


1.
package celue;
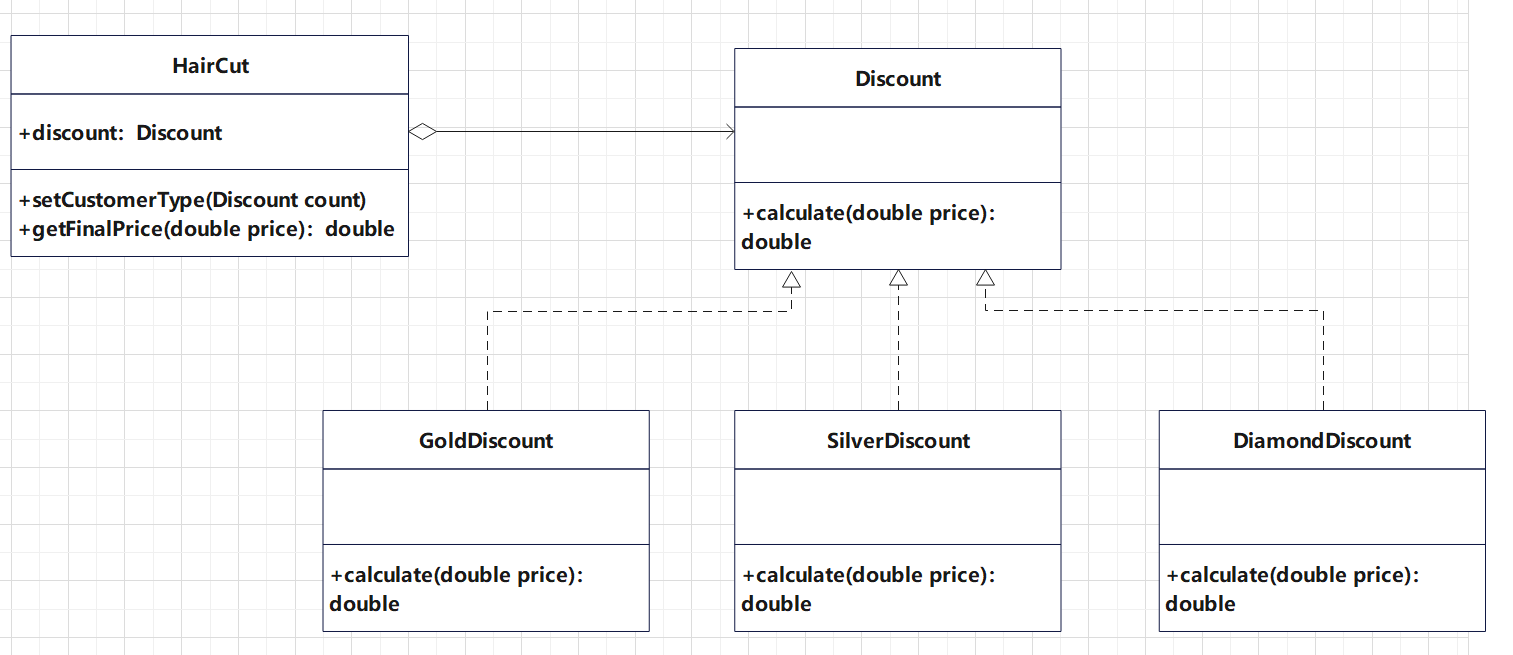
class HairCut {
private Discount discount;
// 设置客户类型
public void setCustomerType(Discount count) {
discount = count;
}
// 计算折后价
public double getFinalPrice(double price) {
return discount.calculate(price);
}
}
package celue;
// 折扣接口
interface Discount {
double calculate(double price);
}
package celue;
// 金卡客户6折优惠
class GoldDiscount implements Discount {
public double calculate(double price) {
return price * 0.6;
}
}
package celue;
// 钻石卡客户5折优惠
class DiamondDiscount implements Discount {
public double calculate(double price) {
return price * 0.5;
}
}
package celue;
// 银卡客户7.5折优惠
class SilverDiscount implements Discount {
public double calculate(double price) {
return price * 0.75;
}
}
package celue;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HairCut hairCut = new HairCut();
// 读取配置文件获取客户类型
Object customerType ;
customerType=XMLUtil.getBean("GoldDiscount");
hairCut.setCustomerType((Discount) customerType);
double originalPrice = 100.0; // 原价
double finalPrice = hairCut.getFinalPrice(originalPrice); // 折后价
System.out.println("Original price: " + originalPrice);
System.out.printf("Discounted price for %s customer: %.2f", customerType, finalPrice);
}
}
策略模式是一种行为型模式,它定义了一系列算法(策略),并将每个算法封装起来,使它们可以相互替换,而且替换过程可以在不改变调用它们的客户端代码的情况下进行。策略模式的优点包括:
易于扩展和维护:添加新的算法或修改现有的算法时,只需要编写新的策略类或修改已有的策略类即可,不会影响到其他代码。
避免使用大量的条件语句:通过将具体的算法封装成策略类,避免了 if-else 或 switch-case 等复杂的条件语句,使得代码更加简洁、易读、易于维护。
可以提高代码的复用性:策略类可以被客户端程序复用,或者在多个项目中共享,从而减少代码重复。







 文章通过一个Java代码示例展示了如何使用策略模式来处理不同类型的折扣算法,如金卡、钻石卡和银卡客户的不同折扣。策略模式允许在运行时动态选择不同的算法,提高了代码的可维护性和扩展性,避免了大量条件语句的使用。
文章通过一个Java代码示例展示了如何使用策略模式来处理不同类型的折扣算法,如金卡、钻石卡和银卡客户的不同折扣。策略模式允许在运行时动态选择不同的算法,提高了代码的可维护性和扩展性,避免了大量条件语句的使用。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










