1.设计循环队列
1.设计循环队列:

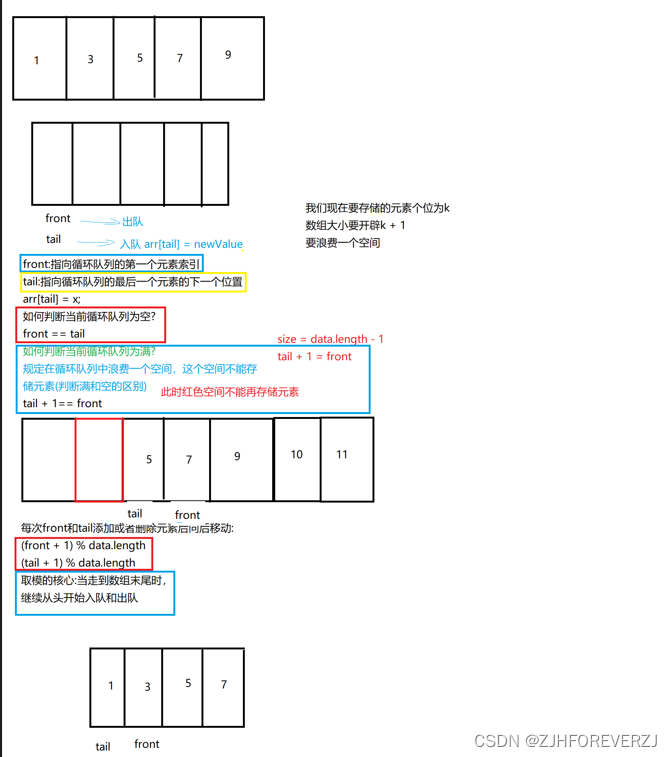
方法一:
(1)代码:
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] array;
private int size;
private int front=0;
private int rear=0;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
array=new int[k];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(size==array.length){
System.out.println("queue is full!");
return false;
}
array[rear]=value;
rear=(rear+1)%array.length;
size++;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(size==0){
System.out.println("queue is empty!");
return false;
}
front=(front+1)%array.length;
size--;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(size==0){
System.out.println("queue is empty!");
return -1;
}
return array[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(size==0){
System.out.println("queue is empty!");
return -1;
}
int last=(rear-1+array.length)%array.length;
return array[last];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size==0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size==array.length;
}
(2)运行截图:
方法二:
package stack_queue.leetcode;
/**
* 设计循环队列
*/
public class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] data;
private int front;
private int tail;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
data = new int[k + 1];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
data[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return data[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int index = tail == 0 ? data.length - 1 : tail - 1;
return data[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == tail;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (tail + 1) % data.length == front;
}
}
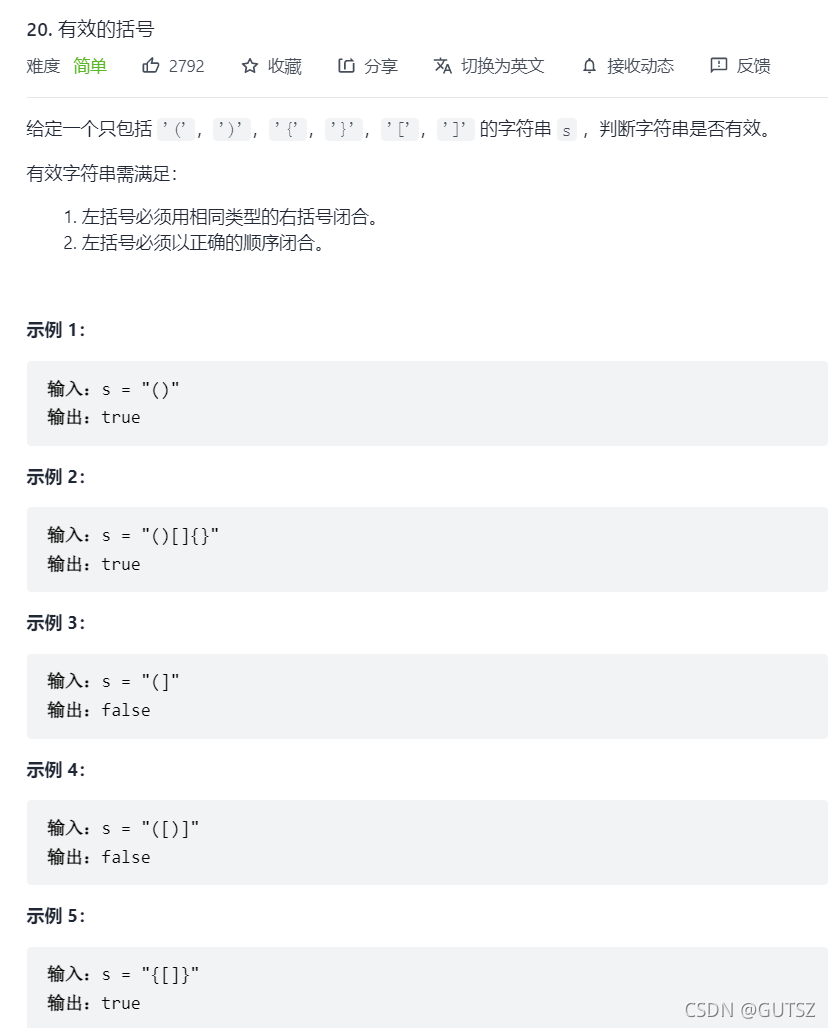
2.有效的括号
2.有效的括号:
(1)代码:
package stack_queue.leetcode;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Num20 {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
//遍历字符串,在遍历过程中,将左括号全部入栈
//碰到右括号就弹出栈顶元素查看括号是否匹配
//1.将字符串转换为字符数组String->char[]
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] ret = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) {
char c = ret[i];
//判断c是否是左括号
if (c == '{' || c == '[' || c == '(') {
stack.push(c);
} else {
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
//此时c是个右括号
char tmp=stack.pop();
if(c=='}'&& tmp !='{'){
return false;
}
if(c==']' && tmp!='['){
return false;
}
if(c==')'&& tmp!='('){
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
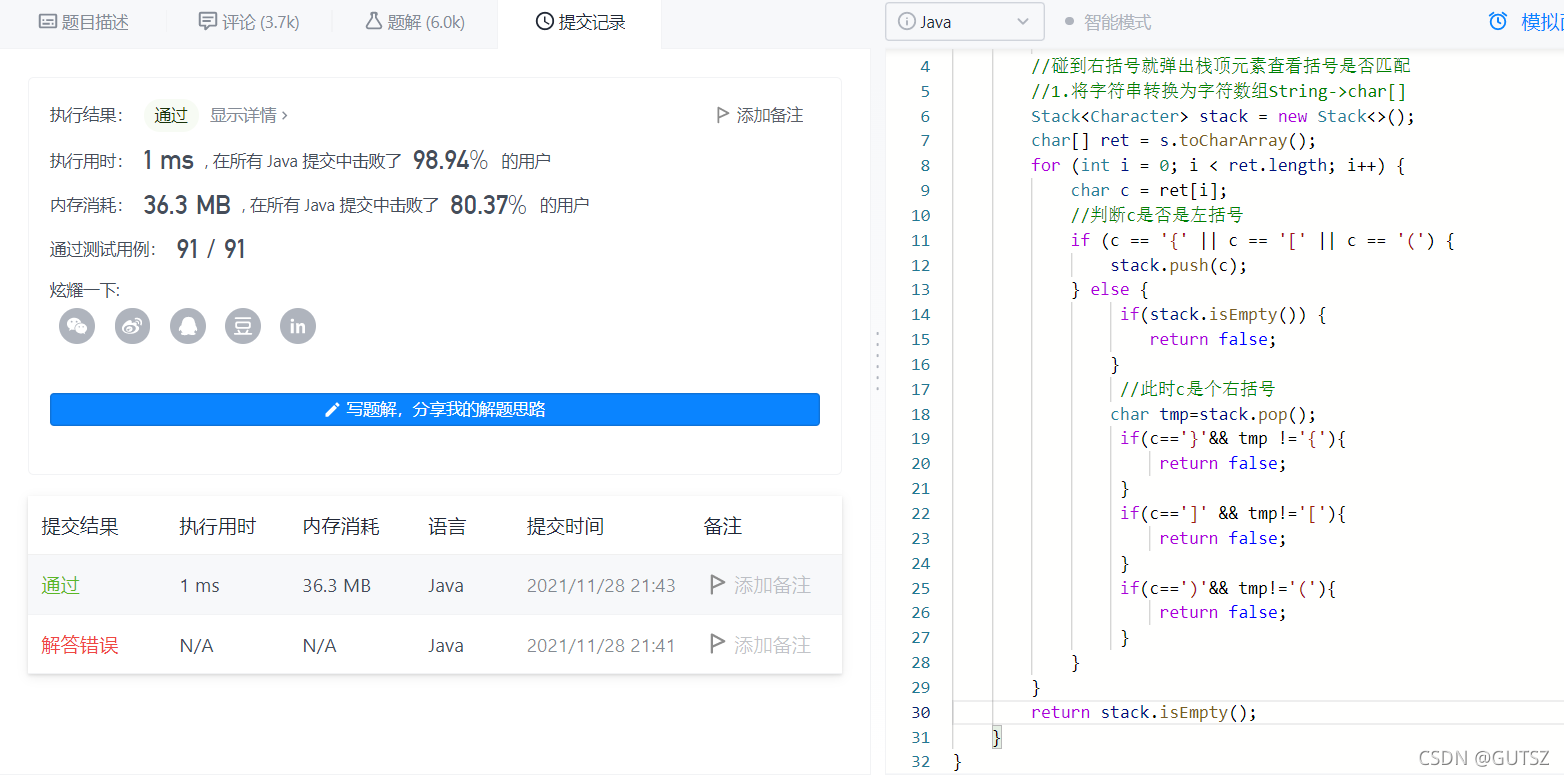
(2)运行截图:
3.最小栈
3.最小栈

(1)代码:
package stack_queue.leetcode;
import java.util.Stack;
//双栈实现最小栈
public class Num155 {
// 具体存储元素
private Stack<Integer> element = new Stack<>();
// 辅助栈,一直保存最小元素
private Stack<Integer> support = new Stack<>();
public Num155() {
}
public void push(int val) {
element.push(val);
if (support.isEmpty()) {
support.push(val);
} else {
int tmpMin = support.peek();
// 比较当前元素和tmpMin谁更小
// 将最小的元素push进辅助栈中
int min = Math.min(val, tmpMin);
support.push(min);
}
}
public void pop() {
element.pop();
support.pop();
}
public int top() {
return element.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return support.peek();
}
}
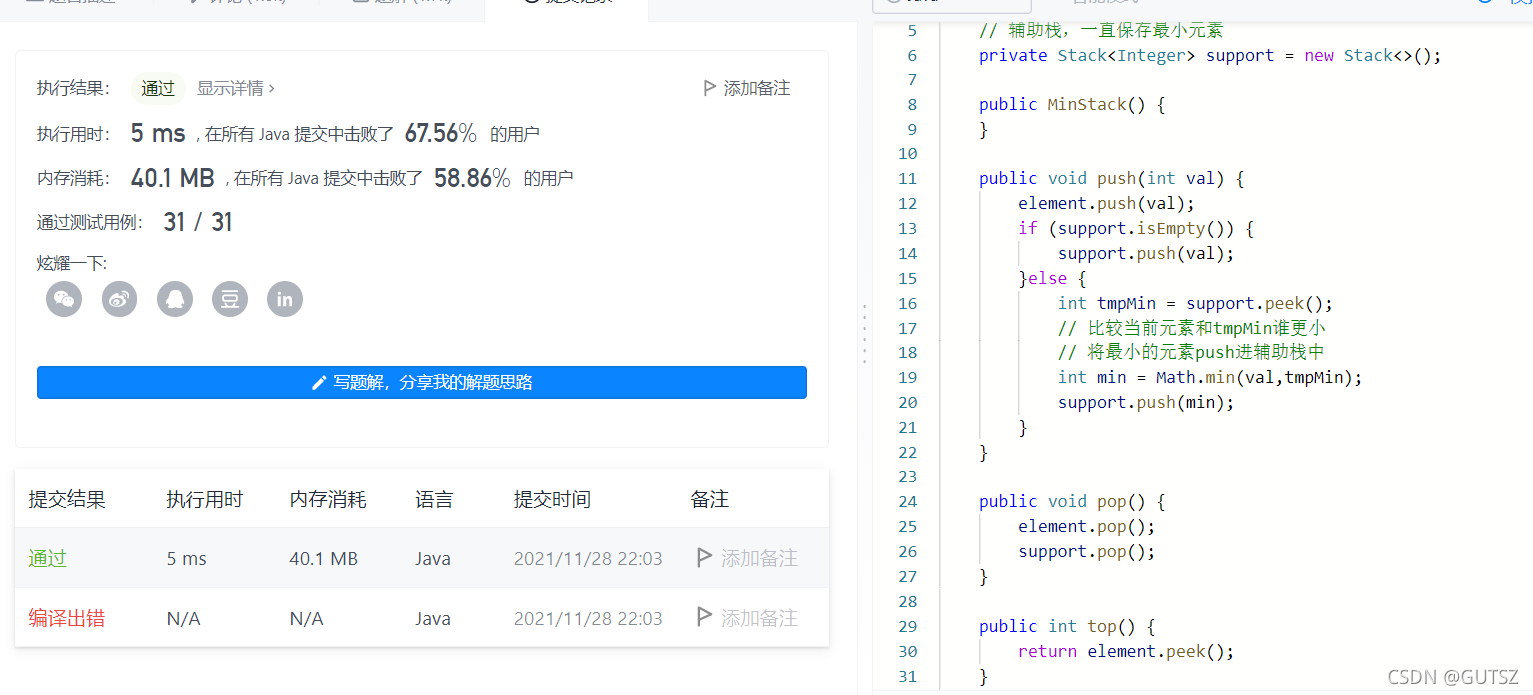
(2)运行截图:
4.用队列实现栈
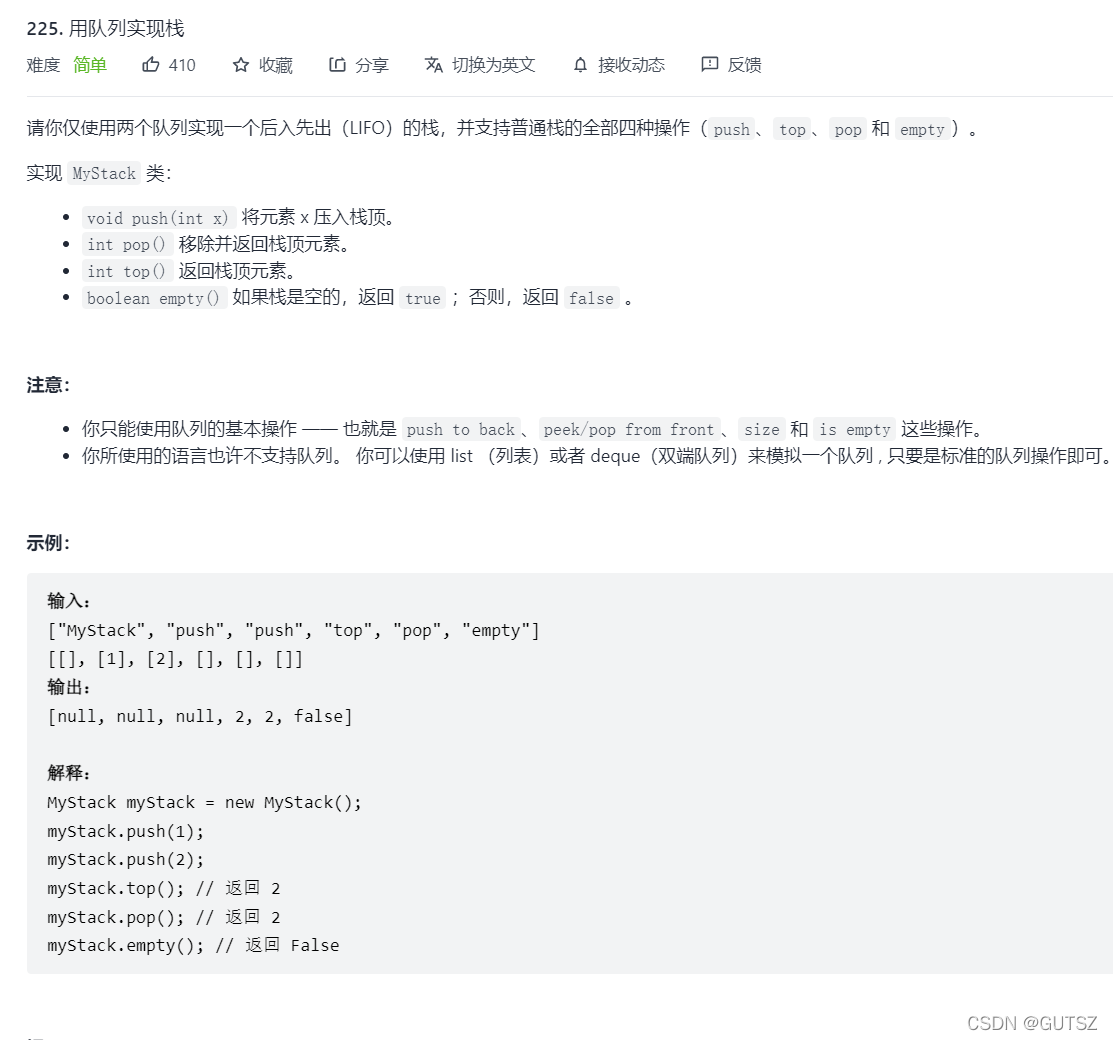
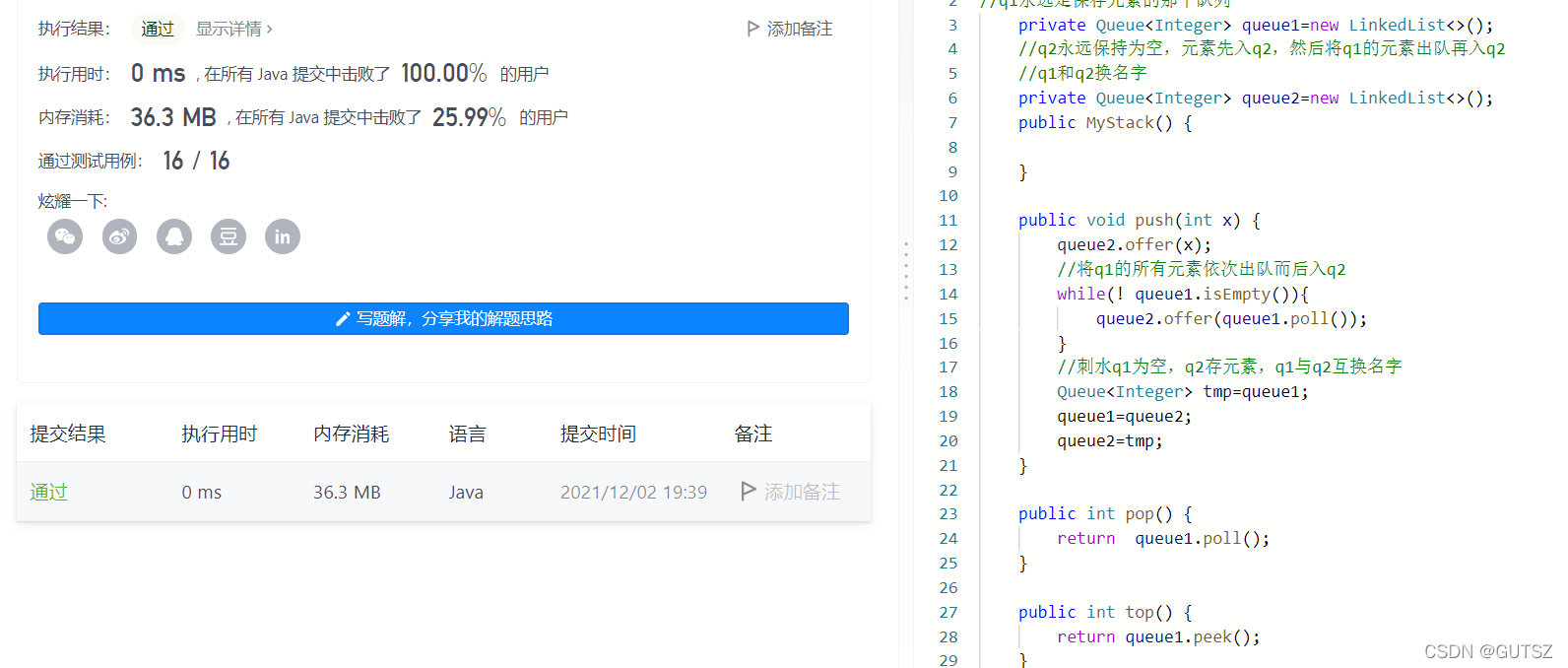
4.用队列实现栈:
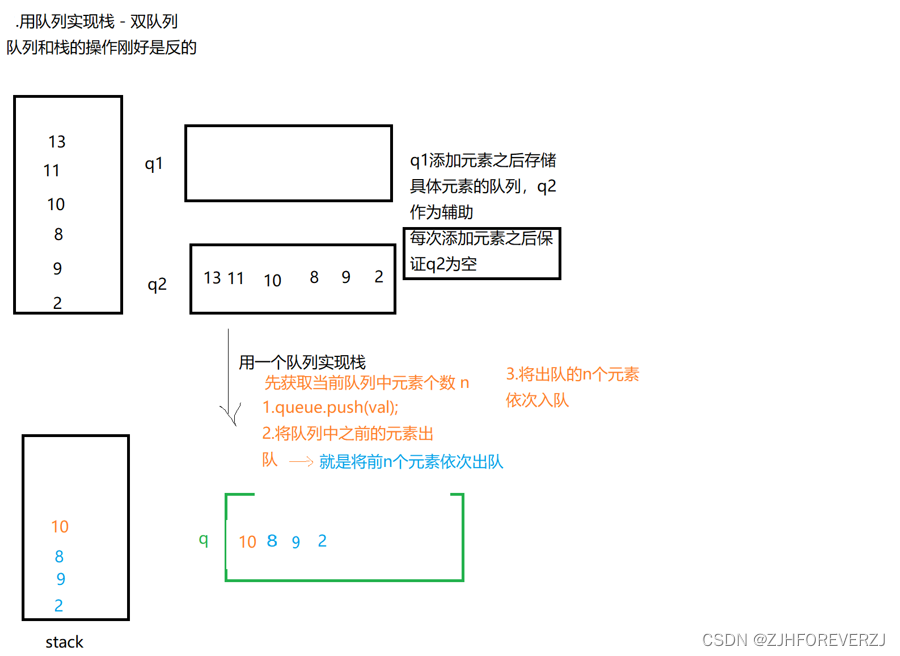
解题思路:
(1)代码实现:
package stack_queue.leetcode;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
//Num225
//双队列实现栈
public class MyStack {
//q1永远是保存元素的那个队列
private Queue<Integer> queue1=new LinkedList<>();
//q2永远保持为空,元素先入q2,然后将q1的元素出队再入q2
//q1和q2换名字
private Queue<Integer> queue2=new LinkedList<>();
public MyStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x);
//将q1的所有元素依次出队而后入q2
while(! queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
//刺水q1为空,q2存元素,q1与q2互换名字
Queue<Integer> tmp=queue1;
queue1=queue2;
queue2=tmp;
}
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
(2)运行截图:
5.双栈实现队列
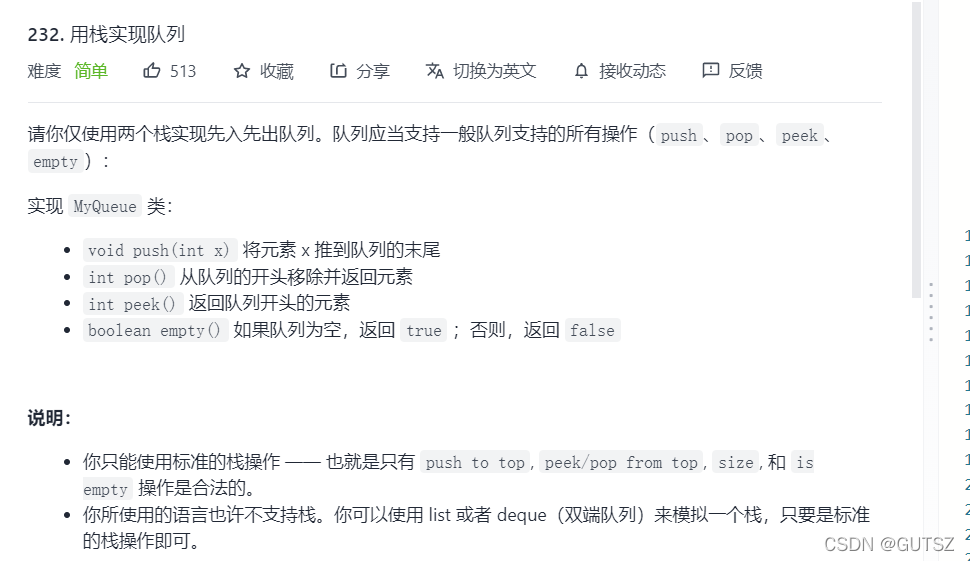
解题思考:
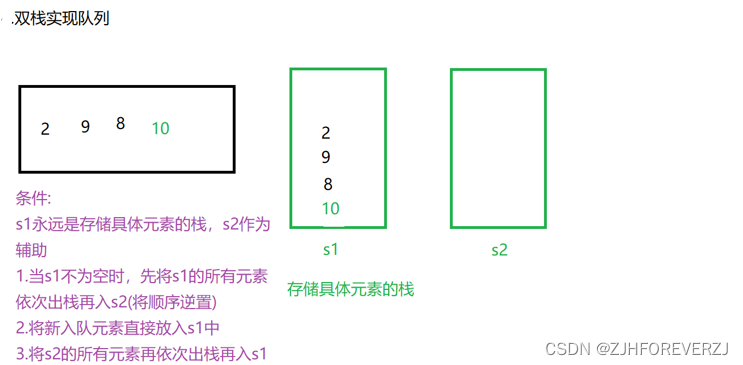
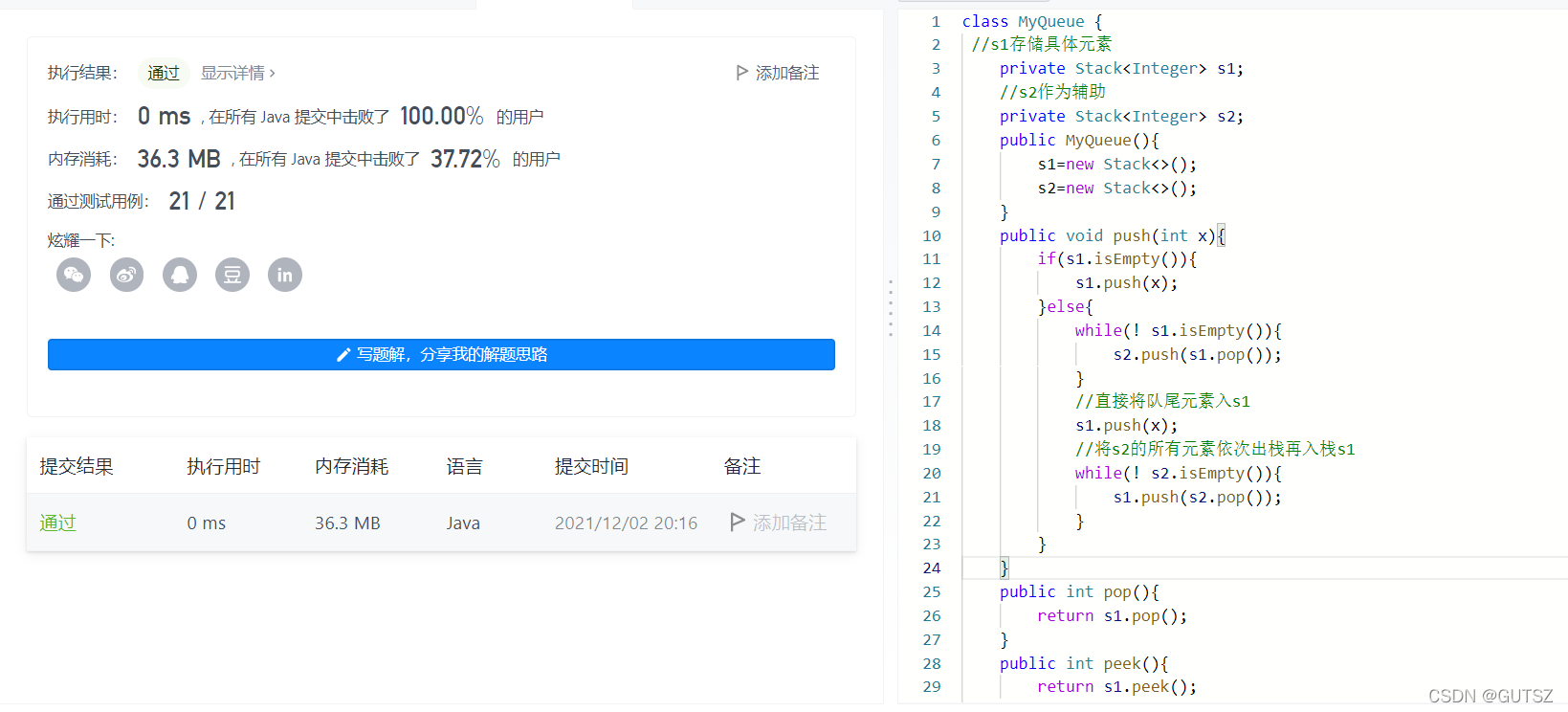
(1)代码实现:
package stack_queue.leetcode;
import java.util.Stack;
//Num232
//双栈实现队列
public class MyQueue {
//s1存储具体元素
private Stack<Integer> s1;
//s2作为辅助
private Stack<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue(){
s1=new Stack<>();
s2=new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x){
if(s1.isEmpty()){
s1.push(x);
}else{
while(! s1.isEmpty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
//直接将队尾元素入s1
s1.push(x);
//将s2的所有元素依次出栈再入栈s1
while(! s2.isEmpty()){
s1.push(s2.pop());
}
}
}
public int pop(){
return s1.pop();
}
public int peek(){
return s1.peek();
}
public boolean empty(){
return s1.isEmpty();
}
}
(2)运行截图:
6.一个队列实现栈结构
package stack_queue.leetcode;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
//一个队列实现栈结构
public class MyStackByOneQueue {
public Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStackByOneQueue(){
queue=new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x){
//获取当前队列元素个数
int n=queue.size();
//1.先入队
queue.add(x);
//2.3将前n个元素依次出队再入队
for (int i = 0; i <n ; i++) {
queue.add(queue.poll());
}
}
public int pop(){
return queue.poll();
}
public int top(){
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty(){
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
























 1306
1306

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










