在 pyhon 中,函数是带有名称的代码块,可以被反复调用。用关键字 def 定义函数。
# 定义函数(进行变量值输出)
def introduction(name):
print('大家好,我是'+name+'!')
# 调用函数
introduction('小虎')
# 定义函数(进行变量值返回)
def add(a,b):
return a+b
# 调用函数
result = add(3,4)
print(result)
# 定义函数(函数有必须参数,也有可选参数)
def greet(name,greeting = 'Hello'): # 此处 greeting 是可选参数
print(greeting+','+name+'!')
# 调用函数
greet('小虎')
greet('小言','Hi')
# 定义函数(函数可有任意数量可选参数)
def print_items(*items): # 用 *args 表示任意数量的参数
for item in items:
print(item)
# 调用函数
print_items('cloudy','sunny','rainy')类,是一种高级的、可扩展的数据类型,可用来模拟实际世界中的概念。用关键字 class 定义类。
# 定义类
class fruits:
def __init__(self,name,color): # __init__初始化对象,并为对象设置属性
self.name = name # 对象的属性一:self.name
self.color = color # 对象的属性二:self.color
def introduction(self): # 定义一个实例方法
print('你好!我是'+self.name+',我的颜色是'+self.color)
# 使用类来创建对象
f1 = fruits('苹果','红色')
f2 = fruits('香蕉','黄色')
# 调用类中的方法
f1.introduction()
f2.introduction()在类体中,根据变量定义的位置、方式不同,可将类属性/类变量分为:1.类属性/类变量、2.实例属性/实例变量、3.局部变量,这三种类型。
# 定义一个类
class water:
# 定义两个类变量
name = 'cola'
color = 'black'
# 定义一个实例方法
def introduction(self,content):
print(content)
# 输出类变量 ********************(1.类变量/类属性)
print(water.name)
w1 = water()
print(w1.color)# 定义一个类
class water:
def __init__(self):
# 定义两个实例变量
self.name = 'cola'
self.color = 'black'
# 定义一个实例方法
def introduction(self):
self.content = '它是一种饮料'
# 输出变量
w1 = water()
print(w1.name) # **************(2.实例属性/实例变量)
print(w1.color)
w1.introduction() # 该方法需要手动调用
print(w1.content) # ************(3.局部变量)类的方法,可分为:1.实例方法(无修饰)、2.类方法(@classmethod 修饰)、3.静态方法(@staticmethod 修饰)
类的特性:封装、继承、多态
附. python 中的 33 个关键字:
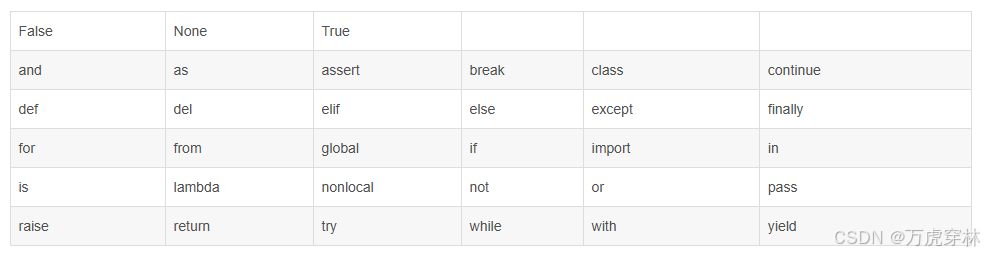
每个关键字的具体介绍,详见:一文读懂python3中的所有33个关键字及其用法_python中33个关键字含义及作用-优快云博客























 1585
1585

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








