今天看到这么一句话,分享给大家:自我塑造的过程很疼,但终将遇到更好的自己。
Linux用户权限解析
我们linux服务器上有严格的权限等级,如果权限过高导致误操作会增加服务器的风险。所以对于了解linux系统中的各种权限及要给用户,服务等分配合理的权限十分重要
1.基本权限ugo
文件权限设置: 可以赋于某个用户或组 能够以何种方式 访问某个文件
- rw- r-- r--. 1 root root 2024 8月 5 15:40 /etc/passwd
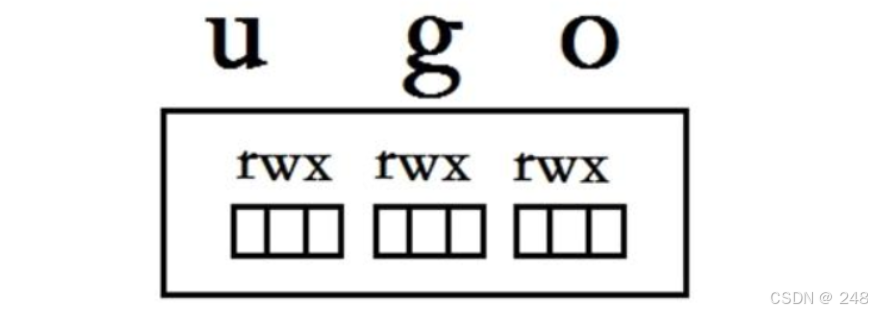
u g o
权限对象:
属主-------->u
属组--------->g
其他人------>o
全限的类型:
读 r 4
写 w 2
执行 x 1
1.1设置权限
chown:改变文件的或目录的所属主(所有者)或者所属组
chmod:为文件或目录设置访问权限
更改文件的属主(所有者)属组
[root@hostname opt]# touch file1.txt
[root@hostname opt]# chown alice.hr file1.txt //所有者和属组都更改
[root@hostname opt]# ll
-rw-r--r-- 1 alice hr 0 8月 26 20:03 file1.txt
[root@hostname opt]# chown xiaozhang file1.txt //更改所有者
[root@hostname opt]# ll
rw-r--r-- 1 xiaozhang hr 0 8月 26 20:03 file1.txt
[root@hostname opt]# chown .it file1.txt //更改属组
[root@hostname opt]# ll
rw-r--r-- 1 xiaozhang it 0 8月 26 20:03 file1.txt
更改权限
符号和数字
[root@hostname opt]# chmod u+x file1.txt //给所有者增加执行权限
[root@hostname opt]# ll
-rwxr--r-- 1 alice hr 0 8月 26 20:03 file1.txt
[root@hostname opt]# chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r //所有者读写执行,属组读执行 ,其他人读
[root@hostname opt]# chmod ug=rwx,o=-
[root@hostname opt]# chmod ugo=761 //761:所有者读写执行,属组读写,其他执行
2.权限案例
r、w、x权限对文件和目录的意义

rwx对文件的影响:
文件的最小权限可以是只读r;
文件单独授予只写或者只执行是没有意义的;
文件要想可以正常写入或者正常执行,必须要授予读的权限;
rwx目录的影响:
r: 可以列出目录下的文件名,但是会报错,因为没有执行权限;
w: 没有任何意义,但是目录时候有w权限,决定着能否在目录下创建或者删除文件;
x: 可以进入目录

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








