1.命令别名(永久有效)仅对root有效,写一个命令命为hello,实现的功能为每输入一次hello命令,就有hello,everyone写入文件/file.txt中。
[root@localhost ~]# pwd
/root
[root@localhost ~]# vim ~/.bashrc
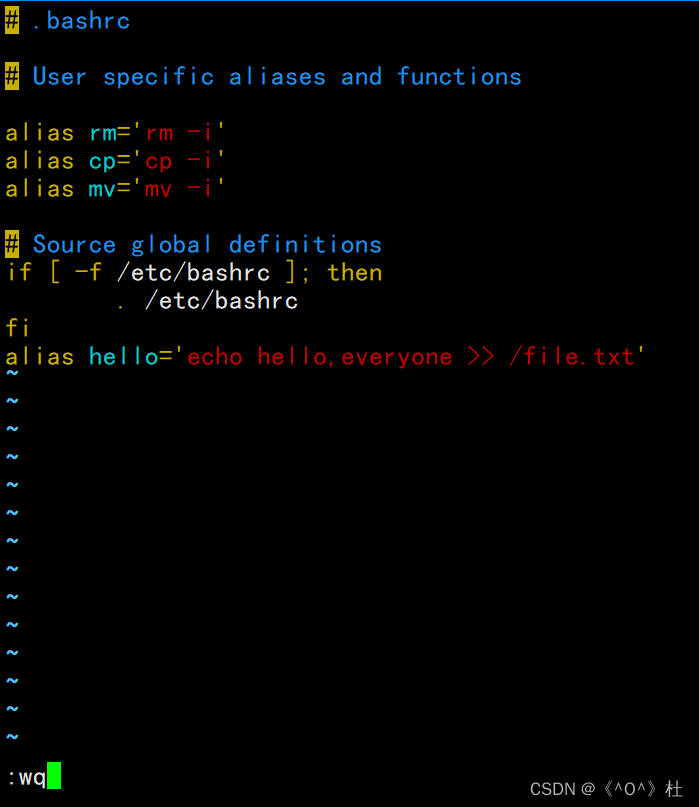
[root@localhost ~]# source ~/.bashrc
[root@localhost ~]# hello
[root@localhost ~]# cat file.txt
hello,everyone
注:重启之后,依然可以使用,再次输入hello依然会写入file.txt中。且只可以在root用户下使用hello。其他用户下,会显示不存在,以下举例:
[root@localhost ~]# su redhat
[redhat@localhost root]$ cd
[redhat@localhost ~]$ hello
bash: hello: command not found...
[redhat@localhost ~]$ pwd
/home/redhat
2. 命令别名(所有用户)写一个命令别名为shuaxin,实现的功能为每输入一次该命令,file.txt文件的所有时间就更新为当前时间。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/bashrc
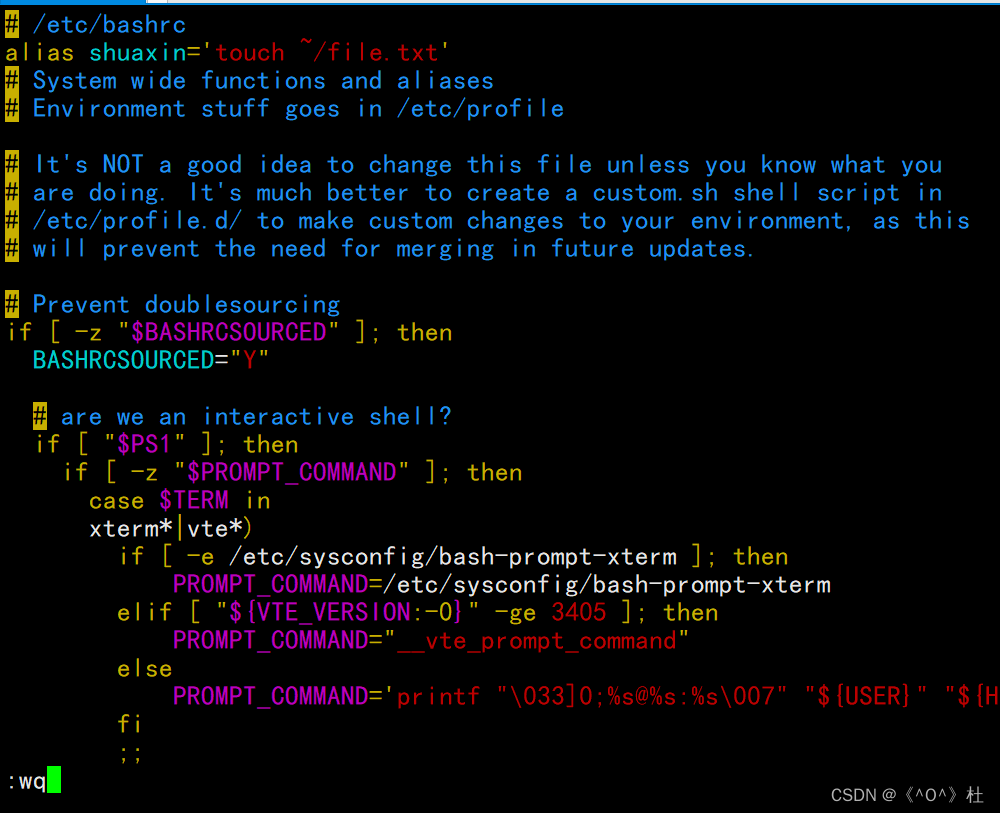
[root@localhost ~]# source /etc/bashrc
[root@localhost ~]# ll file.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 15 Nov 14 18:51 file.txt
[root@localhost ~]# shuaxin
[root@localhost ~]# ll file.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 15 Nov 14 18:57 file.txt
注:此时,所有用户都可以应用“shuaxin”这个命令,在普通用户下也可以使用,举例如下:
[root@localhost ~]# su - redhat
[redhat@localhost ~]$ ll file.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 redhat redhat 15 Nov 14 18:52 file.txt
[redhat@localhost ~]$ shuaxin
[redhat@localhost ~]$ ll file.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 redhat redhat 15 Nov 14 19:02 file.txt
3.文件查找:在$HOME目录及其子目录中,查找2天前被更改过的文件。
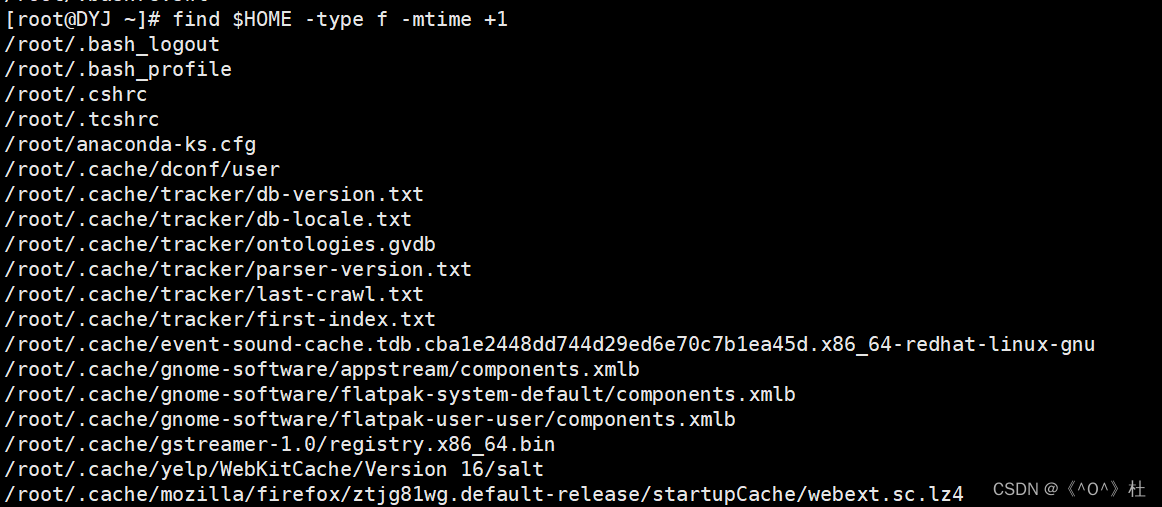
4.打包压缩:将/opt目录下的文件全部打包并用gzip压缩成/test/newfile.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# tar -zcf newfile.tar.gz /opt >> /test/newfile.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# ll /test
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 19 09:57 newfile.tar.gz
思维导图:
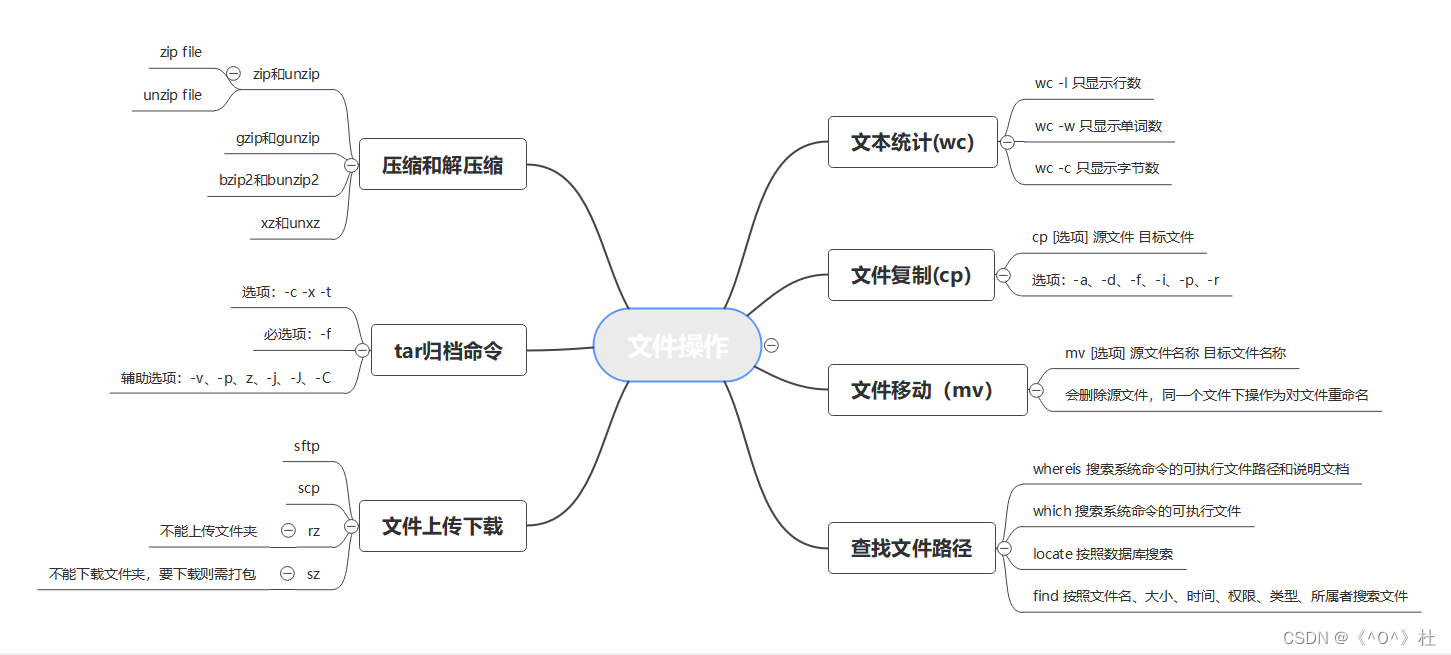







 本文介绍了如何在Linux系统中创建命令别名,使得root用户可以通过'hello'命令向/file.txt写入'hello, everyone',并且设置别名在重启后仍然有效。此外,还展示了如何设置全局命令别名'shuaxin',用于更新file.txt的修改时间,此命令对所有用户都可用。最后,讲解了在$HOME目录及子目录中查找2天内被修改的文件,以及如何使用tar和gzip命令打包并压缩/opt目录下的文件。
本文介绍了如何在Linux系统中创建命令别名,使得root用户可以通过'hello'命令向/file.txt写入'hello, everyone',并且设置别名在重启后仍然有效。此外,还展示了如何设置全局命令别名'shuaxin',用于更新file.txt的修改时间,此命令对所有用户都可用。最后,讲解了在$HOME目录及子目录中查找2天内被修改的文件,以及如何使用tar和gzip命令打包并压缩/opt目录下的文件。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








