普通并查集(朋友的朋友是朋友)
思路:
1.用一个数组 f f f 表示 i i i 的上一层是 f [ i ] f[ i ] f[i] ,初始情况下 f [ i ] = i f[ i ] = i f[i]=i 全部满足;
2.每当两个点连接时,都可以将其中一个点的 f f f 值修改为另一个点的 f f f 值,表示此两点的上一层相同——两个点为同一整体;
3.每次连接时,必须将 a a a 的最上层 f f f 值和 b b b 的最上层 f f f 值连接,这样 a a a 、 b b b 以及 a a a、 b b b 过程中连接过得所有点的 f f f 值都相同,他们都在同一个整体中;
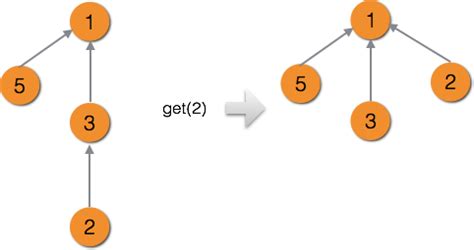
public static int find(int x){
if(f[x] != x)
f[x] = find(f[x]);//将过程中的所有点的f值全部赋值为顶点的f值
return f[x];
}
public static void merge(int x,int y){
int xx = find(x);
int yy = find(y);
if(xx!=yy)
f[yy] = xx;
}
例题:蓝桥幼儿园
题目链接:蓝桥幼儿园 - 蓝桥云课 (lanqiao.cn)

思路:用 f f f 数组表示关系,如果 o p op op 为 1 1 1 ,便进行 m e r g e merge merge 操作,如果 o p op op 为 2 2 2 ,判断两个学生的 f f f 值是否相同。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int[] p;//p[i]表示i的头结点是p[i]
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String[] s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
p = new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
p[i] = i;//第i个小朋友的根节点
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int op = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int x = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(s[2]);
if(op==1)
merge(x,y);
else
System.out.println(find(x)==find(y)?"YES":"NO");
}
}
static int find(int x) {
if(p[x]!=x)
p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
static void merge(int x,int y){
int xx = find(x);
int yy = find(y);
if(xx != yy)
f[yy] = xx;
}
}
种类并查集(敌人的敌人是朋友)
思路:
1.在普通并查集的基础上进行完善,如果 a a a 和 b b b 是敌人, b b b 和 c c c 是敌人,那么 a a a 和 c c c 是朋友,这时可以表示为: a a a 和 ! b !b !b 是朋友, b b b 和 ! a !a !a 是朋友, c c c 和 ! b !b !b 是朋友, b b b 和 ! c !c !c 是朋友;
2.数组 f f f 的大小需要为普通并查集的二倍,前半部分表示 i i i 的 f [ i ] f[ i ] f[i] 值,后半部分表示 ! i !i !i 的 f [ i ] f[ i ] f[i] 值;
例题:蓝桥侦探

思路:
1.种类并查集,如果 a a a 和 b b b 不在一起, b b b 和 c c c 不在一起,那么 a a a 和 c c c 一定在一起,否则,有人说谎;
2.题目输入 x x x, y y y 表示 x x x 和 y y y 不在一起,那么便可以表示为: x x x 和 ! y !y !y 在一起, y y y 和 ! x !x !x 在一起,两个内容都进行 m e r g e merge merge 操作;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int[] f;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String[] s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
f = new int[2*n+2];
for(int i=0;i<2*n+2;i++) {
f[i] = i;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
if(find(x)!=find(y)) {
merge(x, y+n);
merge(x+n, y);
}else {
System.out.println(x);
return;
}
}
}
static int find(int x) {
if(f[x]!=x)//夫点不是自己
f[x]=find(f[x]);
return f[x];
}
static void merge(int x,int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
f[y] = x;
}
}
带全并查集
思路:在普通并查集的基础上还需要记录长度。
例题:蓝桥部队

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int[] f;//存放此列的排头元素
static int[] length;//存放此列的军人数量
static int[] num;//此军人前面有多少人
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String[] s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
f = new int[n+1];
length = new int[n+1];
num = new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
f[i] = i;
length[i] = 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int op = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int x = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(s[2]);
if(op==1) {//合并x和y所在列 x到y后面
merge(x, y);
}else {//求x和y间隔
if(find(x)!=find(y)) {
System.out.println(-1);
}else {
System.out.println(Math.abs(num[x]-num[y])-1);
}
}
}
}
static void merge(int x,int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if(x==y)
return;
num[x] = num[x] + length[y];
length[y] = length[y] + length[x];
f[x] = y;
}
static int find(int x) {
if(x!=f[x]) {
int root = find(f[x]);
num[x] = num[x] + num[f[x]];
return f[x] = root;
}
return f[x];
}
}






















 1262
1262

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








