
int timeSlice = min(TIME_QUANTUM, processes[index].remainingTime);
processes[index].remainingTime -= timeSlice;
currentTime += timeSlice;
cout << "时间" << currentTime - timeSlice << "到" << currentTime
<< ":进程" << processes[index].name << "执行,剩余时间"
<< processes[index].remainingTime << endl;
// 如果进程完成,更新状态并计算相关时间
if (processes[index].remainingTime == 0)
{
processes[index].finishTime = currentTime;
processes[index].turnAroundTime = processes[index].finishTime - processes[index].arrivalTime;
processes[index].weightedTAT = (double)processes[index].turnAroundTime / processes[index].burstTime;
processes[index].state = "完成";
totalTAT += processes[index].turnAroundTime;
totalWeightedTAT += processes[index].weightedTAT;
completed++;
}
else
{
// 如果未完成,重新加入就绪队列
readyQueue.push(index);
}
// 将在当前时间点到达的进程加入就绪队列
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (processes[i].arrivalTime <= currentTime && processes[i].state == "就绪")
{
bool inQueue = false;
queue<int> tempQueue = readyQueue;
while (!tempQueue.empty())
{
if (tempQueue.front() == i)
{
inQueue = true;
break;
}
tempQueue.pop();
}
if (!inQueue)
{
readyQueue.push(i);
}
}
}
}
else
{
// 如果没有进程可以执行,时间推进
currentTime++;
}
}输出最终的调度结果:
// 输出调度结果
cout << "\n调度结果:" << endl;
cout << setw(10) << "进程名"
<< setw(10) << "到达时间"
<< setw(10) << "运行时间"
<< setw(10) << "开始时间"
<< setw(10) << "完成时间"
<< setw(10) << "周转时间"
<< setw(15) << "带权周转时间" << endl;
for (const auto& process : processes)
{
cout << setw(10) << process.name
<< setw(10) << process.arrivalTime
<< setw(10) << process.burstTime
<< setw(10) << process.startTime
<< setw(10) << process.finishTime
<< setw(10) << process.turnAroundTime
<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << process.weightedTAT << endl;
}
cout << "\n平均周转时间T = " << fixed << setprecision(2) << totalTAT / n;
cout << " 平均带权周转时间W = " << fixed << setprecision(2) << totalWeightedTAT / n << endl;程序的入口main函数:
int main()
{
int n; // 进程数
cout << "请输入进程数:";
cin >> n;
vector<PCB> processes(n);
cout << "请输入每个进程的名称、到达时间和运行时间:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cout << "进程" << i + 1 << ":";
cin >> processes[i].name >> processes[i].arrivalTime >> processes[i].burstTime;
processes[i].remainingTime = processes[i].burstTime;
processes[i].state = "就绪";
}
// 调用调度模拟函数
simulateRoundRobin(processes, n);
return 0;
}假设进程的名称、到达时间和处理时间如下所示:
| 进程名 | 到达时间 | 处理时间 |
| A | 0 | 20 |
| B | 0 | 10 |
| C | 0 | 15 |
| D | 0 | 5 |
在时间片为10的情况下,进程调度执行时间图应该如下所示:
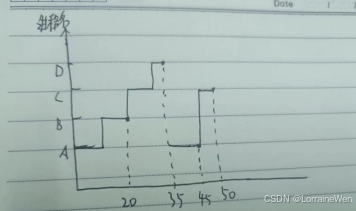
对应的周转时间等变量的值最终应该如下表所示:
| 进程名 | 到达时间 | 运行时间 | 开始时间 | 完成时间 | 周转时间 | 带权周转时间 |
| A | 0 | 20 | 0 | 45 | 45 | 2.25 |
| B | 0 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 2.00 |
| C | 0 | 15 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 3.33 |
| D | 0 | 5 | 30 | 35 | 35 | 7.00 |
| 平均周转时间T=37.50 平均带权周转时间W = 3.65 | ||||||
运行程序。

输入数据:
请输入进程数:4
请输入每个进程的名称、到达时间和运行时间:
进程1:A 0 20
进程2:B 0 10
进程3:C 0 15
进程4:D 0 5
输出调度结果:
开始调度模拟...
时间0到10:进程A执行,剩余时间10
时间10到20:进程B执行,剩余时间0
时间20到30:进程C执行,剩余时间5
时间30到35:进程D执行,剩余时间0
时间35到45:进程A执行,剩余时间0
时间45到50:进程C执行,剩余时间0
调度结果:
进程名 到达时间 运行时间 开始时间 完成时间 周转时间 带权周转时间
A 0 20 0 45 45 2.25
B 0 10 10 20 20 2.00
C 0 15 20 50 50 3.33
D 0 5 30 35 35 7.00
平均周转时间T = 37.50 平均带权周转时间W = 3.65
和纸面推导的结果一样,说明程序结果是有效的。
再次测试程序。

输入数据如下:
进程1:A 0 50
进程2:B 0 30
进程3:C 0 70
程序输出结果如下:
开始调度模拟...
时间0到10:进程A执行,剩余时间40
时间10到20:进程B执行,剩余时间20
时间20到30:进程C执行,剩余时间60
时间30到40:进程A执行,剩余时间30
时间40到50:进程B执行,剩余时间10
时间50到60:进程C执行,剩余时间50
时间60到70:进程A执行,剩余时间20
时间70到80:进程B执行,剩余时间0
时间80到90:进程C执行,剩余时间40
时间90到100:进程A执行,剩余时间10
时间100到110:进程C执行,剩余时间30
时间110到120:进程A执行,剩余时间0
时间120到130:进程C执行,剩余时间20
时间130到140:进程C执行,剩余时间10
时间140到150:进程C执行,剩余时间0
调度结果:
进程名 到达时间 运行时间 开始时间 完成时间 周转时间 带权周转时间
A 0 50 0 120 120 2.40
B 0 30 10 80 80 2.67
C 0 70 20 150 150 2.14
平均周转时间T = 116.67 平均带权周转时间W = 2.40
结果同样是正确的。
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
// 定义PCB结构体
struct PCB
{
string name; // 进程名
int arrivalTime; // 到达时间
int burstTime; // 需要运行的时间
int remainingTime; // 剩余时间
int startTime; // 开始时间
int finishTime; // 完成时间
int turnAroundTime; // 周转时间
double weightedTAT; // 带权周转时间
string state; // 进程状态
};
// 时间片大小
const int TIME_QUANTUM = 10;
// 函数声明
void simulateRoundRobin(vector<PCB>& processes, int n)
{
queue<int> readyQueue; // 就绪队列
int currentTime = 0; // 当前时间
int completed = 0; // 已完成的进程数
double totalTAT = 0; // 总周转时间
double totalWeightedTAT = 0; // 总带权周转时间
cout << "开始调度模拟..." << endl;
// 初始所有到达时间为0的进程进入就绪队列
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (processes[i].arrivalTime == 0)
{
readyQueue.push(i);
}
}
while (completed < n)
{
if (!readyQueue.empty())
{
int index = readyQueue.front();
readyQueue.pop();
// 如果进程是第一次执行,记录开始时间
if (processes[index].remainingTime == processes[index].burstTime)
{
processes[index].startTime = currentTime;
}
// 执行当前进程
int timeSlice = min(TIME_QUANTUM, processes[index].remainingTime);
processes[index].remainingTime -= timeSlice;
currentTime += timeSlice;
cout << "时间" << currentTime - timeSlice << "到" << currentTime
<< ":进程" << processes[index].name << "执行,剩余时间"
<< processes[index].remainingTime << endl;
// 如果进程完成,更新状态并计算相关时间
if (processes[index].remainingTime == 0)
{
processes[index].finishTime = currentTime;
processes[index].turnAroundTime = processes[index].finishTime - processes[index].arrivalTime;
processes[index].weightedTAT = (double)processes[index].turnAroundTime / processes[index].burstTime;
processes[index].state = "完成";
totalTAT += processes[index].turnAroundTime;
totalWeightedTAT += processes[index].weightedTAT;
completed++;
}
else
{
// 如果未完成,重新加入就绪队列
readyQueue.push(index);
}
// 将在当前时间点到达的进程加入就绪队列
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (processes[i].arrivalTime <= currentTime && processes[i].state == "就绪")
{
bool inQueue = false;
queue<int> tempQueue = readyQueue;
while (!tempQueue.empty())
{
if (tempQueue.front() == i)
{
inQueue = true;
break;
}
tempQueue.pop();
}
if (!inQueue)
{
readyQueue.push(i);
}
}
}
}
else
{
// 如果没有进程可以执行,时间推进
currentTime++;
}
}
// 输出调度结果
cout << "\n调度结果:" << endl;
cout << setw(10) << "进程名"
<< setw(10) << "到达时间"
<< setw(10) << "运行时间"
<< setw(10) << "开始时间"
<< setw(10) << "完成时间"
<< setw(10) << "周转时间"
<< setw(15) << "带权周转时间" << endl;
for (const auto& process : processes)
{
cout << setw(10) << process.name
<< setw(10) << process.arrivalTime
<< setw(10) << process.burstTime
<< setw(10) << process.startTime
<< setw(10) << process.finishTime
<< setw(10) << process.turnAroundTime
<< setw(15) << fixed << setprecision(2) << process.weightedTAT << endl;
}
cout << "\n平均周转时间T = " << fixed << setprecision(2) << totalTAT / n;
cout << " 平均带权周转时间W = " << fixed << setprecision(2) << totalWeightedTAT / n << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n; // 进程数
cout << "请输入进程数:";
cin >> n;
vector<PCB> processes(n);
cout << "请输入每个进程的名称、到达时间和运行时间:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cout << "进程" << i + 1 << ":";
cin >> processes[i].name >> processes[i].arrivalTime >> processes[i].burstTime;
processes[i].remainingTime = processes[i].burstTime;
processes[i].state = "就绪";
}
// 调用调度模拟函数
simulateRoundRobin(processes, n);
return 0;
}























 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










