事件驱动编程
ApplicationListener 是 Spring Framework 事件驱动编程模型的核心接口之一。它允许你的应用程序组件(监听器)对 Spring 容器中发生的特定事件做出反应,而无需与事件发布者紧密耦合。这是一种实现观察者模式或发布-订阅模式的优雅方式,有助于:
-
解耦: 事件发布者(通常是框架本身或你的业务组件)不需要知道有哪些监听器存在。监听器只关心自己感兴趣的事件。
-
可扩展性: 可以轻松地添加新的监听器来处理事件,而无需修改发布事件的代码。
-
内聚性: 将与特定事件相关的处理逻辑集中在一个地方(监听器中)。
-
框架集成: Spring 容器自身会发布多种内置事件(如
ContextRefreshedEvent,ContextStartedEvent等),你的应用可以方便地响应这些生命周期事件。
一、 ApplicationListener 接口
ApplicationListener 是一个泛型接口,定义在 org.springframework.context 包中:
package org.springframework.context;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
-
<E extends ApplicationEvent>: 这是一个泛型参数,指定了这个监听器感兴趣的事件类型。E必须是ApplicationEvent或其子类。 -
onApplicationEvent(E event): 这是接口中唯一的抽象方法。当 Spring 容器发布一个类型为E(或其子类型)的事件时,容器会自动调用所有注册的、监听该类型事件的ApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent方法,并将事件对象event传递给它。
二、ApplicationEvent:
所有 Spring 应用事件的基类。自定义事件通常直接或间接继承此类
三、ApplicationEventPublisher:
-
Spring 容器(
核心方法:ApplicationContext实现了此接口)提供的一个核心接口,用于发布事件。你可以在你的 Bean 中注入ApplicationEventPublisher来发布自定义事件或内置事件(虽然通常不需要手动发布内置事件)。publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event)
三、 使用方法
使用 ApplicationListener 主要涉及两个方面:定义监听器 和 发布事件。
1. 定义监听器 (处理事件)
有两种主要方式定义监听器:
-
方式一:实现
ApplicationListener接口 (经典方式)-
创建一个BaseListener抽象类,可以用来自定义一些属性或
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * BaseListener 类描述 * * @author jerry * @date 2025/6/24 14:06 */ @Slf4j @Component public abstract class BaseListener <T extends BaseEvent<?>> implements ApplicationListener<T> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(T event) { log.info("触发事件,source={},event={}", this.getClass().getSimpleName(), event); onApplicationEvent0(event); } /** * 在应用程序event0上 * * @param event 事件 */ public abstract void onApplicationEvent0(T event) ; }
-
-
-
继承BaseListener
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Slf4j public class NoticeListener extends BaseListener<NoticeEnvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent0(NoticeEnvent event) { // 当触发通知逻辑时,执行此逻辑可以进行消息推送,流程记录等操作 log.info("开始推送消息:{}",event); //获取事件内容 NoticeData source = event.getSource(); System.out.println(source); } }
-
-
方式二:使用
@EventListener注解 (推荐方式 - 更简洁)
Spring 4.2+ 引入了更简洁的@EventListener注解。你可以在任何 Spring 管理的 Bean 的方法上使用此注解,将其标记为事件监听器。import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Slf4j public class NoticeListener { @EventListener public void onApplicationEvent0(NoticeEnvent event) { // 当触发通知逻辑时,执行此逻辑可以进行消息推送,流程记录等操作 log.info("开始推送消息:{}",event); //获取事件内容 NoticeData source = event.getSource(); System.out.println(source); } }-
优点:
-
简洁: 不需要实现特定接口。
-
灵活: 方法名可以自由定义,方法参数直接声明为要监听的事件类型(Spring 根据参数类型推断)。
-
复用: 可以在同一个类中定义多个监听不同事件的方法。
-
支持条件: 结合
@Conditional或condition属性(如@EventListener(condition = "#event.success")),可以根据 SpEL 表达式条件化地监听事件。
-
-
关键点:
-
方法所在的类必须是 Spring Bean。
-
方法参数类型定义了要监听的事件类型。
-
方法可以有返回值(支持异步监听处理结果,见下文异步部分),也可以没有(
void)。
-
-
2. 发布事件
-
发布内置事件: Spring 容器会在相应生命周期节点(初始化、启动、停止、关闭等)自动发布对应的内置事件(
ContextRefreshedEvent,ContextStartedEvent等)。你通常不需要手动发布它们。 -
定义自定义事件类: 创建BaseEvent抽象类类继承
ApplicationEvent。import cn.hutool.core.util.IdUtil; import lombok.Getter; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import java.util.function.Function; /** * BaseEvent 类描述 * * @author jerry * @date 2025/6/24 13:59 */ public abstract class BaseEvent<T> extends ApplicationEvent { @Getter private final String eventId; @Override public T getSource () { return (T) super.getSource(); } /** * Create a new {@code ApplicationEvent}. * * @param t the object on which the event initially occurred or with * which the event is associated (never {@code null}) */ public BaseEvent(T t) { super(t); this.eventId = IdUtil.objectId(); } final void mapSource(Function<T, T> mapper) { if (source == null) { return; } this.source = mapper.apply(getSource()); } } -
创建NoticeEvent继承BaseEvent
/** * NoticeData 类描述 * * @author jerry * @date 2025/6/24 14:16 */ public class NoticeEvent extends BaseEvent<NoticeData>{ /** * Create a new {@code ApplicationEvent}. * * @param data the object on which the event initially occurred or with * which the event is associated (never {@code null}) */ public NoticeEvent(NoticeData data) { super(data); } } -
发布自定义事件:
封装ApplicationEventPublisher:/** * @author jerry */ @Slf4j public class EventBus implements ApplicationEventPublisher { /** * Singleton INSTANCE to use. */ public static final EventBus INSTANCE = new EventBus(); /** * 推送事件 * * @param event 事件 */ @Override public void publishEvent(@NonNull Object event) { log.info("event={}", event); SpringUtil.getApplicationContext().publishEvent(event); } }
定义消息实体类
/**
* NoticeData 类描述
*
* @author jerry
* @date 2025/6/24 14:25
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
public class NoticeData {
/**
* 接收消息人员集合
*/
private List<String> loginIds;
/**
* 消息体
*/
private String message;
}
最后在相关的代码里进行使用就可以了
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.example.mqdemo.templateNotice.EventBus;
import org.example.mqdemo.templateNotice.NoticeData;
import org.example.mqdemo.templateNotice.NoticeEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Collections;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MqServiceImpl {
public boolean sendMessage() {
try {
EventBus.INSTANCE.publishEvent(new NoticeEvent(NoticeData.of(Collections.singletonList("jerry"),"测试消息")));
log.info("发送消息成功");
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("发送消息异常",e);
}
return false;
}
}
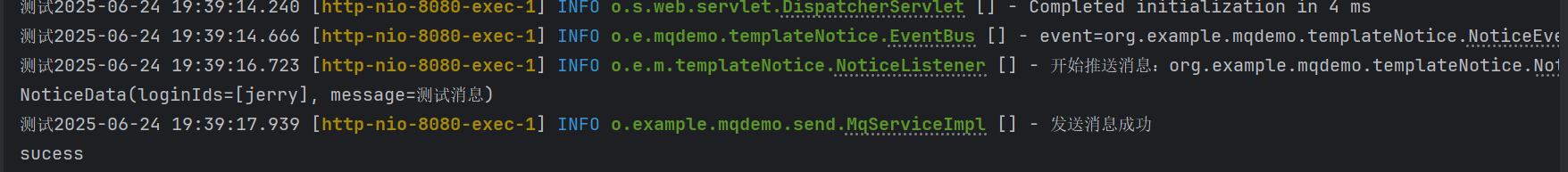
测试类
/**
* @author rui.li
*/
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RestController
public class SendController {
@Resource
private MqServiceImpl mqService;
@GetMapping(value = "send")
public void boardList() {
mqService.sendMessage();
System.out.println("sucess");
}
}
执行结果
四、 高级用法与注意事项
-
监听器执行顺序:
-
默认情况下,监听器的执行顺序是不确定的。
-
如果需要控制顺序,可以让监听器类实现
SmartApplicationListener接口(实现getOrder()方法返回一个Ordered值),或者在@EventListener注解的方法上添加@Order注解。 -
顺序值越小(
Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE),优先级越高,越先执行。
-
-
异步事件监听:
-
默认情况下,所有监听器都是在事件发布者的同一个线程中同步执行的。如果一个监听器执行缓慢,会阻塞后续监听器和发布者的线程。
-
要异步执行监听器逻辑:
使用@Async注解: 在@EventListener注解的方法上同时标注@Async。这需要你在 Spring 配置中启用异步支持(通常在主配置类或@SpringBootApplication类上添 - 加
@EnableAsync)。 -
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Slf4j public class NoticeListener { @EventListener() @Async public void onApplicationEvent0(NoticeEvent event) { // 当触发通知逻辑时,执行此逻辑可以进行消息推送,流程记录等操作 log.info("开始推送消息:{}",event); //获取事件内容 NoticeData source = event.getSource(); System.out.println(source); } }
-
注意:如果是通过实现
ApplicationListener接口的方式实现的事件监听,异步注解可能会失效,需要注意Bean都交给Spring统一管理。如果是对ApplicationListener接口进行了封装则需要对封装的接口里面的 onApplicationEvent也加上@Async注解
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* BaseListener 类描述
*
* @author jerry
* @date 2025/6/24 14:06
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public abstract class BaseListener <T extends BaseEvent<?>> implements ApplicationListener<T> {
@Override
@Async
public void onApplicationEvent(T event) {
log.info("触发事件,source={},event={}", this.getClass().getSimpleName(), event);
onApplicationEvent0(event);
}
/**
* 在应用程序event0上
*
* @param event 事件
*/
public abstract void onApplicationEvent0(T event) ;
}
总结
ApplicationListener 是 Spring 事件机制的关键接口,用于响应容器生命周期事件和自定义应用事件。使用它(或更现代的 @EventListener 注解)可以实现组件间的松耦合通信。
核心步骤:
-
定义事件: 继承
ApplicationEvent(对于自定义事件)。 -
定义监听器:
-
实现
ApplicationListener<E>接口并实现onApplicationEvent。 -
或在 Spring Bean 的方法上使用
@EventListener注解(推荐)。 -
确保监听器类是 Spring Bean (
@Component,@Service等)。
-
-
发布事件:
-
在需要发布事件的地方注入
ApplicationEventPublisher。 -
调用
publishEvent(event)方法发布事件。
-
选择建议:
-
对于新项目或需要简洁性、灵活性和条件监听时,优先使用
@EventListener。 -
需要强制实现接口或处理非常早期的事件(可能在
@EventListener处理器注册之前发生)时,可以考虑实现ApplicationListener。























 1061
1061

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








