他相鄰詞語或相鄰語法環境
how do we learn new words - for computers
- Looking into a dictionary: How to teach computers the meanings of semi-aquatic半截流, tropical and the whole paragraph?
- Pointing to an object: How to teach computers to “understand” images?
- Which strategy is used? Similar contexts suggest similar meanings.
→ Distributional hypothesis 分佈假設 - But
- need to understand the meaning of contexts
Distributional hypothesis
history:
The meaning of a word is its use in the language 單詞的含義是他在語言中的使用
- If A and B have almost identical environments we say that they are synonyms [Zellig Harris (1954)]
- We shall know a word by the company it keeps. [Firth (1957)]
Formalisation:
Given word w and all the contexts C(w)={c1,c2,...}C (w) = \{c_{1} ,c_{2} ,...\}C(w)={c1,c2,...} it appears within, then
meaning(w)=f(c1,c2,...)
meaning (w) = f (c_{1},c_{2},...)
meaning(w)=f(c1,c2,...)meaning (w) = f (c1,c 2,…)
where f is a function compressing some statistics of C (w) into a vector.
The ultimate goal: find f!
如何計算語義相似性
計算詞與詞之間在相同上下文中出現的頻率
詞嵌入(Word Embeddings) 是一種用向量(Vector)來表示詞語的技術,讓詞語的語義關係能夠通過數學方式計算。它將 高維的詞空間壓縮到低維向量空間,並保留語義信息
基於計數的方法(Count-based Methods)
- 共現矩陣(Co-occurrence Matrix):使用詞與詞之間的共現頻率來建模語義關係。
- 降維技術(SVD, PCA):例如使用奇異值分解(SVD)來降低維度。
- 典型模型:LSA(Latent Semantic Analysis)典型模型:LSA(潛在的幼稚agaysisis)
基於預測的方法 (Prediction-based Methods)
這類方法使用神經網絡來學習詞的分佈式表示,效果通常比計數方法更好。
-
Word2Vec(CBOW & Skip-gram)Word2Vec(cbow和跳過)
- CBOW(Continuous Bag of Words):用上下文詞預測中心詞。
- Skip-gram:用中心詞預測上下文詞。
- 例如:
CBOW: “The ____ is barking.” → 預測 "dog"CBOW:“ ____是在吠叫。” →預測“狗”Skip-gram: “dog” → 預測 {“barking”, “pet”, “puppy”}Skip-gram:“狗”→預測{“吠叫”,“寵物”,“ Puppy”}
-
GloVe(Global Vectors for Word Representation)手套((單詞表示形式的全局向量)
- 以詞共現信息為基礎,同時考慮語義信息。
-
FastText快速文字
- 擴展 Word2Vec,考慮子詞(subword)信息,例如 “playing” 由 “play” + “ing” 組成。
-
Contextualized Embeddings(語境化詞嵌入)上下文化嵌入(()
- BERT, ELMo, GPT 等基於 Transformer 的模型可以根據上下文動態改變詞的表示。
WSD:
- 基於詞典(Dictionary-based)(基於字典))
- 例如 WordNet,使用詞義的層次結構來判斷。
- 基於機器學習(Supervised Learning)基於機器學習((監督學習)
- 需要帶標註的語料庫(如 SemCor)來訓練分類模型
- 基於上下文的詞嵌入(Contextualized Word Embeddings)基於上下文的詞嵌入((上下文化的單詞嵌入))
- 使用 BERT、GPT、ELMo 這類模型,能夠根據句子語境動態決定詞義。
| 概念 | 主要內容 | 典型方法 |
|---|---|---|
| Distributional Semantics(分佈式語義)(分銷語義(分佈式語義) | 單詞的語義來自於它的上下文 | 共現矩陣(Co-occurrence Matrix),PMI共現矩陣(共發生矩陣Chesi |
| Word Embeddings(詞嵌入)變成嵌入(詞嵌入) | 將單詞映射到低維向量空間,以捕捉語義關係 | Word2Vec、GloVe、FastText、BERTword2vec,手套,fasttx,bere |
| Word Sense Disambiguation(詞義消歧)單詞感官歧義(詞義消歧) | 根據語境確定詞的正確含義 | WordNet、機器學習、BERT |
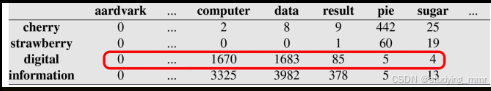
Co-occurrence vectors: word-word matrixes
- Collect a lot of documents / sentences (from, e.g. Wikipedia)
- a. … the first digital computers were developed.
- b. … the system stores enough digital data …
- Apply basic pre-processing steps: lowercase小寫, tokenisation像征化, lemmatisation誘餌
- Count how many times a word u appearing with a word v count (digital, computer) = 1670
- The meaning of word u is vector [count (u, v1), count (u, v2),…] [Term-document matrix](Data%20Science/Natural%20La
- nguage%20Processing%20NLP/Word%20Embeddings.md #Count-based %20Approach)
Pros
The meaning of a word is represented by a vector (named word vector), therefore
Summary
● Distributional semantics is originated from distributional hypothesis
○ Tell me who your friends are, I’ll tell you who you are
● A word is represented by a co-occurrence word vector
● Co-occurrence word vectors can be used to:
○ detect the similarity among words
○ visualise word meanings
○ input to machine learning models





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








