前后段分离
前端一般通过 HTML、CSS、JS、Vue等、来实现
后端一般通过 django 等来实现
常用请求方式
- GET:获取数据
- POST:提交数据,创建数据
- PUT:提交数据,更新数据
- DELETE:删除数据
状态码
200 服务器请求成功
201 用户新建或修改数据成功
204 用户删除数据成功
400 用户发出的请求错误
401没有权限
403 用户的的授权,但是访问时禁止的
404 用户的请求不存在错误
在settings里面配置
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'myapp', #子应用
'rest_framework',
]
APIView处理Request,视图的Response及json处理
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from myapp.models import People
from myapp.serializers import PeopleSerializer
# Create your views here.
class MyView(APIView):
def get(self,request):
print(request.query_params)
return Response({'msg':'success'},status=200)
def post(self,request):
print(request.data)
return Response({'msg':'success'},status=201)
class PeopleView(APIView):
# # 查询所有名人信息
# def get(self,request):
# people = People.objects.all()
# people_list = [] # 手动完成序列化器
# for peo in people:
# people_dict = {
# 'name':peo.name,
# 'sex':peo.sex,
# 'money':peo.money,
# 'ranking':peo.ranking,
# }
# people_list.append(people_dict)
# return Response(people_list,status=200)
def get(self,request):
people = People.objects.all()
# people是序列化的数据,many=True多个数据
ser = PeopleSerializer(people,many=True)
# 注意返回的是.data
return Response(ser.data,status=200)
序列化器
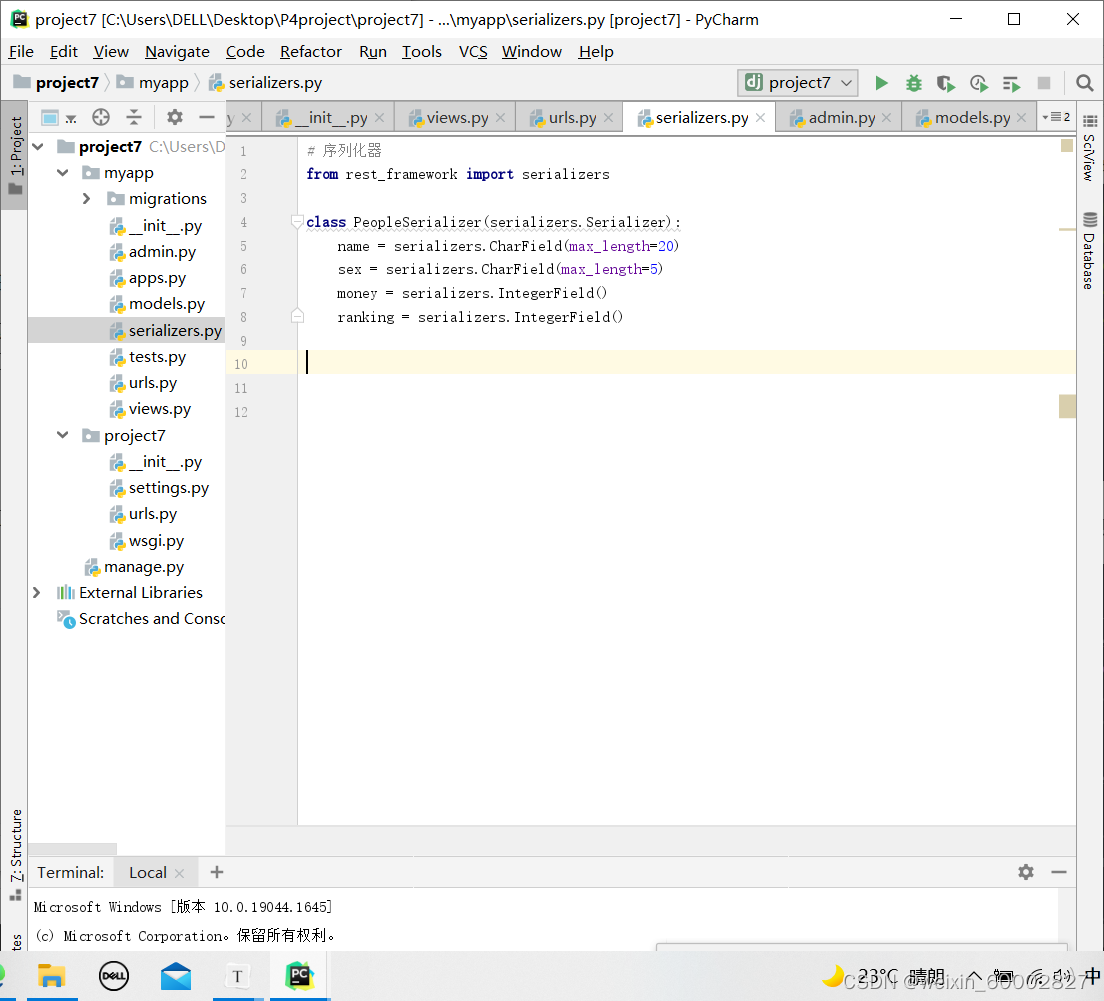




 本文介绍了前后端分离的基本概念,前端通常使用HTML、CSS、JS和Vue等技术,后端则常借助django框架。同时,文章讨论了HTTP的常见请求方式如GET、POST、PUT和DELETE,以及相应状态码的含义,如200、201、204、400、401、403和404。在Django中,还提到了APIView的Request处理、视图的Response和JSON处理,以及序列化器的重要作用。
本文介绍了前后端分离的基本概念,前端通常使用HTML、CSS、JS和Vue等技术,后端则常借助django框架。同时,文章讨论了HTTP的常见请求方式如GET、POST、PUT和DELETE,以及相应状态码的含义,如200、201、204、400、401、403和404。在Django中,还提到了APIView的Request处理、视图的Response和JSON处理,以及序列化器的重要作用。
















 5991
5991

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








