链式存储的线性单链表
本篇博客部分图片来自《黑马程序员数据结构资料》,如有侵权,请联系我。
本章常做面试题注意!
链式存储的线性单链表:
单链表
单向链表是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和一个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据, 指针域用来指向其后继结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
1. 带头结点的单项不循环链表
详细解释请看代码,代码里有详细的解释。
头指针必须指向头结点(进行删减操作时都需要知道待插入结点的前驱)

空表:不可或缺,next为空
1.1 结构体构建
typedef struct node_st
{
int data; //data存储数据
struct node_st *next;
}LIST;
1.2 链表的创建
LIST *list_create()
{
LIST *p;
p = malloc(sizeof(*p)); //申请一个LIST结构体类型的空间
if(p == NULL)
return NULL;
p->next = NULL; //先将头节点的下一个结点置位空,就是第一个有效结点
return p; //创建成功返回节点
}
/*第二种创建方法*/
void list_create1(LIST **p) //通过二级指针回填
{
*p = malloc(sizeof(**p));
if(*p == NULL)
return ;
(*p)->next = NULL;
return ;
}
1.3 链表的插入(按位置、值插入)
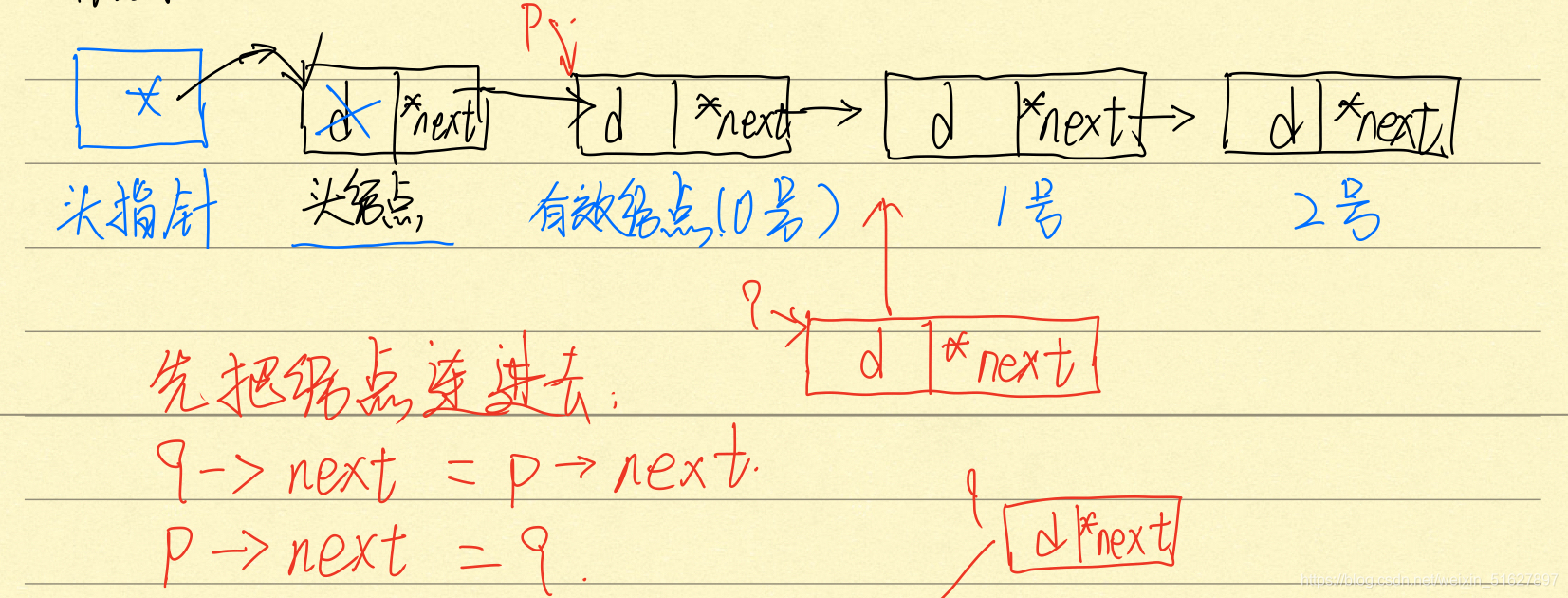
按位置插入:
先寻找到要插入的位置(pos),并且更新p指针的指向,p的后继最终指向待插入结点。
int list_insert(LIST *ptr,int pos, int *newdata)
{
int i = 0;
LIST *p = ptr,*q; //LIST类型的指针p指向头节点
while(i < pos && p ) //从头开始寻找那个位置
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if(p) //只要待插入结点的前驱不为空,就插入
{
q = malloc(sizeof(*q)); //q为新插入的结点,现申请空间。
if(q == NULL)
return -1;
q->data = *newdata; //把我要插入的值插到q结点中
q->next = p->next; //先找到待插入结点的前驱,让待插入的后继指向待插入节点前驱的后继
p->next = q; //让
return 0;
} //p == NULL
else
return -2;
}
按值插入:
int list_insert_value(LIST *ptr,int *newdata)
{// -> - 2 4 6 8 *newdata = 5;
/* p->-
while(2<5) p->2
while(4<5) p->4
while(6<5) -----
*/
LIST *p = ptr,*q;
//只要头结点的后继不为空或者待插入的值小的话就开始插入
while(p->next && p->next->data < *newdata)
p = p->next;
//如结点的数据大于要插入节点的数据,就申请一个结点
q = malloc(sizeof(*q));
if(q == NULL)
return -1;
q->data = *newdata; //把要插入的数据插入到结点中
q->next = p->next; //先找到待插入结点的前驱,让待插入的后继指向待插入节点前驱的后继
p->next = q;
return 0;
}
1.4 链表数据查找
int list_find(LIST *ptr,int *data)
{
LIST *p = ptr->next; //p指向第一个有效结点
if(list_isempty(p))
return -1;
while(p) //只要结点不为空,就开始查找
{
if(p->data == *data) //找到数据了,返回0;
return 0;
p = p->next; //如果没找到,更新p指针的指向,p指向p的后继
}
return -2;
}
1.4 链表数据删除(按位置、值删除)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-emEOm6Ip-1628834159065)(D:\QQ\消息数据\1010122334\FileRecv\MobileFile\IMG_1202(20210802-203424)].PNG)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/3b49ba480b7190055b3793b9783eb084.jpeg)
按位置删除:
先找到待删除结点,让待删除节点前驱的后继指针指向待删除结点后继的指针所指向的结点.
int list_delete(LIST *ptr,int pos, int *newdata)
{// -> - 3 4 5 6; pos = 2
/* i = 0;p-> -
while(0<2 && p) p->3;i=1
while(1<2&&p ) p->4;i=2
while(2<2&&p )
*/
int i = 0;
LIST *p = ptr,*q;
if(list_isempty(ptr))
return -2;
while(i < pos && p ){ //先找到待删除结点的前驱
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if(p) //如果前驱存在开始删除
{
q = p->next; //q用来记录待删除结点的后继
p->next = q->next;//待删除节点前驱的后继指针指向待删除结点next所指向的结点
if(newdata != NULL)
*newdata = q->data;
free(q); //释放已经删除的结点
q = NULL;
return 0;
}
else // p == NULL
return -1;
}
按值删除:
先按值找到待删除结点,让待删除节点前驱的后继指针指向待删除结点后继的指针所指向的结点.
int list_delete_value(LIST *ptr,int *newdata)
{// -> - 2 4 6 8 *newdata = 6;
LIST *p = ptr,*q;
if(list_isempty(ptr))
return -2;
while(p->next && p->next->data != *newdata)
p = p->next;
if(p->next == NULL)
return -1;
else
{
q = p->next; //q用来记录待删除结点的后继
p->next = q->next; //待删除节点前驱的后继指针指向待删除结点后继的指针所指向的结点
free(q); //释放已经删除的结点
q = NULL;
return 0;
}
}
1.5 链表的遍历、打印
void list_display(LIST *ptr)
{
LIST *p = ptr->next;
if(list_isempty(p))
return ;
while(p)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
1.6 销毁_list_destroy
void list_destroy(LIST *ptr)
{
LIST *p = ptr->next,*q;
if(list_isempty(p))
return ;
while(p)
{
q = p->next; //q用来记录当前节点的后继
free(p); //销毁当前结点
p = q; //让p指向销毁当前结点的下一个结点
}
free(ptr); //最后释放头结点
}
1.7 主函数main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
int main()
{
LIST *handler;
int a[] = {4,8,3,9,2};
int i;
// handler = list_create();
list_create1(&handler); //创建链表
if(handler == NULL)
{
printf("list_create() error.\n");
exit(1);
}
for(i = 0 ; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a); i++)
// list_insert(handler, 0, &a[i]);
list_insert_value(handler,&a[i]);
list_display(handler); //显示打印
int tmp = 18;
list_delete_value(handler,&tmp);
list_display(handler);
/*
list_insert(handler,15,&tmp);
list_display(handler);
*/
// list_delete(handler,14,NULL);
// printf("FIND:%d\n",list_find(handler,&tmp));
// list_display(handler);
list_destroy(handler);
exit(0);
}
2. 无头结点的单向不循环链表
无头结点的链表就不需要单独给头结点申请空间(creat)了,而且函数需要传入二级指针
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-MzgeMcYS-1628834159067)(D:\QQ\消息数据\1010122334\FileRecv\MobileFile\IMG_1200(20210802-202959)].PNG)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/c41a95e44b88240e47fe12b70e67ef62.jpeg)
创建一个链表,实现第0个位置的插入和第n个位置的删除
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define NAMESIZE 32
typedef struct student
{
int math;
struct student *next;
}LIST;
//实现第0个位置的插入
int list_insert(LIST **ptr,int *newdata)
{
LIST *new; //这里的new就是第一个有效结点
new = malloc(sizeof(*new));
if(new == NULL)
return -1;
new->math = *newdata; //给要插入的结构体赋值
new->next = *ptr; //当前结点的next指针指向头指针
*ptr = new; //更新头指针的指向
return 0;
}
//实现第0个位置的删除和多个位置的删除
int list_delete(LIST **ptr,int pos)
{
LIST *new=*ptr,*q;
int i=0;
if(pos == 0) //实现第0个位置的删除
{
*ptr = new->next;
free(new);
}
else
{
while(i<pos-1 && new) //-1因为没有头节点,少指向一次
{
new = new->next;
i++;
}
if(new)
{
q = new->next;
new->next = q->next;
free(q);
q = NULL;
return 0;
}
}
}
void list_display(LIST *ptr)
{
int i;
LIST *p = ptr;
while(p)
{
printf("%d ",p->math);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
LIST *handler = NULL;
int a[] = {7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
int i,num=3;
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
list_insert(&handler,&a[i]); //开始循环插入7,6,5,4,3,2,1
}
list_display(handler); //1,2,3,4,5,6,7
list_delete(&handler,num);
list_display(handler);
exit(0);
}
3.无头结点单项循环链表-约瑟夫问题
3.1 循环链表
循环链表,顾名思义,链表整体要形成一个圆环状。在单向链表中,最后一个节点的指针为null,不指向任何结 点,因为没有下一个元素了。要实现循环链表,我们只需要让单向链表的最后一个节点的指针指向头结点即可。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LLF0D074-1628834159068)(C:\Users\10101\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210813134001966.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/ad4d89c3b49e4bb177f0108a7c199993.png)
问题描述:
-
编号为1的人开始从1报数,依次向后,报数为3的那个人退出圈;
-
自退出那个人开始的下一个人再次从1开始报数,以此类推;
-
求出最后退出的那个人的编号。
3.2 单向循环链表的构建
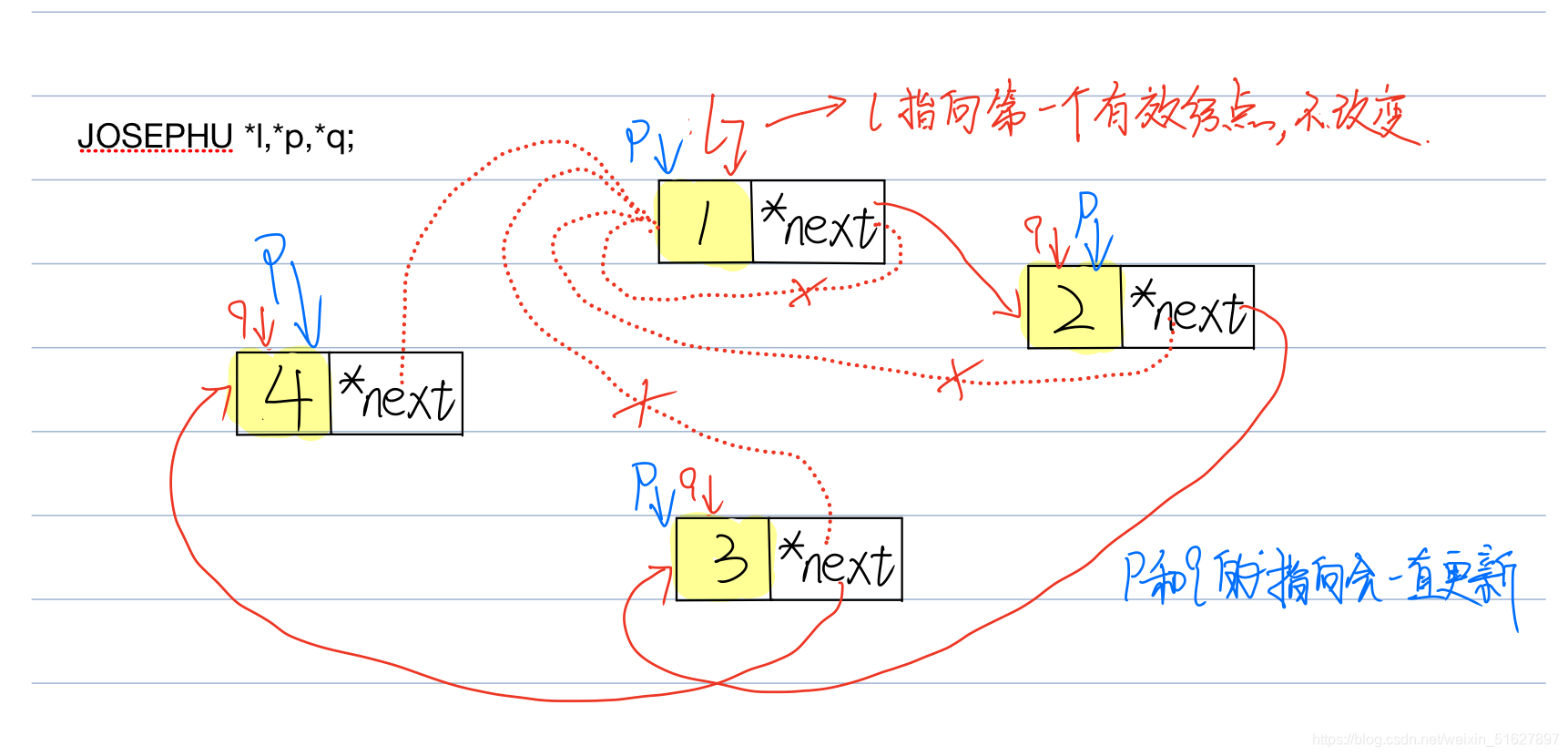
typedef struct node_st
{
int data; //用来存储数据
struct node_st *next;
}JOSEPHU;
JOSEPHU *josephu_create(int n)
{
JOSEPHU *l,*p,*q;
int i = 1;
l = malloc(sizeof(*l)); //给第一个有效结点申请空间
if(l == NULL)
return NULL;
l->data = i; //第一个数据 = 1
l->next = l; //第一个结点的指针指向当前结点
p = l; //p是来记录
i++; //i = 2
while(i <= n)
{
q = malloc(sizeof(*q));
if(q == NULL)
return NULL;
q->data = i;
i++;
q->next = l;
p->next = q;
p = q;
}
return l;
}
3.3 约瑟夫kill程序
注意:要杀的话需要获取待杀死结点的前驱,我们这里用temp来保存待杀死结点的前驱指针
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Rreq2eN0-1628840689335)(E:\笔记 + 资料\02.数据结构笔记\图片\IMG_1247(20210813-154250)].PNG)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/b47095642a9b03c51658483379b1e2f9.jpeg)
void list_delete(LIST **l,int n)
{
//1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
/*
while(1<3) q->1;p->2;i=2;
while(2<3) q->2;p->3;i=3;
while(3<3) -----
*/
LIST *p = *l,*temp; //*temp主要是为了用来存放代删除元素的前驱;
int i=1;
printf("KILL:");
while(p->next != p) //结束条件:当前结点的指针指向自身
{
while(i<n) //每三个杀死一个
{
temp = p;
p = p->next;
i++;
}
//开始杀
temp->next = p->next;
printf("%d ",p->data);
free(p);
i=1;
p = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
*l = p;
}
3.4 单项循环链表的打印
void list_display(LIST *ptr)
{
LIST *p = ptr;
while(p->next != ptr)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("%d\n",p->data);
}
3.5 主函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int i;
LIST *handler;
int num = 8;
int count = 3;
handler = list_insert(num);
list_display(handler);
list_delete(&handler,count);
list_display(handler);
printf("\n");
}
4.链表实现两个多项式合并
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-NHFeQGTC-1628834159070)(D:\QQ\消息数据\1010122334\FileRecv\MobileFile\IMG_1204(20210803-210517)].PNG)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/2d8d89fd8e5d42fbdc6c2c13558d960b.jpeg)
代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node_st
{
int coef;
int exp;
struct node_st *next;
}POLY;
POLY *poly_create(int (*a)[2],int m)
{
POLY *head,*p,*q;
int i;
head = malloc(sizeof(*head));
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
head->next = NULL;
p = head;
for(i = 0 ; i < m ; i++)
{
q = malloc(sizeof(*q));
if(q == NULL)
return NULL;
q->coef = a[i][0];
q->exp = a[i][1];
q->next = NULL;
p->next = q;
p = q;
}
return head;
}
void poly_display(POLY *head)
{
POLY *cur = head->next;
while(cur)
{
printf("(%d,%d) ",cur->coef,cur->exp);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void poly_add(POLY *p1,POLY *p2)
{
POLY *p = p1->next;
POLY *q = p2->next;
POLY *r = p1;
while(p && q)
{
if(p->exp < q->exp)
{
r->next = p;
r = p;
p = p->next;
}
else
{
if(p->exp > q->exp)
{
r->next = q;
r = q;
q = q->next;
}
else // p->exp == q->exp
{
p->coef += q->coef;
if(p->coef)
{
r->next = p;
r = p;
}
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
}
if(p == NULL)
r->next = q;
else
r->next = p;
}
int main()
{
int a[][2] = {{5,0},{2,1},{8,8},{-34,16}};
int b[][2] = {{6,1},{7,6},{-8,8}};
POLY *p1,*p2;
p1 = poly_create(a,4);
poly_display(p1);
p2 = poly_create(b,3);
poly_display(p2);
poly_add(p1,p2);
poly_display(p1);
exit(0);
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








