priority_queue与queue有哪些不同之处呢?引入了优先级,与普通队列(先进先出,FIFO)不同,优先级队列会根据元素的优先级来决定元素的出队顺序。优先级高的元素会优先出队,而优先级低的元素则需要等待。那么它是用什么来作为底层容器的呢?要能够适配优先级,那就要使用到堆,那使用vector连续地址的容器会方便一些。用来存储堆,模拟堆的动作。首先优先级队列默认是less函数,也就是大堆,优先级高的在前面,先出,所以先实现大堆,这里要控制一下<>号的使用,统一一下,大堆用<。
//优先级队列 默认是大堆,是< 小堆是>
template<class T, class container=std::vector<T>>
class priority_queue
{
void Adjustup(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)//不能是parent>=0
{
if (c[parent]< c[child])
{
std::swap(c[child], c[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
Compare com;
while (child<c.size())//父亲为叶节点 孩子超出数组了
{
if (child + 1 < c.size() and c[child] < c[child + 1])
{
child += 1;
}
if (c[parent]< c[child])
{
std::swap(c[child], c[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
break;
}
}
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
c.push_back(x);
Adjustup(c.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
assert(!c.empty());
std::swap(c[0], c[c.size() - 1]);
//用的是vector,vector没有头删,所以首尾要交换一下
c.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return c[0];
}
size_t size()
{
return c.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return c.empty();
}
private:
container c;
};
先大概实现了大堆时的情况,我们知道肯定会有小堆的情况,总不能再写一个prority吧?怎么办?类似前面的迭代器,在模板参数上做文章,这里就引入了仿函数!仿函数顾名思义,模拟函数,但不是函数,而是使用类和对象重载函数,让对象调用成员函数看上去像函数:
//仿函数
template<class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b) const
{
return a > b;
}
};
此时,我们在刚刚的priority中加入函数类型不就ok了?
//优先级队列 默认是大堆,是< 小堆是>
template<class T, class Compare = less<T>, class container=std::vector<T>>
class priority_queue
{
void Adjustup(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)//不能是parent>=0
{
//if (c[parent]< c[child])
if (com(c[parent] , c[child]))
{
std::swap(c[child], c[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
Compare com;
while (child<c.size())//父亲为叶节点 孩子超出数组了
{
//if (child + 1 < c.size() and c[child] < c[child + 1])
if (child + 1 < c.size() and com(c[child], c[child + 1]))
{
child += 1;
}
//if (c[parent]< c[child])
if (com(c[parent], c[child]))
{
std::swap(c[child], c[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
break;
}
}
//..........
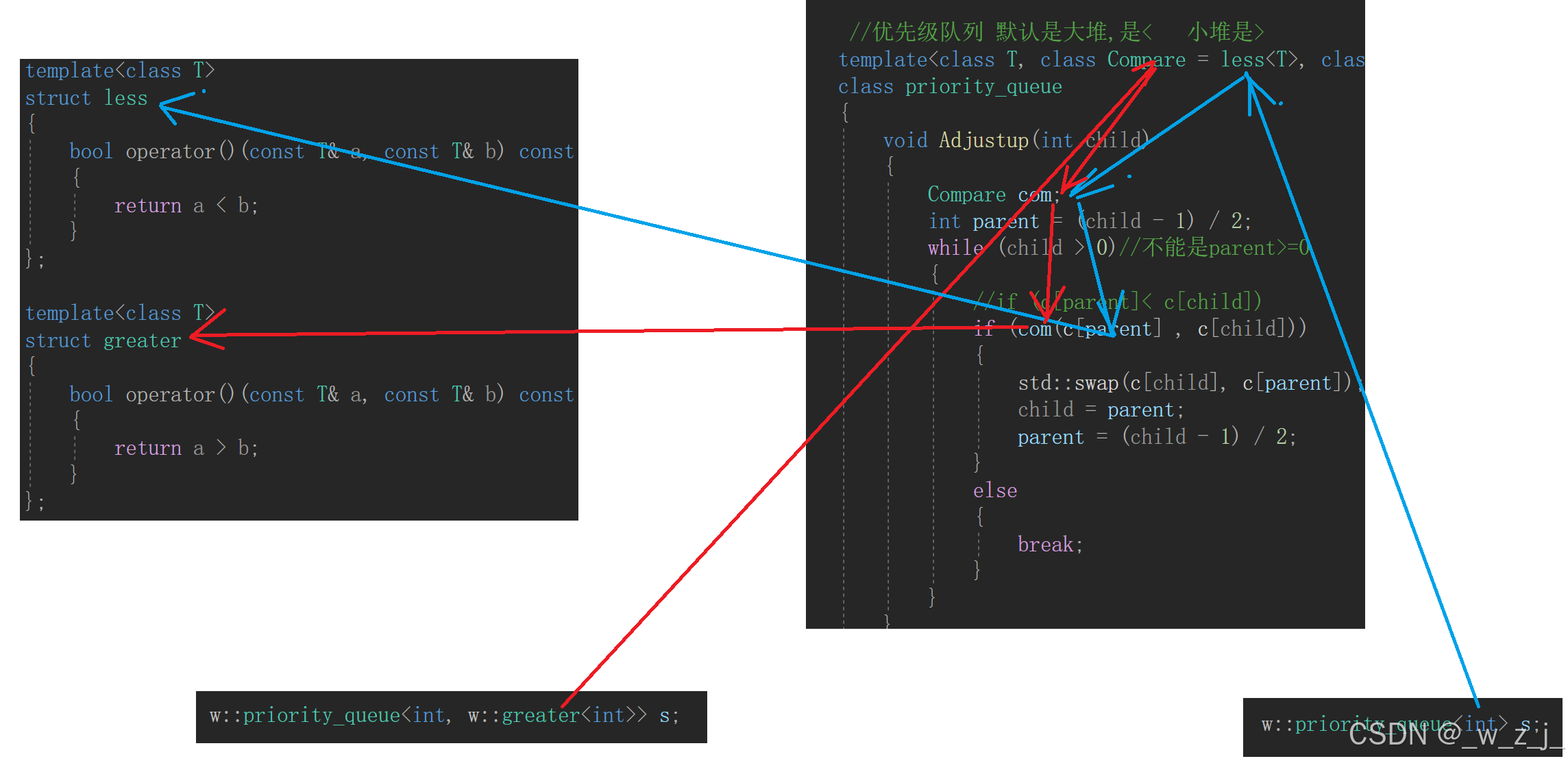
在使用模板参数时,它可以接收任何类型参数,不必太关心class后面的名称,与名称无关!名称只是为了方便我们使用而已,传过去是什么就是什么。比如传greater<T>时,其实就是传过去了类类型,与vector<T>是一样的
使用:
void test3()
{
//w::priority_queue<int> s;
w::priority_queue<int, w::greater<int>> s;
s.push(7);
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;
s.push(4);
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;
s.push(8);
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;
s.push(1);
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;
s.pop();
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;;
s.pop();
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;;
s.pop();
std::cout << s.top() << std::endl;;
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










