目录
Javase学习路线

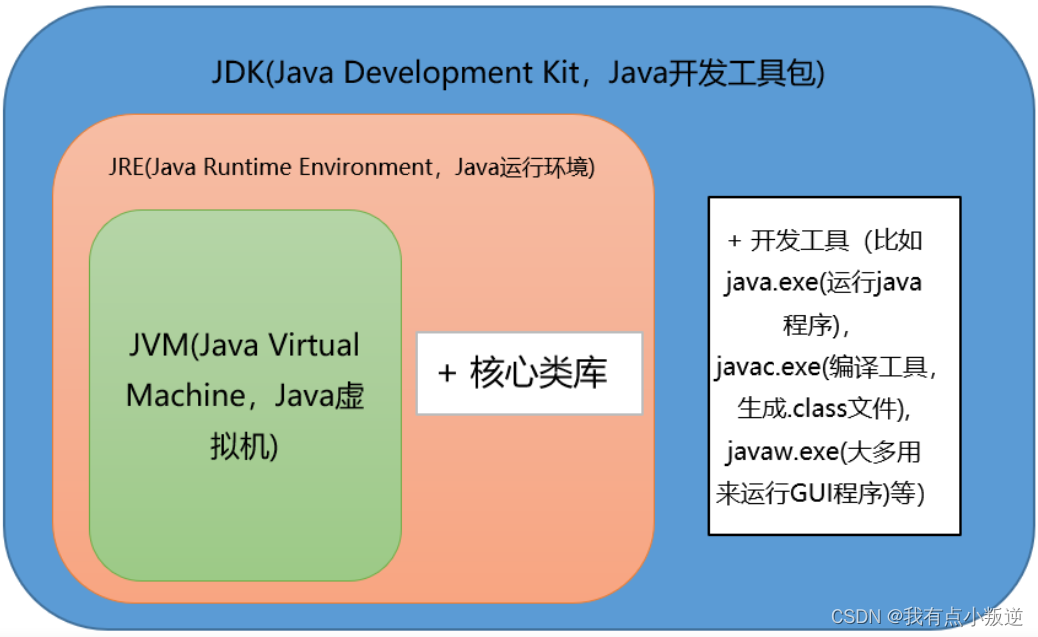
JVM、JRE、JDK的关系
- JVM java Virtual Machine是Java虚拟机,Java程序需要运行在虚拟机上,不同的平台有自己的虚拟机,因此Java语言可以实现跨平台。
- JRE Java Runtime Environment包括Java虚拟机和Java程序所需的核心类库等。核心类库主要是java.lang包:包含了运行Java程序必不可少的系统类,如基本数据类型、基本数学函数、字符串处理、线程、异常处理类等,系统缺省加载这个包。如果想要运行一个开发好的Java程序,计算机中只需要安装JRE即可。
- JDK Java Development Kit是提供给Java开发人员使用的,其中包含了Java的开发工具,也包括了JRE。所以安装了JDK,就无需再单独安装JRE了。其中的开发工具:编译工具(javac.exe),打包工具(jar.exe)等
数据类型
八种基本数据类型
基本数据类型:内存区域中保存的是数据本身

自动类型转换
基本数据的自动类型转换只有7种数据类型,除了布尔型
基本原则:低级别可以转高级别
从左向右可以依次转换:byte-short-int-long-float-double
char-int-long-float-double
运算时的自动转换条件:两种数据类型要兼容,目标类型大于原类型
当范围大的类型与范围小的类型进行运算时,结果会自动转成范围大的类型
强制类型转换
高级别转低级别时必须进行强制类型转换
是否进行强制类型转换取决于数据类型级别的高低,而不取决于数据类型的实际值
格式:(type)value, type是要强制类型转换后的数据类型
public class mainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 3;
long y = 2;
int num = (int) ((x-1)*y);// 强制类型转换,long类型转换为int类型
System.out.println(num);
int test = (int)(x-1)*y;
System.out.println(test);
}
}
引用数据类型
引用数据类型:内存区域中保存的是别的数据的地址.
String
运算符
算数运算符
算术运算符:+ , - , * , / , % , ++ , –
关系运算符
逻辑运算符

赋值运算符

三目运算符
boolean?语句块1:语句块2
执行规则: Boolean值为true 则执行 语句块1;
Boolean值为false 则执行 语句块2;
字符串连接运算符
字符串连接用 + 来实现,“ + ”是算术运算符又是字符串拼接运算符,即 若同时出现则字符串连接前的运算符为算术运算符,字符串连接后的都为字符串连接运算符
流程控制函数
分支结构
//结构1
public class IfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
// 定义两个变量
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
if (a == b) {
System.out.println("a等于b");
}
int c = 10;
if (a == c) {
System.out.println("a等于c");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
}
//结构2
public class IfDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
// 判断给定的数据是奇数还是偶数
// 定义变量
int a = 100;
// 给a重新赋值
a = 99;
if (a % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("a是偶数");
} else {
System.out.println("a是奇数");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
}
//结构三
public class IfDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x和y的关系满足如下:
// x>=3 y = 2x + 1;
// -1<=x<3 y = 2x;
// x<=-1 y = 2x – 1;
// 根据给定的x的值,计算出y的值并输出。
// 定义变量
int x = 5;
/*
int y;
if (x >= 3) {
y = 2 * x + 1;
} else if (x >= -1 && x < 3) {
y = 2 * x;
} else if (x <= -1) {
y = 2 * x - 1;
}else {
y = 0;
}
*/
int y = 0;
if (x >= 3) {
y = 2 * x + 1;
} else if (x >= -1 && x < 3) {
y = 2 * x;
} else if (x <= -1) {
y = 2 * x - 1;
} else{
y = 10;
}
System.out.println("y的值是:"+y);
}
}
//结构4
public class SwitchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建键盘录入对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//接收数据
System.out.println("请输入一个数字(1-7):");
int weekday = sc.nextInt();
//switch语句实现选择
switch(weekday) {
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你输入的数字有误");
break;
}
}
}
循环结构
for循环结构
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//原始写法
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//用循环改进
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
}
}
foreach循环结构
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for ( int x : numbers ) {
System.out.print( x );
System.out.print(",");
}
System.out.print();
String [] names = {"James", "Larry", "Tom", "Lacy"};
for ( String name : names ) {
System.out.print( name );
System.out.print(",");
}
}
}
while循环结构
public class WhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//输出10次HelloWorld
/*
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) {
System.out.println("HellloWorld");
}
*/
//while循环实现
int x=1;
while(x<=10) {
System.out.println("HellloWorld");
x++;
}
}
}
do while循环结构
public class DoWhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//输出10次 HelloWorld
/*
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
*/
//do...while改写
int x=1;
do {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
x++;
}while(x<=10);
}
}
跳转语句(break、continue、return)
/*
* break:中断的意思
* 使用场景:
* A:switch语句中
* B:循环中
* 注意:
* 离开使用场景是没有意义的。
* 作用:
* 跳出循环,让循环提前结束
*/
public class BreakDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//break;
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) {
if(x == 3) {
break;
}
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
}
}
/*
* continue:继续的意思
* 使用场景:
* 循环中
* 注意:
* 离开使用场景是没有意义的
* 作用:
* 结束一次循环,继续下一次的循环
* 区别:
* break:退出循环
* continue:结束一次循环,继续下一次的循环
*/
public class ContinueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//continue;
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) {
if(x == 3) {
//break;
continue;
}
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
}
}
public class ReturnDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getStr();
}
public String getStr() {
return "Hello";
}
}
























 5285
5285

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








