今天我们同学第一天上班,他们写的是mybatis,但是使用的是xml写sql语句,我听到我好想不会写了呀,还得好好的复习一下,不能让自己忘记了,这可是我好不容易学来的技术哟,可花了我不少的时间了
-------对于一个转行的我来说
我还是一个有追求的:
一个好的程序员是底层走,但是大多数都是往框架走(一种人往底层走,一种人往框架走)
mybtais我编程测第一个框架orm,持久层框架(就是一个连接数据库的框架)轻量级的ORM框架
优点:MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集
使用连接池,用连接池来管理数据库的链接和释放资源。
mybatis框架将sql语句提取到xml配置文件中,每一次修改sql语句,只需要修改配置文
件中的语句即可,和代码无关
mybatis框架将视线关系对象映射,mybatis存在输入对象映射和输出对象映射。
缺点:
(说实话这没有好的一点的写sql语句的能力还真不好使用这个框架)
- SQL语句的编写工作量较大,尤其是字段多、关联表多时,更是如此,对开发人员编写SQL语句的功底有一定要求。
- SQL语句依赖于数据库,导致数据库移植性差,不能随意更换数据库。
原理
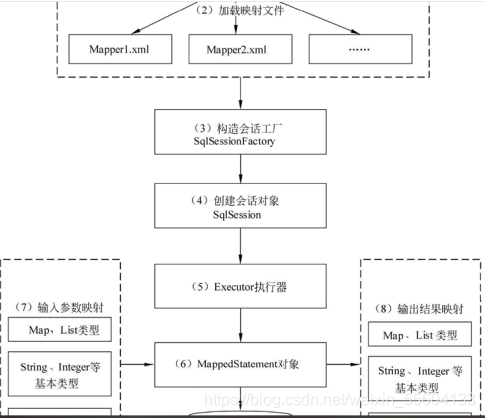
这个是mybtais的基本架构:以ecpilse为例
编写sqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 使用mybatis需要的数据源和事务配置,后续如果整合spring之后,将不再需要 -->
<environments default="development">
<!-- 配置数据源和事务 -->
<environment id="development">
<!-- 配置事务管理,将事务管理交给mybatis管理 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name = "driver" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载**.xml配置文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="Food.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
编写log4j.properties标签
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
# MyBatis logging configuration...
log4j.logger.org.mybatis.example.BlogMapper=TRACE
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
编写失血模型
package model;
/**
* @ClassName: food.java
* @Description: 该类的功能描述
* @version: v1.0.0
* @author: 169986432
* @date: 2020年10月11日 下午2:38:05
*/
public class Food {
private int id;
private String last_name;
private String gender;
private String email;
public Food() {
super();
}
public Food(int id, String last_name, String gender, String email) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.last_name = last_name;
this.gender = gender;
this.email = email;
}
/**
* @return the id
*/
public int getId() {
return id;
}
/**
* @param id the id to set
*/
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
/**
* @return the last_name
*/
public String getLast_name() {
return last_name;
}
/**
* @param last_name the last_name to set
*/
public void setLast_name(String last_name) {
this.last_name = last_name;
}
/**
* @return the gender
*/
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
/**
* @param gender the gender to set
*/
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
/**
* @return the email
*/
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
/**
* @param email the email to set
*/
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Food [id=" + id + ", last_name=" + last_name + ", gender=" + gender + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}
`编写单个映射关系的sql.xml:Food.xml``
public interface FoodDao {
public Food queryProductById(String last_name) throws Exception;
}
编写dao接口的实现类:FoodImpl实现类
public class FoodDaoImpl implements FoodDao {
//声明一个会话工厂
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
//由构造方法进行创建对象赋值
public FoodDaoImpl(SqlSessionFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
@Override
public Food queryProductById(String last_name) throws Exception {
//开启会话
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
Food prod = sqlSession.selectOne("test.foodAll", last_name);
//关闭会话
sqlSession.close();
return prod;
}
}
测试类:测试
public class Test {
//创建dao的实现类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String path = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream config = Resources.getResourceAsStream(path);
//创建一个会话工厂
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(config);
testQuery1(factory);
}
public static void testQuery1(SqlSessionFactory factory) throws Exception {
FoodDao dao = new FoodDaoImpl(factory);
int id = 1;
Food food=dao.queryProductById("张三");
System.out.println(food);
}
}
mybatis的最简单的增,删,改,查
思路:
1.导入jr包,创建xml里面配置增,删,改。查的sql语句
2.创建xml文件在SqlMapConfig.xml文件中进行配置加载
3.创建一个失血模型要跟数据库的字段一致
4.创建一个接口,接口当中包含5个方法,两个查询、增、删、改的方法。只有定义。
5.创建实现类,实现定义的接口,按照规定进行重写方法。声明工厂类对象,该对象由该类的构造方法进行赋值。
6.编写测试类,在测试类中,创建工厂对象,传递给dao的实现类。
编写xml:food.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="first">
<!-- 根据id查询 -->
<select id="queryId" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="model.Food">
SELECT * FROM t_product WHERE p_id = #{p_id}
</select>
<!-- 根据名称模糊查询,返回多条结果集 -->
<select id="queryName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="model.Food">
SELECT * FROM t_product WHERE name like "%${value}%"
</select>
<!-- 新增一条数据 -->
<insert id="insert" parameterType="model.Food">
INSERT INTO t_product(name,p_number,price) value(#{name},#{p_number},#{price})
</insert>
<!-- 根据id值更新 -->
<update id="update" parameterType="model.Food">
UPDATE t_product SET name = #{name} WHERE p_id = #{p_id}
</update>
<!-- 根据id删除 -->
<delete id="delete" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
DELETE FROM t_product WHERE p_id = #{p_id}
</delete>
</mapper>
编写xml:加载food。xml
编写接口增,删,改,查
public interface FoodDao {
public Food queryId(int id) throws Exception;
public List<Food> queryName(String name) throws Exception;
public Food insert(Food product) throws Exception;
public int update(Food product) throws Exception;
public int delete(int id) throws Exception;
}
编写接口的实现类
public class FoodDaoImpl implements FoodDao {
//声明一个会话工厂
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
//由构造方法进行创建对象赋值
public FoodDaoImpl(SqlSessionFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
@Override
public Food queryId(int id) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
Food food= sqlSession.selectOne("first.queryId", id);
sqlSession.close();
return food;
}
@Override
public List<Food> queryName(String name) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
List<Food> list = sqlSession.selectList("first.queryName", name);
sqlSession.close();
return list;
}
@Override
public Food insert(Food food) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
int row = sqlSession.insert("first.insert", food);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
return food;
}
@Override
public int update(Food food) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
int row = sqlSession.update("first.update", food);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
return row;
}
@Override
public int delete(int id) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
int row = sqlSession.delete("first.delete", id);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
return row;
}
}
测试类:测试
public class Test {
//创建dao的实现类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String path = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream config = Resources.getResourceAsStream(path);
//创建一个会话工厂
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(config);
// testQuery1(factory);
// testQuery2(factory);
testQuery3(factory);
}
public static void testQuery1(SqlSessionFactory factory) throws Exception {
FoodDao dao = new FoodDaoImpl(factory);
int id = 1;
Food food = dao.queryId(id);
System.out.println(food);
}
public static void testQuery2(SqlSessionFactory factory) throws Exception {
FoodDao dao = new FoodDaoImpl(factory);
String name = "牛奶";
List<Food> list = dao.queryName(name);
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void testQuery3(SqlSessionFactory factory) throws Exception {
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
Food food=session.getMapper(Food.class);
Food food1=new Food();
food1.setP_id(7);
food1.setName("阿萨姆奶茶");
food1.setP_number(788);
food1.setPrice(90);
food1.setAdd_time("2020-09-23 17:59:46.0");
}
}
总结:什么是mybatis、结构、一个案例
明天再来复习重点,mapper代理方式进行CRUD





 本文讲述了新员工如何通过XML配置MyBatis,回顾SQL编写、映射及框架优缺点,介绍了从底层到框架的程序员发展路径,并详细讲解了MyBatis的基本架构、配置、映射文件和CRUD操作实例。
本文讲述了新员工如何通过XML配置MyBatis,回顾SQL编写、映射及框架优缺点,介绍了从底层到框架的程序员发展路径,并详细讲解了MyBatis的基本架构、配置、映射文件和CRUD操作实例。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










