一、会话管理
Shiro提供了完整的企业级会话管理功能,不依赖于底层容器(如Tomcat),不管是J2SE还是J2EE环境都可以使用,提供了会话管理,会话事件监听,会话存储/持久化,容器无关的集群,失效/过期支持,对Web的透明支持,SSO单点登录的支持等特性。
所谓会话,即用户访问应用时保持的连接关系,在多次交互中应用能够识别出当前访问的用户是谁,且可以在多次交互中保存一些数据。如访问一些网站时登录成功后,网站可以记住用户,且在退出之前都可以识别当前用户是谁。
二、基础组件
1.SessionManager
会话管理器管理着应用中所有 Subject 的会话的创建、维护、删除、失效、验证等工作。是Shiro 的核心组件,顶层组件SecurityManager直接继承了SessionManager,且提供了SessionsSecurityManager实现直接把会话管理委托给相应的SessionManager
- 1)DefaultSessionManager:使用的默认实现,用于JavaSE环境
- 2)ServletContainerSessionManager:使用的默认实现,用于Web环境,其直接使用Servlet容器的会话
- 3)DefaultWebSessionManager:用于Web环境的实现,可以替代ServletContainerSessionManager,自己维护着会话,直接废弃了Servlet容器的会话管理
2.SessionListener
SessionListener会话监听器用于监听会话创建、过期及停止事件。
实现方式:
- 1)实现SessionListener,必须实现所有方法
- 2)继承SessionListenerAdapter,重写指定方法
三、入门案例演示
在shrio配置文件spring-shrio.xml中配置以下内容
1)创建Session ID生成器
<!-- Session ID 生成器 -->
<bean id="sessionIdGenerator" class="org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.eis.JavaUuidSessionIdGenerator">
</bean>2)自定义会话管理
<!--sessionDao自定义会话管理,针对Session会话进行CRUD操作-->
<bean id="customSessionDao" class="org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.eis.MemorySessionDAO">
<property name="sessionIdGenerator" ref="sessionIdGenerator"/>
</bean>3)创建会话监听器
<!--会话监听器-->
<bean id="shiroSessionListener" class="com.zking.ssm.book.shiro.ShiroSessionListener"/>4)会话cookie模板
<!--会话cookie模板-->
<bean id="sessionIdCookie" class="org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.SimpleCookie">
<!--设置cookie的name-->
<constructor-arg value="shiro.session"/>
<!--设置cookie有效时间-->
<property name="maxAge" value="-1"/>
<!--设置httpOnly-->
<property name="httpOnly" value="true"/>
</bean>5)SessionManager会话管理器
<!--SessionManager会话管理器-->
<bean id="sessionManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager">
<!--设置session会话过期时间 毫秒 3分钟=180000-->
<property name="globalSessionTimeout" value="180000"/>
<!--设置sessionDao-->
<property name="sessionDAO" ref="customSessionDao"/>
<!--设置间隔多久检查一次session的有效性 默认60分钟-->
<property name="sessionValidationInterval" value="1800000"/>
<!--配置会话验证调度器-->
<!--<property name="sessionValidationScheduler" ref="sessionValidationScheduler"/>-->
<!--是否开启检测,默认开启-->
<!--<property name="sessionValidationSchedulerEnabled" value="true"/>-->
<!--是否删除无效的session,默认开启-->
<property name="deleteInvalidSessions" value="true"/>
<!--配置session监听器-->
<property name="sessionListeners">
<list>
<ref bean="shiroSessionListener"/>
</list>
</property>
<!--会话Cookie模板-->
<property name="sessionIdCookie" ref="sessionIdCookie"/>
<!--取消URL后面的JSESSIONID-->
<property name="sessionIdUrlRewritingEnabled" value="false"/>
</bean>6)创建监听器
实现方式有两种: * 1)实现SessionListener,必须实现所有方法 * 2)继承SessionListenerAdapter,重写指定方法
package com.zking.ssm.book.shiro;
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.session.SessionListener;
/**
* Shrio的Session监听器
* 实现方式:
* 1)实现SessionListener,必须实现所有方法
* 2)继承SessionListenerAdapter,重写指定方法
*/
public class ShrioSessionListener implements SessionListener {
@Override
public void onStart(Session session) {
System.out.println("session监听器---onStart ---sessionId="+session.getId());
}
@Override
public void onStop(Session session) {
System.out.println("session监听器---onStop ---sessionId="+session.getId());
}
@Override
public void onExpiration(Session session) {
System.out.println("session监听器---onExpiration ---sessionId="+session.getId());
}
}
7)把会话管理加入安全管理器
<!--2、创建安全管理器,并更换Realm-->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
<property name="realm" ref="shiroRealm" />
<!--设置会话管理器-->
<property name="sessionManager" ref="sessionManager"/>
</bean>8)测试


四、缓存
1.为什么要使用缓存
在没有使用缓存的情况下,我们每次发送请求都会调用一次doGetAuthorizationInfo方法来进行用户的授权操作,但是我们知道,一个用户具有的权限一般不会频繁的修改,也就是每次授权的内容都是一样的,所以我们希望在用户登录成功的第一次授权成功后将用户的权限保存在缓存中,下一次请求授权的话就直接从缓存中获取,这样效率会更高一些。
2.常见缓存方式
package com.zking.ssm.book.ehcache;
import com.zking.ssm.book.model.Book;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* 常见缓存方式
*/
public class Demo {
private static Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
public static String findStr(String Key){
//从map集合中获取对应数据值
String value=map.get(Key);
//判断value是否为空
if(value==null){
//创建uuid
value= UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("创建成功了哦~~~~~~~");
//根据key存储uuid
map.put(Key,value);
}
return value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(findStr("zs"));
System.out.println(findStr("zs"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));
}
}
3.测试
向方法中加入两个zs
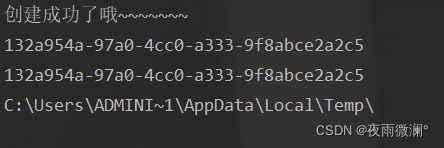
可以看出"创建成功了哦~~~~~~~"只输出了一次
五、Ehcache
1.什么是Ehcache
Ehcache是现在最流行的纯Java开源缓存框架,配置简单、结构清晰、功能强大。是Hibernate中默认CacheProvider。Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存,Java EE和轻量级容器。它具有内存和磁盘存储,缓存加载器,缓存扩展,缓存异常处理程序,一个gzip缓存servlet过滤器,支持REST和SOAP api等特点。
2.Ehcache特点
1) 够快
Ehcache的发行有一段时长了,经过几年的努力和不计其数的性能测试,Ehcache终被设计于large, high concurrency systems.
2) 够简单
开发者提供的接口非常简单明了,从Ehcache的搭建到运用运行仅仅需要的是你宝贵的几分钟。其实很多开发者都不知道自己用在用Ehcache,Ehcache被广泛的运用于其他的开源项目
3) 够袖珍
关于这点的特性,官方给了一个很可爱的名字small foot print ,一般Ehcache的发布版本不会到2M,V 2.2.3 才 668KB。
4) 够轻量
核心程序仅仅依赖slf4j这一个包,没有之一!
5) 好扩展
Ehcache提供了对大数据的内存和硬盘的存储,最近版本允许多实例、保存对象高灵活性、提供LRU、LFU、FIFO淘汰算法,基础属性支持热配置、支持的插件多
6) 监听器
缓存管理器监听器 (CacheManagerListener)和 缓存监听器(CacheEvenListener),做一些统计或数据一致性广播挺好用的
7) 分布式缓存
从Ehcache 1.2开始,支持高性能的分布式缓存,兼具灵活性和扩展性
3. Ehcache入门
1.导入相关依赖(注意:这里使用shiro的1.4.1版本)
注:之前是使用的1.3.1版本,在安全退出的时候引发了UnknownSessionException: There is no session with id错误,通过升级shiro版本后问题解决!!!o(╥﹏╥)o 一下午时间啊!!!
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>
2.实现spring与ehcache缓存
创建spring-ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<!--磁盘存储:将缓存中暂时不使用的对象,转移到硬盘,类似于Windows系统的虚拟内存-->
<!--path:指定在硬盘上存储对象的路径-->
<!--java.io.tmpdir 是默认的临时文件路径。 可以通过如下方式打印出具体的文件路径 System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));-->
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<!--defaultCache:默认的管理策略-->
<!--eternal:设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断-->
<!--maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目-->
<!--overflowToDisk:如果内存中数据超过内存限制,是否要缓存到磁盘上-->
<!--diskPersistent:是否在磁盘上持久化。指重启jvm后,数据是否有效。默认为false-->
<!--timeToIdleSeconds:对象空闲时间(单位:秒),指对象在多长时间没有被访问就会失效。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--timeToLiveSeconds:对象存活时间(单位:秒),指对象从创建到失效所需要的时间。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存的3 种清空策略-->
<!--FIFO:first in first out (先进先出)-->
<!--LFU:Less Frequently Used (最少使用).意思是一直以来最少被使用的。缓存的元素有一个hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存-->
<!--LRU:Least Recently Used(最近最少使用). (ehcache 默认值).缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存-->
<defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<!--name: Cache的名称,必须是唯一的(ehcache会把这个cache放到HashMap里)-->
<cache name="shiroAuthzCache" eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="100"
overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="0"
timeToLiveSeconds="300" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>3.定义缓存管理器
package com.zking.ssm.book.ehcache;
import net.sf.ehcache.Cache;
import net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager;
import net.sf.ehcache.Element;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class EhcacheUtil {
//流程:cacheManager-->cache-->Element
//定义缓存管理器
private static CacheManager cacheManager;
//静态块,只执行一次
static {
try {
//加载读取ehcache的核心配置文件并转换成文件输入流
InputStream is = EhcacheUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/ehcache.xml");
//根据ehcache的文件输入流创建CacheManager
cacheManager = CacheManager.create(is);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private EhcacheUtil() {
}
//从缓存对象中获取指定的缓存元素
public static void put(String cacheName, Object key, Object value) {
//根据缓存对象名从缓存过滤器中获取缓存对象
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
if (null == cache) {
//以默认配置添加一个名叫cacheName的Cache
cacheManager.addCache(cacheName);
//根据缓存对象获取缓存过滤器中新加入的缓存对象
cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
}
cache.put(new Element(key, value));
}
//从缓存对象中获取指定缓存元素
public static Object get(String cacheName, Object key) {
//根据缓存对象名从缓存过滤器中获取缓存对象
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
//从缓存对象中根据缓存元素的名字获取指定缓存元素
Element element = cache.get(key);
return null == element ? null : element.getValue();
}
//从缓存元素中删除指定的缓存元素
public static void remove(String cacheName, Object key) {
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
cache.remove(key);
}
}
4.浅测一下


然鹅并没有感受到缓存的效果,所以接下来集成到spring中
六、Ehcache与spring集成
1.创建集成配置文件spring-ehcache.xml,并引入到spring.xml中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--使用ehcache缓存-->
<bean id="cacheManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/>
<property name="shared" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!-- 默认是cacheManager -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManagerFactory"/>
</bean>
</beans>2.导入支持依赖
<!-- spring对ehcache的相关支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>3.在SecurityManager安全管理器中设置缓存管理器
<!--设置缓存管理器-->
<property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/>4.开启Shiro的授权或者认证数据缓存
在自定义Realm配置中开启并设置授权或者认证数据缓存
<!--开启缓存-->
<property name="cachingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--开启授权缓存-->
<property name="authorizationCachingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--设置ehcache的中的缓存对象名-->
<property name="authorizationCacheName" value="shiroAuthzCache"/>注:这里只开启了授权缓存,避免每次请求都要重新查询授权数据!!!
5.测试
登录管理员

点击方法

这里就可以很明显的看出来点击方法的是候没有去数据库查询角色与权限了








 本文详细介绍了Apache Shiro的会话管理机制,包括默认的会话管理器、会话监听器及其在JavaSE和Web环境下的实现。此外,文章还展示了如何配置和自定义会话管理,以及如何使用Ehcache实现缓存以提高性能。通过创建Spring配置文件,集成Ehcache并设置缓存管理器,实现了Shiro的授权数据缓存,有效减少了数据库查询。
本文详细介绍了Apache Shiro的会话管理机制,包括默认的会话管理器、会话监听器及其在JavaSE和Web环境下的实现。此外,文章还展示了如何配置和自定义会话管理,以及如何使用Ehcache实现缓存以提高性能。通过创建Spring配置文件,集成Ehcache并设置缓存管理器,实现了Shiro的授权数据缓存,有效减少了数据库查询。
















 197
197

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








