前面使用了第一种的三个方法,1、<h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2> 2、...mapState(['count']) 3、...mapState({a:'count' }),这是设置别名,后两种使用计算属性,前面的直接使用标签调用state。
后续补充
mutations部分
mutations使用来改变state数据的,相当于使用页面的methods方法。
1.2.在页面中如果要操作页面上的mutations里面的方法,就要用到$store下的commit方法
<template>
<div>
<h2>home</h2>
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法2 -->
<!-- <h2>{{count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法3 -->
<h2>{{a}}</h2>
<button @click="handelClick">增加+1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 可以借助辅助函数
import {mapState} from'vuex'//要加上大括号
export default {
name:'HomeView',
mounted(){
console.log(this)
console.log(this.$store)
},
computed:{
//...mapState(['count'])//方法2 不管传多少数据都会通过mapState来进行接受,还要加上三点--数组写法
...mapState({
a:'count'//方法三,注意count要加上引号,若a命名为count不能使用同名省略的方法,因为有引号
})
},
methods:{
handelClick(){
// this.a++
//直接按照原来的写法是错误的,缺少setter,只能在store文件中的mutations中改变对state进行改变
//store里index.js中的mutations设置方法后要传到这里---mutations方法一
this.$store.commit('add')//this.$store中有commit,可以用来解决mutations的问题
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count:4
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
add(state){
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
实现了点击加一的操作。
mutations中方法内有连个参数,第一个state是必须的,第二个是载荷preload
所以mutations中的方法相当于派发给handelClick来执行。来触发add方法
2.辅助函数使用
store问价夹内的index不用变化,点击的标签需要更改。
<template>
<div>
<h2>home</h2>
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法2 -->
<!-- <h2>{{count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法3 -->
<h2>{{a}}</h2>
<!-- <button @click="handelClick">增加+1</button>方法一 -->
<button @click="add">增加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 可以借助辅助函数
import {mapState,mapMutations} from'vuex'//要加上大括号
export default {
name:'HomeView',
mounted(){
console.log(this)
console.log(this.$store)
},
computed:{
//...mapState(['count'])//方法2 不管传多少数据都会通过mapState来进行接受,还要加上三点--数组写法
...mapState({
a:'count'//方法三,注意count要加上引号,若a命名为count不能使用同名省略的方法,因为有引号
})
},
methods:{
// handelClick(){
// // this.a++
// //直接按照原来的写法是错误的,缺少setter,只能在store文件中的mutations中改变对state进行改变
// //store里index.js中的mutations设置方法后要传到这里---mutations方法一
// //this.$store.commit('add')//this.$store中有commit,可以用来解决mutations的问题
// },
//方法二,使用辅助函数,引入
...mapMutations(['add'])
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
3.另一种辅助函数的用法
按钮点击事件名称改为对象中的别名
<template>
<div>
<h2>home</h2>
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法2 -->
<!-- <h2>{{count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法3 -->
<h2>{{a}}</h2>
<!-- <button @click="handelClick">增加+1</button>方法一 -->
<!-- <button @click="add">增加</button>方法二 -->
<button @click="aaa">增加</button>方法三
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 可以借助辅助函数
import {mapState,mapMutations} from'vuex'//要加上大括号
export default {
name:'HomeView',
mounted(){
console.log(this)
console.log(this.$store)
},
computed:{
//...mapState(['count'])//方法2 不管传多少数据都会通过mapState来进行接受,还要加上三点--数组写法
...mapState({
a:'count'//方法三,注意count要加上引号,若a命名为count不能使用同名省略的方法,因为有引号
})
},
methods:{
// handelClick(){
// // this.a++
// //直接按照原来的写法是错误的,缺少setter,只能在store文件中的mutations中改变对state进行改变
// //store里index.js中的mutations设置方法后要传到这里---mutations方法一
// //this.$store.commit('add')//this.$store中有commit,可以用来解决mutations的问题
// },
//方法二,使用辅助函数,引入
// ...mapMutations(['add'])
//方法三
...mapMutations({
aaa:'add'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
复杂数据操作
显示:和简单数据一样{{$store.state.list}}
增加数据:传递复杂数据作为参数。
<template>
<div>
<h2>home</h2>
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <h2>{{$store.state.count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法2 -->
<!-- <h2>{{count}}</h2> -->
<!-- 方法3 -->
<h2>{{a}}</h2>
<!-- <button @click="handelClick">增加+1</button>方法一 -->
<!-- <button @click="add">增加</button>方法二 -->
<!-- <button @click="aaa">增加</button>方法三 -->
<!-- +5和+10 方法扩充-->
<button @click="add(5)">+5</button>
<button @click="add(10)">+10</button>
<!-- state中复杂数据的显示渲染 -->
<h3>{{$store.state.list}}</h3>
<button @click="sum">增加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 可以借助辅助函数
import {
mapState,
mapMutations
} from 'vuex' //要加上大括号
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
mounted() {
console.log(this)
console.log(this.$store)
},
computed: {
//...mapState(['count'])//方法2 不管传多少数据都会通过mapState来进行接受,还要加上三点--数组写法
...mapState({
a: 'count' //方法三,注意count要加上引号,若a命名为count不能使用同名省略的方法,因为有引号
})
},
data() {
return {
list2 : {
id: 4,
name: "商品四",
status: false
}
}
},
methods: {
//不传参的方法
// handelClick(){
// // this.a++
// //直接按照原来的写法是错误的,缺少setter,只能在store文件中的mutations中改变对state进行改变
// //store里index.js中的mutations设置方法后要传到这里---mutations方法一
// //this.$store.commit('add')//this.$store中有commit,可以用来解决mutations的问题
// },
//方法二,使用辅助函数,引入
// ...mapMutations(['add'])
//方法三
// ...mapMutations({
// aaa:'add'
// })
//方法扩充,传参
// add(n){//这个add是上面的点击事件
// this.$store.commit('add',n)//这里的add是store派发的add方法
// }
...mapMutations(['add']), //传参也不用在辅助函数中写这些参数
//传复杂数据的参数
// 1不适用辅助函数方法,暂时只使用这个
sum() {
this.$store.commit('sum', this.list2)
}
//第二种,辅助函数
//...mapMutations(['sum'])//这样直接传递是不行的结果:{ "isTrusted": true }
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 4,
list: [{
id: 1,
name: "商品一",
status: false
},
{
id: 2,
name: "商品二",
status: true
},
{
id: 3,
name: "商品三",
status: false
}
]
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
// add(state){
// state.count++
// }
add(state, n) { //n就是载荷
state.count += n
},
sum(state, preload) {
state.list.push(preload)
}
},
actions: {},
modules: {}
})
数据的筛选过滤使用getters
使用getters筛选数据,就和计算属性类似,所以,页面上在computed中运行
可以筛选更多的条件
还能进行传参,通过传递的参数可以更精确的筛选内容。
state: {
count: 4,
list: [{
id: 1,
name: "商品一",
status: false
},
{
id: 2,
name: "商品二",
status: true
},
{
id: 3,
name: "商品三",
status: false
}
]
},
getters: {
activeList : (state)=>{//同样第一个参数state必写,第二参数不是辟邪
return state.list.filter((v)=>{
return v.status
})
},
unactiveList:(state)=>{
return state.list.filter(v=>{
return !v.status
})
}
},
<template>
<div>
<!-- <h2 @click="about">about</h2>
app.count--{{num}} -->
<!-- getters过滤使用方法 方法一 -->
<!-- <h2>{{$store.getters.activeList}}</h2>
<h2>{{$store.getters.unactiveList}}</h2> -->
<!-- <h3>{{activeList}}</h3>方法二
<h3>{{unactiveList}}</h3> -->
<h3>{{a}}</h3>
<h3>{{b}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'AboutView',
inject:['app'],
methods:{
// about(){
// console.log(this.app.userid)
// this.app.changeapp()
// // console.log()
// }
},
computed: {//state和getters放在计算属性中
//方法二
//...mapGetters(['activeList','unactiveList'])
//方法三
...mapGetters({
a:'activeList',
b:'unactiveList
})
},
methods:{//mutations和action放在方法中
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
actions
处理异步的方法,暂时使用setInterval来代替模拟异步,每个一段时间执行一次
context,上下文环境,全局的运行环境
页面调用actions方法是可以使用dispatch,也能使用commit,但是actions中的方法还是只是用context.commit的方法来调用上面的mutations的方法
在使用Async类似方法中将context结构后使用,就不用context一直点了通过{comit}简单的事件,
结构后不用在通过context来获得commit
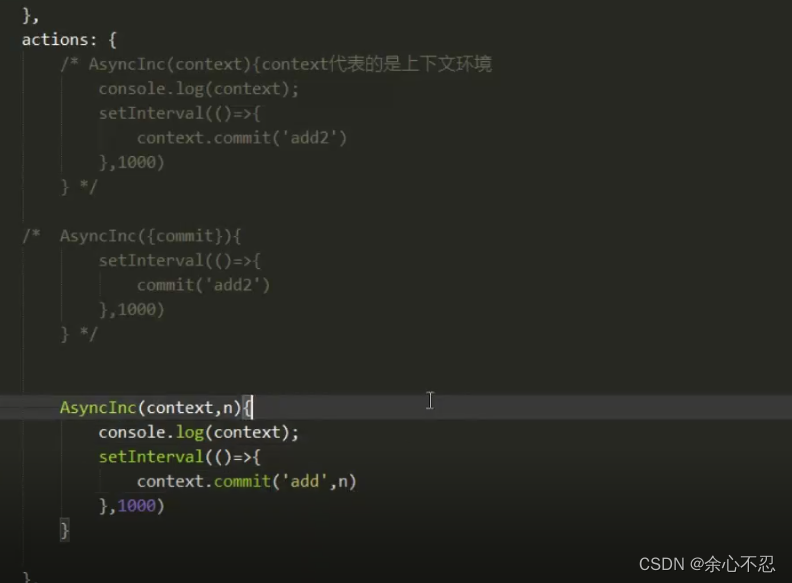
传参数与不传的区别在AsyncInc中第二个参数就是传递的参数。
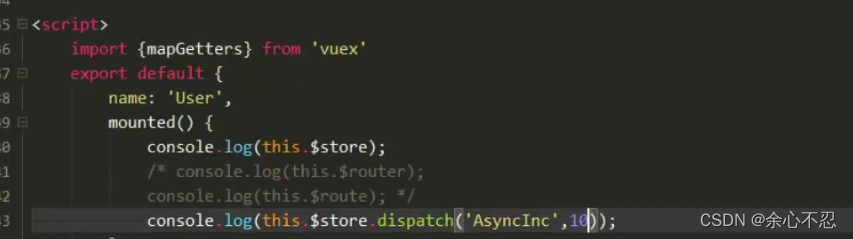
这里是调用了actions里的方法,并进行了传参,这里不用打印也可行
辅助函数方法
mutations和action放在方法中,使用辅助函数,需要在import中先加入后在直接使用,要在methods中使用
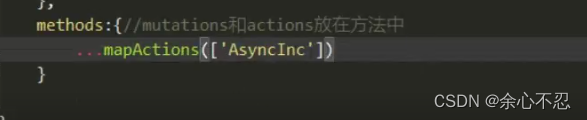
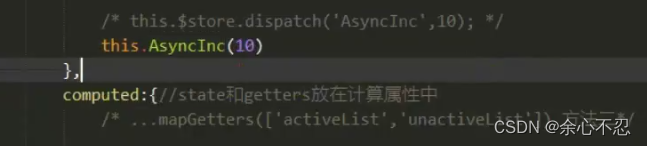
还需要在生命周期总调用,传参
modules模块
暂时一种方法
在store文件夹中设置一个modules文件夹,在之后创建一个js文件,对应文件夹对应不同的页面显示
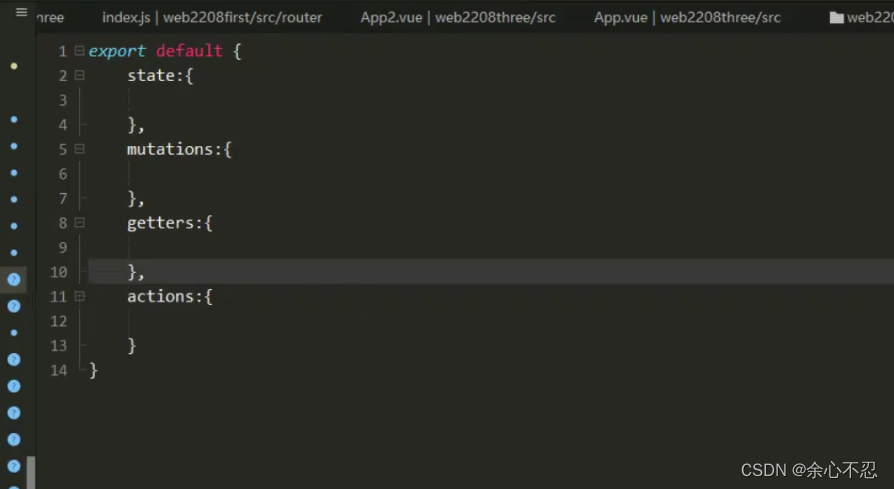
并在store中的index.js中引入该文件,可以将之前写的其他内容全部删除,指保留一个modules,里面是创建的文件引入的名字。
最后在export default store导出。
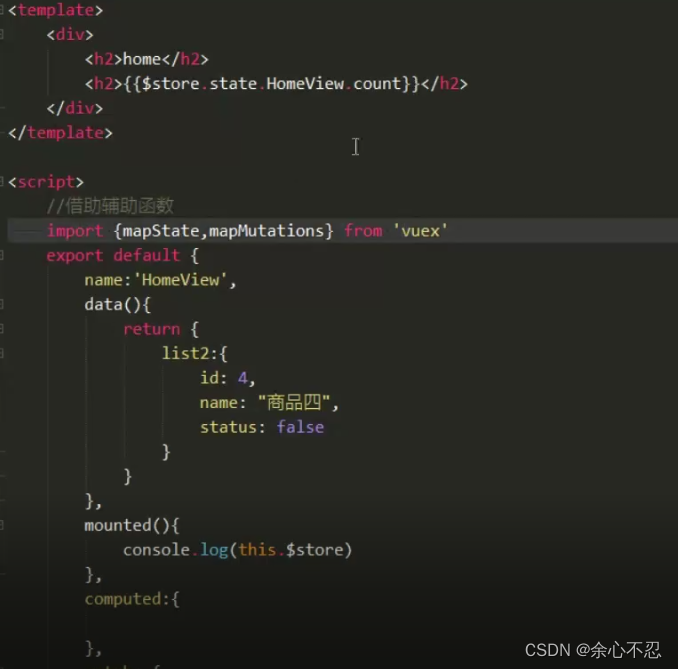
这个时候的调用就不能直接通过$store,还要加上Home View(文件名)。
辅助函数的写法同样改变,不能直接使用辅助函数的格式来调用
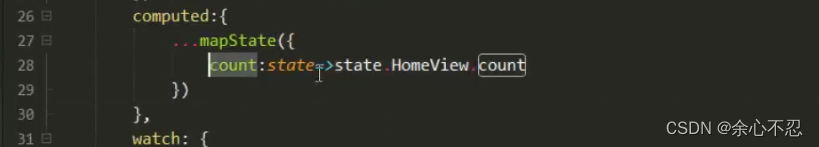
但是对于mutations和getters都不影响。




















 5626
5626


 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?







