参考的视频
本文说明
本文只是提供参考视频中讲解人讲解模拟框架的代码,不包含框架基本信息的讲解。如果想要了解反射的基本信息,极力推荐观看参考视频。
那是一个非常精彩的视频,如果你和我一样是新手小白,观看完视频后,会让你对反射和注解有个新的认知。
代码仓库
项目结构
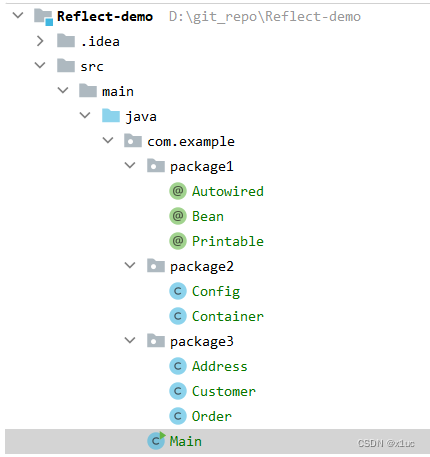
package1
autowired
package com.example.package1;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
}
Bean
package com.example.package1;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Bean {
}
Printable
package com.example.package1;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Printable {
}
package2
Config
package com.example.package2;
import com.example.package1.Bean;
import com.example.package3.Address;
import com.example.package3.Customer;
public class Config {
@Bean
public Customer customer() {
return new Customer("pony", "pony@qq.com");
}
@Bean
public Address address() {
return new Address("center street", "114514");
}
}
Container
package com.example.package2;
import com.example.package1.Autowired;
import com.example.package1.Bean;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Container {
private Map<Class<?>, Method> map; // 储存的是 加@Bean注解的方法
private Map<Class<?>, Object> instanceMap; // 实现单例
private Object config;
public void init() throws ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException {
map = new HashMap<>();
instanceMap = new HashMap<>();
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.package2.Config");
Method[] methods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getAnnotation(Bean.class) != null)
this.map.put(method.getReturnType(), method); // 拿到所有生成对象的方法
}
this.config = aClass.getConstructor().newInstance(); // 获得可以调用 map 集合方法生成实例的对象
}
public Object getServiceInstanceByClass(Class<?> clazz) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
if (this.map.containsKey(clazz)) {
if (!this.instanceMap.containsKey(clazz)) {
Method method = map.get(clazz);
Object instance = method.invoke(config);
this.instanceMap.put(clazz, instance);
}
return this.instanceMap.get(clazz);
}
return null;
}
public Object createInstance(Class<?> clazz) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException {
Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
if (constructor.getAnnotation(Autowired.class) != null) {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes();
Object[] argument = new Object[parameterTypes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < argument.length; i++) {
argument[i] = getServiceInstanceByClass(parameterTypes[i]);
}
return constructor.newInstance(argument);
}
}
return clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
}
}
package3
Address
package com.example.package3;
public class Address {
public String street;
public String postCode;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String street, String postCode) {
this.street = street;
this.postCode = postCode;
}
public void printStreet() {
System.out.println(this.street);
}
public void printPostCode() {
System.out.println(this.postCode);
}
}
Customer
package com.example.package3;
import com.example.package1.Printable;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String email;
public Customer(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public Customer() {
}
@Printable
public void printEmail() {
System.out.println(email);
}
public void printName() {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
Order
package com.example.package3;
import com.example.package1.Autowired;
import com.example.package3.Address;
import com.example.package3.Customer;
public class Order {
private Customer customer;
private Address address;
public Order() {
}
@Autowired
public Order(Customer customer, Address address) {
this.customer = customer;
this.address = address;
}
}
Main
package com.example;
import com.example.package1.Printable;
import com.example.package2.Container;
import com.example.package3.Customer;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Container container = new Container();
container.init();
String className = "com.example.package3.Order";
String fieldName = "customer";
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
Object instance = container.createInstance(clazz);
Field filed = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
filed.setAccessible(true);
Object fieldValue = filed.get(instance);
System.out.println(fieldValue);
Method[] methods = fieldValue.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getAnnotation(Printable.class) != null) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
method.invoke(fieldValue);
}
}
System.out.println(fieldValue == container.getServiceInstanceByClass(Customer.class)); // true
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








