1、Java8概述
java8(又称JDK 1.8) 是Java语言开发的一个主要版本
Oracle公司于2014年3月18日发布Java8
支持Lambda表达式
函数式接口
新的Stream API
新的StreamAPI
新的日期 API
其他特性
2、Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式:特殊的匿名内部类,语法更简洁
Lmbda表达式允许把函数作为一个方法的参数(函数作为方法参数传递), 将代码像数据一样传递
基本语法:
<函数式接口> <变量名> = (参数1, 参数2...) -> {
//方法体
}
Lambda引入了新的操作符:->(箭头操作符), ->将表达式分成两部分
左侧:(参数1, 参数2...)表达参数列表
右侧:{}内部是方法体
注意事项:
形参列表的数据类型会自动判断
如果形参列表为空, 只需保留()
如果形参只有1个,()可以省略,若有返回值,则若想去省{},则必须同时省略return,且执行 语句也保证只有一句
Lambda不会生成一个单独的内部类文件
没有参数
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行的是lambda之前的方法");
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable);
thread1.start();
Runnable runnable1 = () -> {
System.out.println("执行的是lambda的方法");
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable1);
thread2.start();
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("执行的是Thread中的方法");});
thread3.start();
}
}

有参数
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.*;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("张三",30);
Student student2 = new Student("李四",80);
Student student3 = new Student("王五",15);
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
list.add(student1);
list.add(student2);
list.add(student3);
Comparator<Student> comparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
};
Collections.sort(list,comparator);
for (Student stu:list) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
Comparator<Student> comparator1 = (Student o1, Student o2 )->{
return o2.getAge()- o1.getAge();
};
Collections.sort(list,comparator1);
for (Student stu1:list){
System.out.println(stu1);
}
}
}

自己定义的抽象方法
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Play play = new Play() {
@Override
public void platBall(String name, String where) {
System.out.println(name + "去了" + where);
}
};
play.platBall("张三","北京");
//play是类名,参数是类中唯一一个抽象方法中的参数
Play play1 = (String name, String where) ->{
System.out.println(name + "去了" + where);
};
play1.platBall("张三", "上海");
}
}

数据类型可以省略

如果形参只有1个,()可以省略,只需要参数的名称即可。

如果执行语句只有一句,且无返回值,{}可以省略,若有返回值,则若想省去{},则必须同时省略return,且执行语句也保证只有一句。

package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当抽象方法有返回值的时候 这里省略return
Play play1 = name -> "我叫" + name;
//如果想加上return 一定也要加上 {}
Play play2 = name -> {return "我叫" + name;};
String m =play1.platBall("张三");
System.out.println(m);
}
}
最后一个分号也可以省略
Play play1 = name ->System.out.println(name);【说明】@FunctionalInterface注解检测接口是否符合函数式接口。

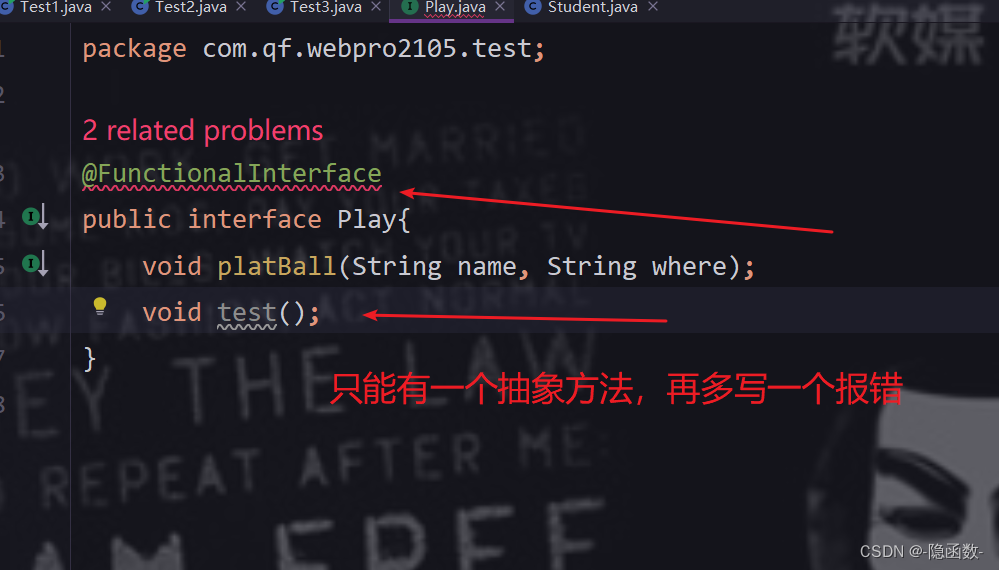
3、函数式接口
如果一个接口只有一个抽象方法,则该接口称之为函数式接口,函数式接口可以使用Lambda 表达式,Lambda表达式会被匹配到这个抽象方法上,只能是自身有一个抽象方法,如果是从 父类中继承下来的方法不算
【说明】如果方法中有一个自身的抽象方法,有一个从父类中继承下来的抽象方法,那么也算是函数式接口,因为它本身的抽象方法只有一个
4、常见函数式接口

消费型接口 Consumer
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//消费型函数式接口:接口中有一个方法:1个参数、类型指定,无返回值
//使用accept来进行输出
Consumer<Integer> consumer = t -> {
if (t > 18) {
System.out.println("年龄大于18");
}else {
System.out.println("年龄小于等于18");
}
};
consumer.accept(20);
}
}
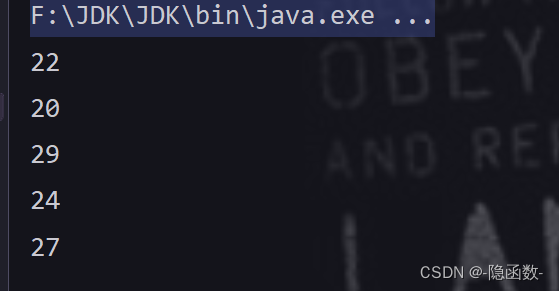
供给型接口 Supplier<T>
package com.qf.javasepro2105.day25;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class SupplierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
//供给型函数式接口
//抽象方法get() 无参数 有返回值 return
Supplier<Integer> supplier=()->new Random().nextInt(30-20+1)+20;
int[] ary=new int[5];
setAry(ary,supplier);
//遍历数组里的值
for(int i:ary){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void setAry(int[] ary,Supplier<Integer> sup){
for(int i=0; i<ary.length; i++){
ary[i]=sup.get();
}
}
}
函数型接口Function<T,R>
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//函数型接口
//抽象方法apply 参数t 返回值是r
//功能:对参数t进行处理,返回处理的结果r
// 参数类型 -> String 返回值类型 -> String
Function<String, String> fun=t->"北京:"+t.toLowerCase();
String result=fun.apply("张三");
System.out.println(result);
}
}

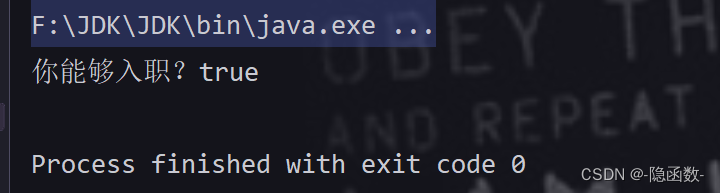
断言型接口 Predicate<T>
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//断言型接口
//抽象方法test(T t) 返回值boolean
Predicate<JobCondition> pre = t -> {
if (t.getScore() >= 60 && t.getCheckResult().equals("良好")) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
};
JobCondition jiaoCondition = new JobCondition(99, "良好");
boolean result = pre.test(jiaoCondition);
System.out.println("你能够入职?" + result);
}
}
5、方法引用
方法引用是Lambda表达式的一种简写形式。如果Lambda表达式方法体中只是掉用一个特定的已经存在的方法,则可以使用方法引用。
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//单纯使用lambda表达式
Consumer<String> con1 = t -> System.out.println(t);
con1.accept("大家好,我是张三");
//使用方法引用
Consumer<String> con2 = System.out::println;
con2.accept("大家好,我是李四");
}
}

常见形式
对象::实例方法
类::静态方法
类::实例方法
类::new
//1 对象::实例方法
Consumer<String> consumer=s->System.out.println(s);
consumer.accept("hello");
Consumer<String> consumer2=System.out::println;
consumer.accept("world");
//2类::静态方法
Comparator<Integer> com=(o1,o2)->Integer.compare(o1, o2);
Comparator<Integer> com2=Integer::compare;
//3类::实例方法
Function<Employee, String> function=e->e.getName();
Function<Employee, String> function2=Employee::getName;
System.out.println(function2.apply(new Employee("小明", 50000)));
//4类::new
Supplier<Employee> supplier=()->new Employee();
Supplier<Employee> supplier2=Employee::new;
Employee employee=supplier.get();
System.out.println(employee.toString());

6、Stream
流(Stream)与集合类似,但集合中保存的是数据,而Stream中保存对集合或数组数据的操作

7、Stream特点
Stream自己不会存储元素
Stresam不会改变源对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stram
Stream操作是延迟执行的,会等到需要结果的时候才执行
8、Stream使用步骤
创建:
创建一个流。
中间操作:
在一个或多个步骤中,将初始Stream转化到另一个Stream的中间操作
终止操作:
使用一个终止操作来产生一个结果。该操作会强制之前的延迟操作立即执行,在此之后,该 Stream就不能使用了
9、创建Stream
通过Collection对象的stream()或parallelStream()方法
通过Arrays类的stream()方法。
通过Stream接口的of()、iterate()、generate()方法
通过InStream、LongStream、DoubleStream接口中的of、range、rangeClosed方法。
10、中间操作、终止操作
中间操作:
filter、limit、skip、distinct、sorted
map
paraller
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>();
stus.add(new Student("wangbao", 23));
//stus.add(new Student("agui",20));
stus.add(new Student("huangqi", 18));
stus.add(new Student("taoshier", 22));
stus.add(new Student("agui", 20));
//stus.add(new Student("huangqi",18));
//创建流
Stream<Student> stream = stus.parallelStream();
//对流进行操作
//1、过滤操作
stream.filter(t->t.getAge()<=20).forEach(System.out::println);;
//2、只获取流中的指定个数的元素
stream.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
//3、跳过获取
stream.skip(2).forEach(System.out::println);
//4、去重---注意需要重写hashCode equals
stream.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
//5、排序
stus.stream().sorted((o1,o2)->{return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();}).forEach(System.out::println);
//6、map
Function<Student, String> fun = t -> t.getName();
stus.stream().map(t -> t.getName()).forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println("--------------------------------");
// for(Student stu:stus){
// System.out.println(stu);
// }
}
}
终止操作:
forEach、min、max、count
reduce、collect
package com.qf.javasepro2105.day25;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class StreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<Student> stus=new ArrayList<Student>();
stus.add(new Student("wangjiabao",23));
stus.add(new Student("zhenghaotian",18));
stus.add(new Student("taoxiansheng",22));
stus.add(new Student("agui",20));
//终止操作
//1、forEach
//2、min
//Optional<Student> minAge=stus.stream().min((o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge());
//System.out.println(minAge.get());
//3、max操作同min相同
//4、个数
long count=stus.stream().count();
System.out.println("个数:"+count);
//5、规约 reduce
Optional<Integer> totalAge=stus.stream().map(s->s.getAge()).reduce((x,y)->x+y);
System.out.println("总年龄:"+totalAge.get());
//6、收集操作
List<String> names=stus.stream().map(s->s.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
for(String name :names){
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
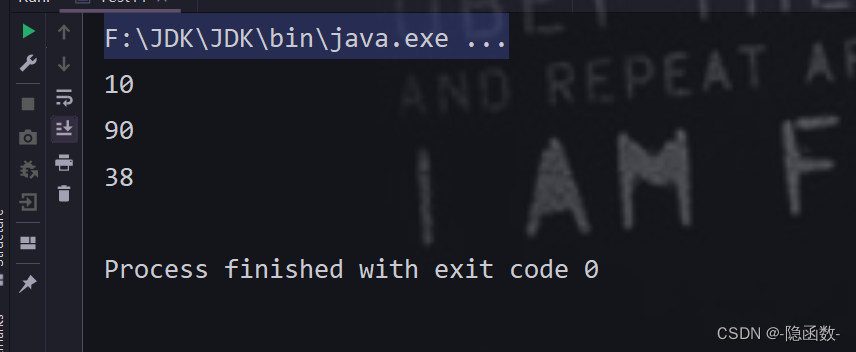
forEach
package com.qf.webpro2105.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("38");
list.add("10");
list.add("90");
//创建Stream
//创建流的时候,数据类型要与集合中的数据类型保持一致
Stream<String> stream = list.parallelStream();
//终止操作 将集合中的元素进行遍历
//他只是将集合中的元素进行遍历,
//但是遍历出来的顺序并不是我们添加进集合中的顺序
// stream.forEach(t -> System.out.println(t));
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Arrays
String[] array = {"38","10","90"};
Stream<String> stream1 = Arrays.stream(array);
stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
of方法
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.of(10,100,30,80,50);
stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
迭代流
Stream<Integer> iterate = Stream.iterate(0, x->x+2);
//limit 从0开始只要五个
iterate.limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);
生成流
Stream<Integer> generate = Stream.generate(()->new Random().nextInt(100));
generate.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
11、新时间API
之前时间API存在的问题:线程安全问题,设计混乱。
本地化日期时间 API:
LocalDate
LocalTime
LocalDateTime
Instant:时间戳
Zoneld:时区
Date、Instant、LocalDateTime的转换
DateTimeFormatter:格式化类
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








