1.创建和启动服务器
2.req对象
3.响应
4.http请求(两种方式)和axios的底层技术(浏览器和node)
1.创建和启动服务器
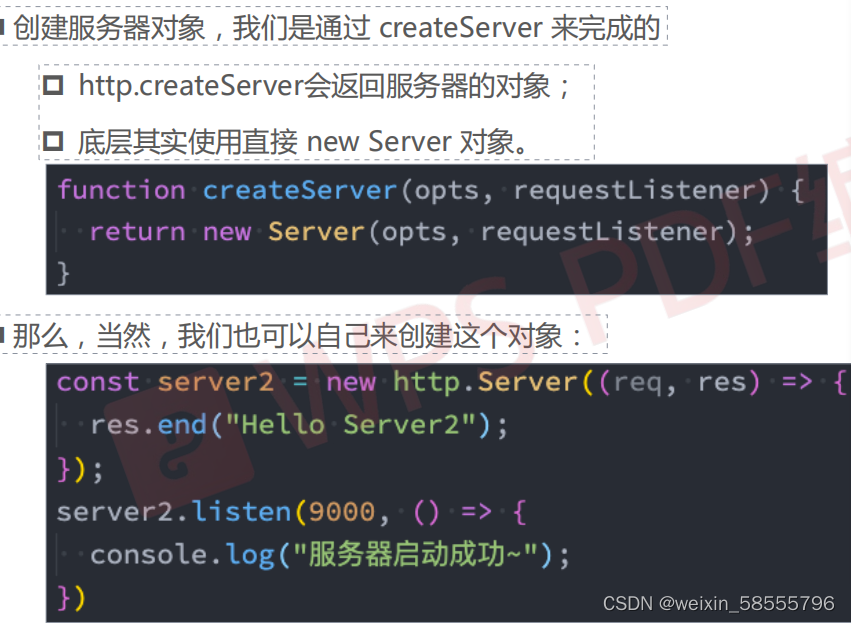
a.createServe的底层和自我实现:
b.启动服务器的参数:
当默认的时候如何获取端口和地址 : serve.address()
端口的默认值和可写范围,以及系统常用:可写0-65535 默认值是系统随机分配 系统常用1024以下 因此最好不要设置1024以下的端口号
c.localhost和回环地址127.0.0.1和0.0.0.0:
如果第二个参数写127.0.0.1或localhost:127.0.0.1和localhost会捕获 127.0.0.1可以捕获localhost是因为localhost通常被解析成127.0.0.1 ipv6会解析成::(不管是访问的时候还是起服务的时候) 因为ip地址需要经过五个层,因此不能捕获ipv4
写0.0.0.0或不写:除0.0.0.0外都可以捕获 默认是0.0.0.0 (ipv4)或::(ipv6)
写ip地址:只有ip地址可以捕获
0.0.0.0代表未指定地址,监听了ipv4上所有的地址(包括ip和127.0.0.1),就是当不知道自己的ip地址是什么的时候用这个代替,当发数据包的时候他会找到本机上的ipv4地址,然后发送出去,所以当0.0.0.0启动后,我们用0。0.0.0去访问是获取不到数据的
d.实例:
let http=require('http')
// 创建服务器
// let serve=http.createServer((req,res)=>{
// res.end('我是服务器')
// })
// createServer其底层其实是返回了一个http里面的Serve对象 所以我们也可以这样来创建
let serve=new http.Server((req,res)=>{
// 这个回调函数是当访问服务器的时候 服务器做出的反应 比如end就会返回该数据
res.end('我是服务器')
})
//第一个参数是端口号 可以不传,不传系统就会自己分配
// 第二个参数是地址 也可以不传 默认是localhost
// 假如都不传 本实例可以在http://localhost:51307/ 访问到
serve.listen(()=>{
console.log('服务启动成功');
})
console.log(serve.address());//{ address: '::', family: 'IPv6', port: 6000 }
2.req对象
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');
// 对于query的解析需要引入querystring
const querystring = require('querystring');
// 创建一个web服务器
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 获取url
console.log(req.url);///auto/99?name=998
// request对象中封装了客户端给我们服务器传递过来的所有信息
//可以解析url
let obj=url.parse(req.url)
console.log(obj);
// Url {
// protocol: null,
// slashes: null,
// auth: null,
// host: null,
// port: null,
// hostname: null,
// hash: null,
// search: '?name=998',
// query: 'name=998',
// pathname: '/auto/99',
// path: '/auto/99?name=998',
// href: '/auto/99?name=998'
// }
// 可以解析query
console.log(querystring.parse(obj.query));//[Object: null prototype] { name: '998' }
// 先进行反编码
req.setEncoding('utf-8')
// 是异步的回调函数
req.on('data',(data)=>{
console.log(data);//{ "name":"why","password":"11"}
})
// 请求方法
console.log(req.method);//POST
// 请求头
console.log(req.headers);
// 响应码的设置要在write前面 writeHead如果在write后面就会报错 statuscode如果在后面就不起作用
res.end('')
});
a.获取url
b.获取query
c.获取body
d.获取methods
e.获取header
f.常见的header有哪些


3.响应
const http = require('http');
// 创建一个web服务器
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
//写入请求头 也可以写入相应码
// res.writeHead(300)
//写入相应码
// res.statusCode=400
// 设置herder set只能设置一个请求头 writeHead可以设置多个
//res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf8")
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf8"
});
//写入返回数据
res.write("Hello Server");
res.write("Hello Write");
//结束写入并且write 不结束的话客户端是得不到相应的
res.end('')
});
a.响应数据write 结束请求end和close 以及不调用会怎么样:客户端将会一直等待结果
b.响应code:res.end()
c.响应请求头 setHeader和writeHead
4.http请求(两种方式)和axios的底层技术(浏览器和node)
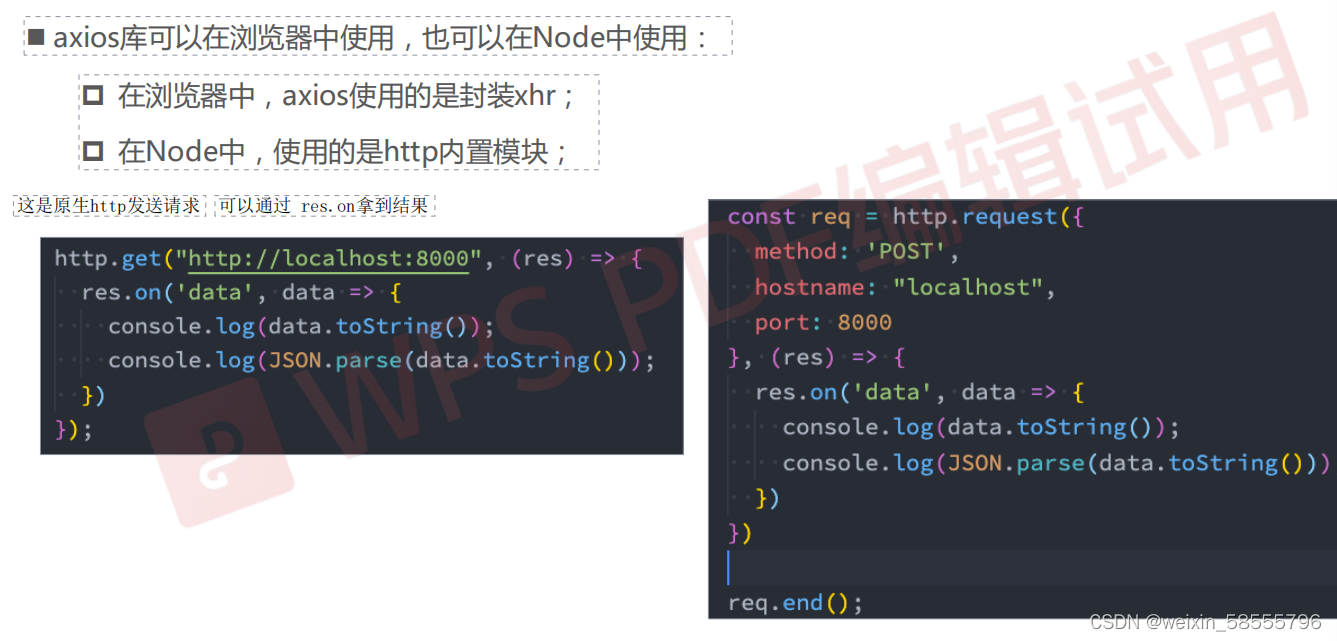








 文章详细介绍了如何创建和启动HTTP服务器,包括使用http模块创建服务器、listen方法的参数以及端口的默认值和范围。讨论了req对象在处理URL、查询参数和请求体中的作用,以及响应过程中的writeHead、statusCode和end方法。此外,还提到了http请求的两种方式和axios在浏览器与Node.js环境下的底层技术应用。
文章详细介绍了如何创建和启动HTTP服务器,包括使用http模块创建服务器、listen方法的参数以及端口的默认值和范围。讨论了req对象在处理URL、查询参数和请求体中的作用,以及响应过程中的writeHead、statusCode和end方法。此外,还提到了http请求的两种方式和axios在浏览器与Node.js环境下的底层技术应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








