1.反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。

方法1:双指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//双指针,链表的最后一位为null
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;//前驱
ListNode cur = head;//当前节点为head
ListNode temp = null;//用于暂时存放节点
while(cur!=null){
temp = cur.next;//暂时存储cur节点的下一个节点
cur.next= prev;//当第一次执行时,连接到null
prev = cur;//向后移动
cur = temp;//向后移动
}
return prev;
}
}
方法二:递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//递归
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null,head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev,ListNode cur){
if(cur==null){
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;//先保存下一个节点
cur.next=prev;//反转
//更新prev,cur的位置
prev =cur;
cur =temp;
return reverse(prev,cur);
}
}
2.反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
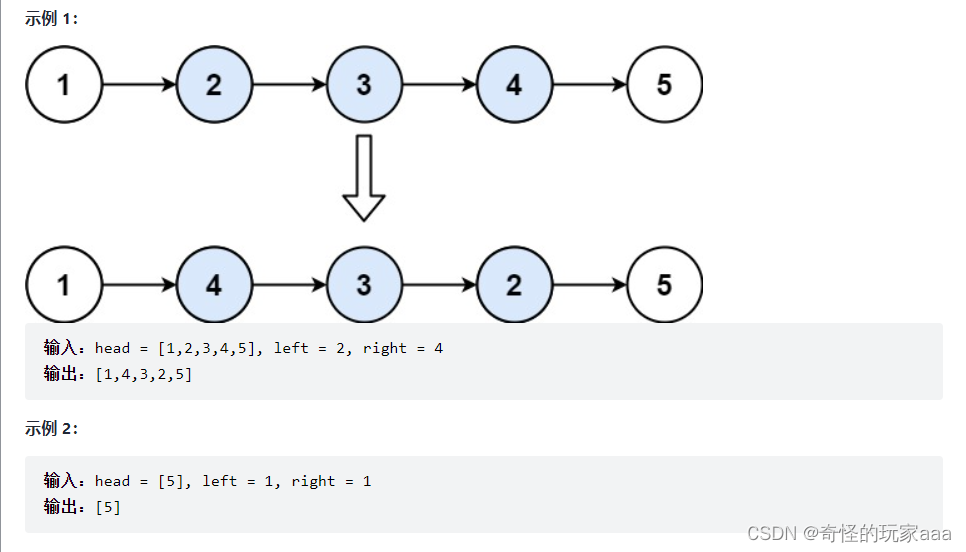
思路:
1.先得到left前的第一个节点
2.然后进行反转链表。同上
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
//得到left的前一个节点
for(int i =1;i<left;i++){
prev =prev.next;
}
ListNode cur = prev.next;//为我们当前要操作的节点
for(int i=left;i<right;i++){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = temp.next;
temp.next=prev.next;//以prev为标准,注意不能为cur
prev.next = temp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
3.回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
方法一:模拟数组
1.先的到链表的长度
2.将链表里的值放入新建等长数组中
3.回文处理
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/*
* 模拟数组
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
int len = 0;
//统计链表长度
ListNode cur =head;
while(cur!=null){
cur = cur.next;
len++;
}
cur = head;//回归头节点
int [] res = new int[len];//建立数表模拟
//将元素添加到数组中
for(int i =0;i<res.length;i++){
res[i]=cur.val;
cur =cur.next;
}
//比较是否回文
for(int i =0,j=len-1;i<j;i++,j--){
if(res[i]!=res[j]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
方法二:快慢指针
1.用快慢指针,快指针有两步,慢指针走一步,快指针遇到终止位置时,慢指针就在链表中间位置。
2.我们得到慢指针前一个位置,然后断开。链表将分为两个部分。
3.将第二部分反转链表,然后与第一部分比较。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/*
* 快慢指针
*/
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//如果链表为空,或者只有一个节点,返回true
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return true;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode prev = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
prev = slow;//记录slow的前一个节点
slow = slow.next;//慢节点移动一位
fast = fast.next.next;//快节点移动两位
}
prev.next = null;//根据prev,分割两个链表
//前半部分
ListNode cur1 = head;
//后半部分,这里使用了反转链表,反转slow后的部分
ListNode cur2 = reverseList(slow);
// 前后部分进行比较
while(cur1!=null){
if(cur1.val!=cur2.val) return false;
cur1=cur1.next;
cur2 =cur2.next;
}
return true;
}
//反转链表
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode temp = head;
while(head!=null){
temp = head.next;
head.next =prev;//第一位指向null
prev=head;
head=temp;
}
return prev;
}
}





















 3231
3231

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








