摘要:本博文主要介绍使用卷积神经网络完成
MNIST-Fashion数据集分类任务的算法过程。
0、背景介绍
-
MNIST-Fashion数据集:包含了10个不同种类的时尚商品的灰度图像。每个图像的尺寸为28×2828\times 2828×28像素。
这10个类别为:T恤/上衣(T-shirt/top)、裤子(Trouser)、毛衣(Pullover)、连衣裙(Dress)、外套(Coat)、凉鞋(Sandal)、衬衫(Shirt)、运动鞋(Sneaker)、包(Bag)和踝靴(Ankle boot)。
-
LeNet-5模型: 经典的卷积神经网络(CNN),由Yann LeCun等人于1998年提出。这一发明非常超前,跨越了传统视觉算法的思路,历史性的提出了“卷积”的思想用于图像特征的提取。LeNet-5模型由7个层组成,包括3个卷积层、2个池化层和2个全连接层。
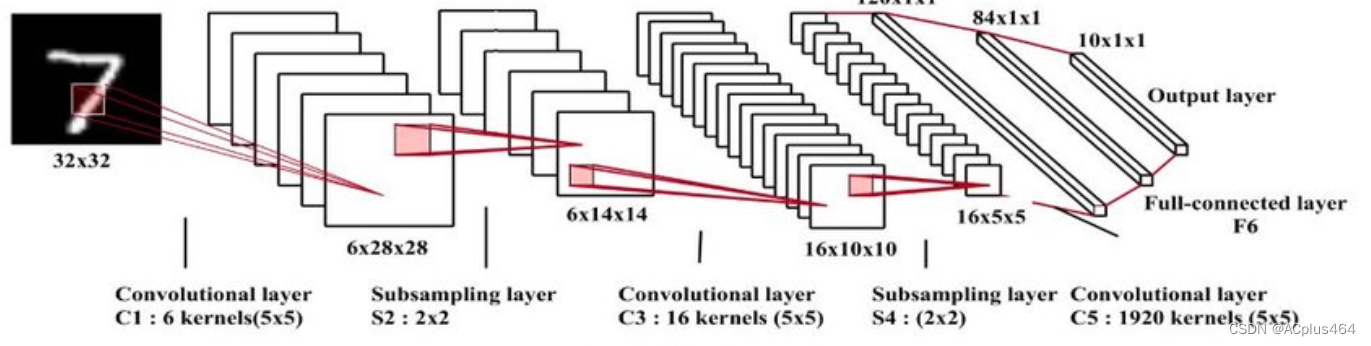
下面是LeNet-5模型的层次结构:
- 第一层(卷积层):输入是32×3232\times3232×32的灰度图像。使用6个5×55\times55×5的卷积核对输入进行卷积操作,得到6个特征图。每个特征图的大小为28×2828\times 2828×28。
- 第二层(池化层):对每个特征图进行2×22\times 22×2的均值池化操作,将特征图的尺寸减半,得到6个14×1414\times 1414×14的特征图。
- 第三层(卷积层):使用16个5×55\times 55×5的卷积核对第二层的特征图进行卷积操作,得到16个10×1010\times 1010×10的特征图。
- 第四层(池化层):对每个特征图进行2×22\times 22×2的平均池化操作,将特征图的尺寸减半,得到16个5×55\times 55×5的特征图。
- 第五层(全连接层):将第四层的特征图展平为一个向量,并与120个神经元进行全连接。
- 第六层(全连接层):与84个神经元进行全连接。
- 第七层(输出层):使用softmax激活函数将84个神经元的输出映射为10个类别的概率分布,表示输入图像属于每个类别的概率。
1、网络定义
根据上文的描述,我们使用nn.Sequential()方法,一层一层地堆叠7层网络的结构即可:
class Reshape(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 1, 28, 28)
return x
net = nn.Sequential(
Reshape(),
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10),
)
2、使用GPU
使用GPU进行训练和测试的加速。思路如下:
- 配置device
- 将
net迁移到device上 - 将训练数据和测试(验证)数据迁移到device上
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
net.to(device)
3、网络参数初始化
此处使用了nn.apply()方法,对nn.Sequential()搭建的网络进行参数初始化。后续的网络很多也沿用了这一方法:
def weights_init(layer):
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(layer, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(layer.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(layer.bias)
net.apply(weights_init)
4、数据加载
使用d2l算法库,直接拉取数据集即可,这样非常简单,不用自己下载和保存:
batch_size = 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size=batch_size)
两行代码就能搞定。这样返回的train_iter, test_iter是迭代器函数,每调用一次返回一个批次的数据。
5、损失函数与优化器
使用CrossEntropy损失函数和随机梯度下降(SGD)算法:
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.9)
6、训练
对于图像分类任务,除了要定义损失函数外,还要定义精度(acc,accuracy)函数:
def calculate_accuracy(trues, preds):
total_samples = len(trues)
correct_predictions = sum(1 for true, pred in zip(trues, preds) if true == pred)
accuracy = correct_predictions / total_samples
return accuracy
下面开始训练:
epochs = 20
lr = 0.05
train_err_list = [] # loss列表,画图用
train_acc_list = []
test_err_list = [] # acc列表,画图用
test_acc_list = []
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_start_time = time.time()
train_err = 0
net.train() # 一些深度模型可能需要手动开启,之前那些小模型如线性回归模型可能就不需要?
for batch_X, batch_Y in train_iter:
# batch_X = batch_X.float()
# batch_Y = batch_Y.float()
# print(batch_X)
batch_X = batch_X.to(device)
batch_Y = batch_Y.to(device)
# print(type(batch_X))
# 前向传播
outputs = net(batch_X) # torch.Size([256, 10])
# print(outputs)
# print(outputs.shape)
# print(batch_Y.shape)
loss_val = loss(outputs, batch_Y)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss_val.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 记录训练损失
train_err_list.append(loss_val.item())
# 计算训练Acc,记录
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(batch_Y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(outputs.argmax(axis=1))
train_acc = calculate_accuracy(trues, preds)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
# 进行测试
with torch.no_grad():
for test_X, test_Y in test_iter:
# 测试数据的迁移
test_X = test_X.to(device)
test_Y = test_Y.to(device)
# 计算测试输出和测试loss
test_outputs = net(test_X)
test_err = loss(test_outputs, test_Y) # torch.sum(test_outputs != test_Y).item() / test_Y.shape[0]
# 计算测试acc
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(test_Y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(test_X).argmax(axis=1))
test_acc = calculate_accuracy(trues, preds)
# 记录测试loss和测试acc
print(f'At epoch {epoch+1}: train_acc {train_acc:.8f}, test_acc {test_acc}')
test_err_list.append(test_err.item())
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
break
epoch_end_time = time.time()
print(f"{device} time At epoch {epoch+1}: {epoch_end_time - epoch_start_time}")
end_time = time.time()
print(f"{device} time: {end_time - start_time}")
输出:
At epoch 1: train_acc 0.09166667, test_acc 0.105625
cuda time At epoch 1: 33.74168109893799
At epoch 2: train_acc 0.51250000, test_acc 0.54375
cuda time At epoch 2: 32.65597414970398
At epoch 3: train_acc 0.66458333, test_acc 0.675
cuda time At epoch 3: 32.79549026489258
At epoch 4: train_acc 0.88541667, test_acc 0.759375
cuda time At epoch 4: 33.176368951797485
At epoch 5: train_acc 0.82416667, test_acc 0.7828125
cuda time At epoch 5: 33.19402623176575
At epoch 6: train_acc 0.83583333, test_acc 0.775
cuda time At epoch 6: 32.876006841659546
At epoch 7: train_acc 0.83666667, test_acc 0.790625
cuda time At epoch 7: 33.013068437576294
At epoch 8: train_acc 0.83583333, test_acc 0.815
cuda time At epoch 8: 32.882542848587036
At epoch 9: train_acc 0.85833333, test_acc 0.8271875
cuda time At epoch 9: 32.794219970703125
At epoch 10: train_acc 0.88750000, test_acc 0.8328125
cuda time At epoch 10: 32.84580612182617
绘制训练和测试过程中损失和精度的变化曲线:
# print(train_err_list)
# 绘制4个子图
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
# 训练损失子图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.plot(train_err_list)
plt.title('Train Loss VS batch')
# 训练准确率子图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.plot(train_acc_list)
plt.title('Train Accuracy VS batch')
# 测试损失子图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.plot(test_err_list)
plt.title('Test Loss VS epoch')
# 测试准确率子图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.plot(test_acc_list)
plt.title('Test Accuracy VS epoch')
# 调整子图之间的间距
plt.tight_layout()
# 显示图形
plt.show()
7、预测
对于测试数据集,随机选取5个进行预测输出。(此处不展示效果)
def predict(net, test_iter, n=5):
for X, y in test_iter:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
break
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1))
# print(trues)
# print(preds)
titles = [true + '\n' + pred for true, pred in zip(trues, preds)]
d2l.show_images(X[0:n].reshape((n,28,28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n])
predict(net, test_iter)
⭐如果你都看到这里了,不妨点个免费的赞吧~







 本文详细介绍了如何使用经典的LeNet-5卷积神经网络对MNIST-Fashion数据集进行图像分类,包括网络结构、GPU加速、参数初始化、数据加载、损失函数和优化策略,以及训练过程中的性能评估和可视化。
本文详细介绍了如何使用经典的LeNet-5卷积神经网络对MNIST-Fashion数据集进行图像分类,包括网络结构、GPU加速、参数初始化、数据加载、损失函数和优化策略,以及训练过程中的性能评估和可视化。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








