一、playbook
playbook是剧本的意思
通过 task 调用 ansible 的模块将多个 play 组织在一 个playbook中运行。
playbook本身由以下各部分组成:
- Tasks: 任务,即调用模块完成的某操作
- Variables: 变量
- Templates: 模板
- Handlers: 处理器,当某条件满足时,触发执行的操作
- Roles: 角色
1、yaml基本语法规则
1、大小写敏感
2、使用缩进表示层级关系
3、缩进时不允许使用tab键、只允许使用空格
4、缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
2、yaml支持的数据结构
1、对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/ 哈希(hashes)/ 字典(dictionary)
2、数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence)/ 列表(list)
3、纯量:单个的、不可再分的值
二、Inventory中变量
1)主机变量
[webserver]
www1.xxxxxxx.com http_port=80 maxRequestsChild=808
www2.xxxxxxx.com http_port=8080 maxRequestsChild=909
2)组变量
[servers:vars]
ntp_server=ntp.xxxxxx.com
nfs_server=nfs.xxxxxx.com
3)组嵌套
[apache]
http1.xxxxxxx.com
http2.xxxxxxx.com
[nginx]
ngx1.xxxxxxx.com
ngx2.xxxxxxx.com
[webservers:children]
apache
nginx
4)inventory变量参数
参数 说明
ansible_ssh_host 将要连接的远程主机名,与你想要设定的主机的别名不同的话,可通过此变量设置
ansible_ssh_port ssh端口号,如果不是默认的端口号,通过此变量设置
ansible_ssh_user 默认的ssh用户名
ansible_ssh_pass ssh密码(这种方式并不安全,强烈建议使用--ask-pass或SSH密钥)
ansible_ssh_private_key_file ssh使用的私钥文件,适用于有多个密钥,而你不想用SSH代理的情况
ansible_ssh_common_args 此设置附加到sftp,scp和ssh默认命令行
ansible_sftp_extra_args 此设置附加到默认sftp命令行
ansible_scp_extra_args 此设置附加到默认scp命令行
ansible_ssh_extra_args 此设置附加到默认ssh命令行
ansible_ssh_pipelining 确定是否使用SSH管道,可以覆盖ansible.cfg中的设置
ansible_shell_type 目标系统的shell类型,默认情况下,命令的执行使用”sh“语法,可设置为”csh“或”fish“
ansible_python_interpreter 目标主机的python路径,适用于的情况系统中有多个 Python, 或者命令路径不是"/usr/bin/python
ansible_*_interpreter 这里的*可以是ruby或Perl或者其他语言的解释器,作用和ansible_python_interpreter类似
ansible_shell_executable 将设置ansible控制器将在目标机器上使用的shell,覆盖ansible.cfg中的默认为/bin/sh
三、playbooks事例
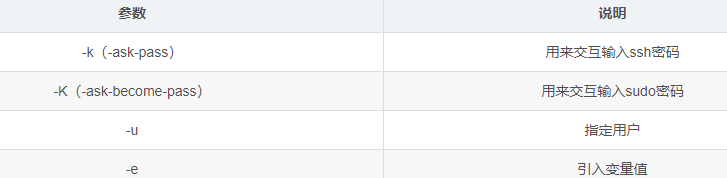
ansible-playbook xxx.yaml --syntax-check #检查yaml文件的语法是否正确
ansible-playbook xxx.yaml --list-task #检查tasks任务
ansible-playbook xxx.yaml --list-hosts #检查生效的主机
ansible-playbook xxx.yaml --start-at-task='xxx' #指定从某个task开始运行
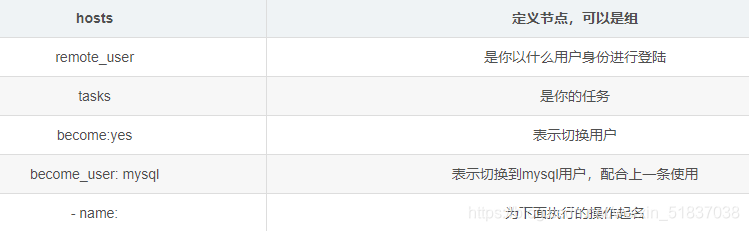
- hosts: webserver #指定主机组,可以是一个或多个组
remote_user: root #指定远程主机执行的用户名
1、为每个任务定义远程执行用户
cd /opt
vim 1.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
remote_user: mysql
ansible mysql -m user -a 'name=mysql'
ansible mysql -m shell -a 'echo 123123 | passwd --stdin mysql'
ansible-playbook 1.yaml -k
123123
2、指定远程主机切换用户执行剧本
vim 2.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
become: yes
become_user: mysql
tasks:
- name: copy text
copy: src=/etc/fstab dest=/home/mysql/fstab.bak
ansible-playbook 2.yaml
3、tasks忽略错误
错误示例:遇到错误task自动停止,apache服务不会继续安装
vim 3.yaml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: stop selinux
command: '/usr/sbin/setenforc 0'
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
ansible-playbook 3.yaml
加入ignore_errors: True 忽略错误,报错后继续执行
vim 3.yaml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: stop selinux
command: '/usr/sbin/setenforc 0'
ignore_errors: True
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
ansible-playbook 3.yaml
4、针对多个主机节点执行剧本
vim 4.yaml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: remove httpd
yum: name=httpd state=absent
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: src=/etc/fstab dest=/opt/haha.txt
5、Handlers概述
Handlers也是一些task的列表, 和一般的task并没有什么区别。
是由通知者进行的notify,如果没有被notify,则Handlers不会执行,假如被notify了 ,则Handlers被执行不管有多少个通知者进行了notify,等到play中的所有task执行完成之后,handlers也只会被执行一次
vim 5.yaml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: remove httpd
yum: name=httpd state=absent
- name: start firewalld
service: name=firewalld state=started
- name: setenforce 0 && install httpd
command: '/usr/sbin/setenforce 0'
notify:
- step one
- name: stop firewalld && start httpd
service: name=firewalld state=stopped
notify:
- step two
handlers:
- name: step one
yum: name=httpd
- name: step two
service: name=httpd state=started
ansible-playbook 5.yaml
6、变量
playbook引入变量有三种方式
1、通过ansible命令参数-e传递
2、直接在yaml中定义
3、引用主机清单中定义的变量
1、通过ansible命令参数-e传递
vim 6_1.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
vars:
- user:
tasks:
- name: add user
user: name={{user}}
ansible-playbook 6_1.yaml -e "user=wangwu"
ansible mysql -a 'tail -1 /etc/passwd'
2、直接在yaml中定义,或者内置变量
vim 6_2.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
vars:
- user: lisi
tasks:
- name: add user
user: name={{user}}
ansible-playbook 6_2.yaml
ansible mysql -a 'tail -1 /etc/passwd'
vim 6_2.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: content="{{ansible_all_ipv4_addresses}}" dest=/opt/vars.txt
ansible-playbook 6_2.yaml
ansible mysql -a 'ls /opt'
ansible mysql -a 'cat /opt/vars.txt'
3、引用主机清单内自定义变量
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
192.168.184.20
[mysql]
192.168.184.30 user=zhaoliu
vim 6_3.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add user
user: name={{user}}
ansible-playbook 6_3.yaml
ansible mysql -a 'tail -1 /etc/passwd'
7、条件测试
1、单条件判断
vim 7_1.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "shutdown CentOS"
command: /sbin/shutdown -h now
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
ansible-playbook 7_1.yaml
2、多条件判断
vim 7_2.yaml
- hosts: mysql
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "shut down CentOS 7 systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -r now
when:
- ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
ansible-playbook 7_2.yaml
4、迭代
vim 7_5.yaml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install
yum: name={{item}} state=latest
with_items:
- httpd
- rpcbind
- nfs-utils
ansible-playbook 7_5.yaml
ansible webserver -a 'rpm -q httpd'
ansible webserver -a 'rpm -q rpcbind'
ansible webserver -a 'rpm -q nfs-utils'
也可以自己定义item变量
vim 7_5.yaml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add user && join group
user: name={{item.x}} state=present group={{item.y}}
with_items:
- {x: 'qianqi', y: 'wheel'}
- {x: 'sicong', y: 'root'}
ansible-playbook 7_5.yaml
ansible webserver -a 'tail -2 /etc/passwd'







 本文介绍Ansible Playbook的基本概念及使用方法,包括Playbook结构、Inventory变量配置、实际案例演示等内容,帮助读者掌握Ansible自动化运维的核心技能。
本文介绍Ansible Playbook的基本概念及使用方法,包括Playbook结构、Inventory变量配置、实际案例演示等内容,帮助读者掌握Ansible自动化运维的核心技能。
















 1535
1535

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








