顺序结构:程序从上到下逐行地执行,中间没有任何判断和跳转。
分支结构:
1.根据条件,选择性地执行某段代码。
2.有if…else和switch-case两种分支语句。
循环结构:
1.根据循环条件,重复性的执行某段代码。
2.有while、do…while、for三种循环语句。
分支结构
if-else(也叫 条件判断结构)

2.(二选一)

- 多选一(if 如果都不满足,就执行最后一个 else)

实例:
情况一:
int heartBeats = 79;
if(heartBeats < 60 || heartBeats > 100){
System.out.println("需要做进一步检查");
System.out.println("检查结束");
情况二:
int age = 23;
if(age <18){
system.out.println("你还可以看动画片");
}else{
System.out.println("你可以看电影了");
}
情况三:
if(age<0){
System.out.println("您输入的数据非法");
}else if(age <18){
System.out.println("青少年时期");
}else if(age < 35){
System.out.println("青壮年时期");
}else if(age <60){
System.out.println("中年时期")﹔
}else if(age <120){
System.out.println("老年时期");
}else{
System.out.println("厉害了");
}
每日一考
1.以下程序输出的 z 是多少?
boolean x = true;
boolean y = false;
short z = 40;
if ((z++ == 40) && (y = true)) {
z++;
}
if ((x = false) || (++z == 43)){
z++;
}
System.out.println("z = " + z);
注意:
y = true 这里是赋值,是把 true 赋给 y。先执行第一个 if,再执行第二个 if。
输出结果:

2.输出三个数中的最大值。
int num1 = 10,num2 = 20,num3 = 30;
int max;
if(num1 >= num2 && num1 >= num3){
max = num1;
}else if(num2 >= num1 && num2 >= num3){
max = num2;
}else{
max = num3;
}
System.out.println("三个数中的最大值为:" +max);
3.交换两个数的值。
Scanner 类
具体实现步骤:
1.导包:import java.util.Scanner
2.Scanner的实例化
3.调用Scanner类的相关方法(String型 next()/其他数据类型:nextXxx),来获取指定类型的变量
import java.util.Scanner;
class ScannerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//2.Scanner的实例化
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//3.调用Scanner类的相关方法
System.out.println("please input your name: ");
String name = scan.next();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("please input your age: ");
int age = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println("please input your weight: ");
double weight = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.println(weight);
System.out.println("do you fall in love with me? (true/false)");
boolean love = scan. nextBoolean();
System.out.println(love);
//对于 char型的获取,Scanner没有提供相关的方法。只能获取一个字符串。
System.out.println("please input your gender:(man/women)");
String gender = scan.next();
System.out.println(gender);
}
}
对于最后一种情况,我就是要用 char型去获取,应该怎么办
String gender = scan.next();
char genderChar = gender.charAt(0);//获取索引为0位置上的字符
System.out.println(genderChar);
输出:

if-else 练习
例:1
岳小鹏参加Java考试,他和父亲岳不群达成承诺:
如果:
成绩为100分时,奖励一辆BMW;
成绩为(80,99]时,奖励一台iphone xs max;
当成绩为[60,80]时,奖励一个iPad;
其它时,什么奖励也没有。
请从键盘输入岳小鹏的期末成绩,并加以判断
import java.util.Scanner;
class marry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入岳小鹏期末成绩:(0-100)");
int score = scan.nextInt();
if(score == 100){
System.out.println("奖励一辆BMW");
}else if(score > 80 &&score <= 99){
System.out.println("奖励一台iphone xs max");
}else if(score >= 60 && score <= 80){
System.out.println("奖励一个iPad");
}else{
System.out.println("什么奖励也没有");
}
}
}
特别注意:
不能写: 80 < score <= 99 .java里不能这么写。因为 80 < score 得出一个boolean型的结果,boolean不能和其他数据类型做运算。
说明:
1.else结构是可选的。
2.针对于条件表达式:
1)如果多个条件表达式之间是"互斥”关系(或没有交集的关系),哪个判断和执行语句声明在上面还是下面,无所谓。
2)如果多个条件表达式之间有交集的关系,需要根据实际情况,考虑清楚应该将哪个结构声明在上面。
3)如果多个条件表达式之间有包含的关系,通常情况下,需要将范围小的声明在范围大的上面,否则,范围小的就没机会执行了。
例:2
编写程序:由键盘输入三个整数分别存入变量num1、num2.num3,对它们进行排序,并且从小到大输出。
老师写的:
import java.util.Scanner;
class marry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个整数:");
int num1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个整数:");
int num2 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第三个整数:");
int num3 = scanner.nextInt();
if(num1 >= num2){
if(num3 >= num1){
System.out.println(num2 +"," +num1 + "," +num3);
}else if(num3 <= num2){
System.out.println(num3 +"," +num2 + "," +num1);
}else{
System.out.println(num2 + "," +num3 + "," +num1);
}
}else{
if(num3 >= num2){
System.out.println(num1 + "," +num2 + "," +num3);
}else if(num3 <= num1){
System.out.println(num3 + "," + num1 + "," +num2);
}else{
System.out.println(num1 + "," +num3 +"," +num2);
}
}
}
}
先假设 num1 和 num2 的大小,比如 num1 > num2 .然后 num3,要么比 num1 还大,要么比 num2 还小,要么就是在它们中间。
自己写的:
import java.util.Scanner;
class order{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the integer: ");
int num1 = scan.nextInt();
int num2 = scan.nextInt();
int num3 = scan.nextInt();
int max;
int mini;
if(num1 > num2){
max = num1;
mini = num2;
}else{
max = num2;
mini = num1;
}
if(num3 > max){
System.out.println("min = " + mini + ",mid1 = " +max + ",max = " + num3);
}if(num3 < mini){
System.out.println("min = " + num3 + ",mid2 = " + mini + ",max = " + max);
}if(mini < num3 && max > num3){
System.out.println("min = " + mini + ",mid3 = " + num3 + ",max = " + max);
}
}
}
说明:
1.if-else 结构是可以相互嵌套的。
2.如果 if-else 结构中的执行语句只有一行时,对应的一对 { } 可以省略的。但是,不建议省略。
例:3
1)对下列代码,若有输出,指出输出结果。
int x = 4;
int y = 1;
if(x > 2){
if(y > 2)
System.out.println(x + y);
System.out.println("atguigu");
}else
System.out.println("x is " + x);
输出结果:

按照题意加上括号就看的明白了。
int x = 4;
int y = 1;
if (x > 2){
if(y > 2){
System.out.println(x + y);
}
System.out.println("atguigu");
}else //这个 else 和上面的 if(x > 2)配对
System.out.println("x is " +x);
变式:
int x = 4;
int y = 1;
if (x > 2)
if(y > 2)
System.out.println(x + y);
else //这个 else 和上面的 哪个 if 配对? 就近原则!!!(和 if(y > 2)配对)
System.out.println("x is " +x);

例:4
我家的狗5岁了,5岁的狗相当于人类多大呢?其实,狗的前两年每一年相当于人类的10.5岁,之后每增加一年就增加四岁。那么5岁的狗相当于人类多少年龄呢?应该是:10.5+10.5+4+4+4= 33岁。
编写一个程序,获取用户输入的狗的龄,通过程序显示其相当于人类的年龄。如果用户输入负数,请显示一个提示信息。
import java.util.Scanner;
class one {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the age of the dog: ");
double age = scan.nextDouble();
if(age <= 2 && age > 0){
age = age * 10.5;
System.out.println("the age of the dog is:" + age);
}else if(age > 2){
age = (21 + (age - 2) * 4);
System.out.println("the age of the dog is:" + age);
}else if(age < 0){
System.out.println("please input the age once again(age > 0)");
}
}
}
例:5
假设你想开发一个玩彩票的游戏,程序随机地产生一个两位数的彩票,提示用户输入一个两位数,然后按照下面的规则判定用户是否能赢。|
1)如果用户输入的数匹配彩票的实际顺序,奖金10 000美元。
2)如果用户输入的所有数字匹配彩票的所有数字,但顺序不一致,奖金3000美元。
3)如果用户输入的一个数字仅满足顺序情况下匹配彩票的一个数字,奖金1000美元。
4)如果用户输入的一个数字仅满足非顺序情况下匹配彩票的一个数字,奖金500美元。
5)如果用户输入的数字没有匹配任何一个数字,则彩票作废。
import java.util.Scanner;
class one {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.out.println(Math.random());//产生[0,1)
int number = (int)(Math.random()*90 + 10);//得到[10,99],即[10,100)
System.out.println(number);//输出这个随机数,方便检查程序
int numShi = number / 10;
int numGe = number % 10;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the number: ");
int num = scan.nextInt();
int guessShi = num / 10;
int guessGe = num % 10;
if(guessShi == numShi && guessGe == numGe){
System.out.println("$10 000");
}else if(guessShi == numGe && guessGe == numShi){
System.out.println("$3 000");
}else if(guessShi == numShi || guessGe == numGe){
System.out.println("$1 000");
}else if(guessShi == numGe || guessGe == numShi){
System.out.println("$500");
}else{
System.out.println("Sorry! You got nothing ");
}
}
}
总结:如何获取一个随机数:10 - 99
int value = (int)(Math.random()* 90 +10); //[0.0,1.0)–>[0.0,90.0)—>[10.0,100.0)–>int强转后:[10,99]
公式:[a,b]:(int)(Math.random()* (b - a + 1)+a)
例:6
大家都知道,男大当婚,女大当嫁。那么女方家长要嫁女儿,当然要提出
一定的条件:高:180cm以上;富:财富1千万以上;帅:是。
1)如果这三个条件同时满足,则:“我一定要嫁给他!!!”
2)如果三个条件有为真的情况,则:“嫁吧,比上不足,比下有余。”
3)如果三个条件都不满足,则:“不嫁!”
import java.util.Scanner;
class marry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input your height: (cm)");
int height = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("please input your wealth: (million)");
double wealth = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.println("are you handsome: (true/false)");
boolean Handsome = scan.nextBoolean();
if(height > 180 && wealth > 1 && Handsome){
System.out.println("我一定要嫁给他!!!");
}else if(height > 180 || wealth > 1 || Handsome ){
System.out.println("嫁吧,比上不足,比下有余.");
}else{
System.out.println("不嫁.");
}
}
}
如果最后一个是否帅,想用汉字“是/否”来表示,怎么做?
System.out.println("请输入你是否帅:(是/否)");
String Handsome = scan.next();
if(height > 180 && wealth > 1 && Handsome.equals("是")){
System.out.println("我一定要嫁给他!!!");
}else if(height > 180 || wealth > 1 || Handsome.equals("是")){
System.out.println("嫁吧,比上不足,比下有余.");
}else{
System.out.println("不嫁.");
}
这里的 equals() 方法 ,是判断用户输入的字符串和括号里是否一样。一样就返回 true。
switch-case
说明:
1.根据switch表达式中的值,依次匹配各个case中的常量。一旦匹配成功,则进入相应case结构中,调用其执行语句。当调用完执行语句以后,则仍然继续向下执行其他case结构中的执行语句,直到遇到break关键字或此switch-case结构
末尾结束为止。
2.break 可以使用在switch-case结构中,表示一旦执行到此关键字,就跳出switch-case结构。
3.switch结构中的表达式,只能是如下的6种数据类型之一: byte . short、char、int、枚举类型(JDK5.0新增)、String类型(JDK7.0新增)。
4.case 之后只能声明常量。不能声明范围。
5.break关键字是可选的。
6.default:相当于if-else结构中的else。default结构是可选的,而且位置是灵活的。
例1:
使用switch把小写类型的char型转为大写。只转换a, b,c,d,e.其它的输
出“other”。
提示:String word = scan.next(); char c = word.charAt(0); switch(c){}
因为(String word = scan.next())不支持 char型,所以要先获取一个字符串,再获得字符串某个指定位置的字符(charAt)第一个字符的位置是 “0”。
import java.util.Scanner;
class SwitchCaseTset{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the letter: ");
String word = scan.next();
char c = word.charAt(0);
switch(c){
case 'a' :
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 'b' :
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 'c' :
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 'd' :
System.out.println("D");
break;
default :
System.out.println("other");
}
}
}
例2:
对学生成绩大于60分的,输出“合格”。低于60分的,输出“不合格”。
import java.util.Scanner;
class two {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input your grade: ");
int score = scan.nextInt();
switch(score / 10){
case 0 :
case 1 :
case 2 :
case 3 :
case 4 :
case 5 :
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
case 6 :
case 7 :
case 8 :
case 9 :
case 10 :
System.out.println("合格");
break;
}
}
}
更好的方法并不是 score / 10. 而是 score / 60;
switch(score / 60){
case 0 :
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
case 1 :
System.out.println("合格");
break;
同类型练习:
根据用于指定月份,打印该月份所属的季节。3,4,5春季6,7,8夏季9,10,11秋季12,1,2冬季
import java.util.Scanner;
class SwitchCaseTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the month: ");
int month = scan.nextInt();
switch(month){
case 1 :
case 2 :
case 12 :
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 3 :
case 4 :
case 5 :
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6 :
case 7 :
case 8 :
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9 :
case 10 :
case 11 :
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
default :
System.out.println("wrong");
}
}
}
例3:
编写程序:从键盘上输入2019年的“month"和“day”,要求通过程序输出输入的日期为2019年的第几天。
import java.util.Scanner;
class two {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input month: ");
int month = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("please input day: ");
int day = scan.nextInt();
int sumDay = 0;
switch(month){
case 12 :
sumDay += 31;
case 11 :
sumDay += 30;
case 10 :
sumDay += 31;
case 9 :
sumDay += 30;
case 8 :
sumDay += 31;
case 7 :
sumDay += 30;
case 6 :
sumDay += 31;
case 5 :
sumDay += 30;
case 4 :
sumDay += 31;
case 3 :
sumDay += 28;
case 2 :
sumDay += 31;
case 1 :
sumDay += day;
}
System.out.println("这是2019年的第" + sumDay + "天");
}
}
变式:
从键盘分别输入年、月、日,判断这一天是当年的第几天。
注:判断一年是否是闰年的标准:
1)可以被4整除,但不可被100整除
或
2)可以被400整除
我自己写的版本:
import java.util.Scanner;
class order{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the year: ");
int year = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("please input the month: ");
int month = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("please input the day: ");
int day = scan.nextInt();
int sumDay = 0;
int month2;
if(year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0){
month2 = 29;
}else if(year % 400 == 0){
month2 = 29;
}else{
month2 = 28;
}
switch(month){
case 12 : sumDay += 31;
case 11 : sumDay += 30;
case 10 : sumDay += 31;
case 9 : sumDay += 30;
case 8 : sumDay += 31;
case 7 : sumDay += 30;
case 6 : sumDay += 31;
case 5 : sumDay += 30;
case 4 : sumDay += 31;
case 3 : sumDay += month2;
case 2 : sumDay += 31;
case 1 : sumDay += day;
}
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" +day + "天:" + "这是" + year + "的第" + sumDay + "天");
}
}
老师的版本:
将判断是否是闰年的循环放到了 case 里。
case 3 :
if((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 ) || year % 400 == 0)
sumDays += 29;
}else{
sumDays += 28;
}
练习:
编写程序:从键盘上读入一个学生成绩,存放在变量score中,根据score的值输出其对应的成绩等级:I
score>=90 等级:A
70<=score<90 等级:B
60<=score<70 等级:C
score<60 等级:D
import java.util.Scanner;
class marry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生成绩:(0-100)");
int score = scan.nextInt();
int num = score / 10;
switch(num){
case 10:
case 9 :
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 7 :
case 8 :
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 6 :
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 5 :
System.out.println("D");
break;
default:
System.out.println("input again(0-100)");
}
}
}
总结说明:
1.凡是可以使用switch-case的结构,都可以转换为if-else。反之,不成立。
2.我们写分支结构时,当发现既可以使用switch-case,(同时,switch中表达式的取值情况不本多),又可以使用if-else时,我们优先选择使用switch-case。原因: switch-case执行效率稍高。
循环结构

for 循环
1.for循环的结构:
for(①;②;④){
③
}
2.for 循环的顺序:
① --> ②–> ③–> ④–> ②–> ③–> ④ ...
直到迭代后的条件(④),不满足循环条件(②),结束循环。
3.for循环结构的使用
循环结构的4个要素:
①初始化条件
②循环条件—>是 boolean类型
③循环体
④迭代条件
for(int i = 1;i <= 5;i++){//i:1,2,3,4,5
System.out.println( "Hello World!");
}
/*特别注意:
i:在 for循环内有效,出了 for循环就失效了。
*/
//System.out.println(i);//会报错,因为已经出了 for循环了。
/*如果在后面的 for循环仍定义一个叫 i 的变量是完全没有问题的。
因为 i 的作用域仅限于这对 for循环的大括号里
*/
例1:
例题:遍历100以内的偶数,输出所有偶数,偶数和,偶数的个数。
class traversing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
int sum = 0;//记录偶数的和
int j = 0;//记录偶数的个数
for(i = 1;i < 101;i++){
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
sum += i;
j++;
}
}
System.out.println("总和为:" + sum + "偶数的个数为:" + j);
}
}
例2:
编写程序从1循环到150,并在每行打印一个值,另外在每个3的倍数行
上打印出“foo",在每个5的倍数行上打印“biz",在每个7的倍数行上打印
输出“baz"。(如果同时是多个数的倍数,就输出相应的字母)
实际效果:
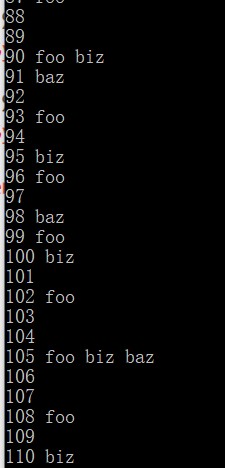
自己写的版本:
class Exer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
for(i = 1;i < 151;i++){
System.out.print(i + " ");
if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0 && i % 7 == 0){
System.out.println("foo" + " " + "biz" + " "+ "baz");
}else if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0){
System.out.println("foo" +" "+ "biz");
}else if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 7 == 0){
System.out.println("foo" +" " + "baz");
}else if(i % 5 == 0 && i % 7 == 0){
System.out.println("biz" + " " + "baz");
}
else if(i % 3 == 0){
System.out.println("foo");
}else if(i % 5 == 0){
System.out.println("biz");
}else if(i % 7 == 0){
System.out.println("baz");
}else {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
老师写的版本:
class Exer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
for(i = 1;i <= 150;i++){
System.out.print(i + " ");
if(i % 3 == 0){
System.out.print("foo ");
}
if(i % 5 == 0){
System.out.print("biz ");
}
if(i % 7 == 0){
System.out.print("baz ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
每日一考
1.switch后面使用的表达式可以是哪些数据类型的。
2.如何从控制台获取string和int型的变量,并输出?
特别注意
变量在使用前一定要赋值。
例3:
输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。比如:12和20的最大公约数是4,最小公倍数是60。
说明:break关键字的使用
import java.util.Scanner;
class two {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个整数:");
int num1 = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个整数:");
int num2 = scan.nextInt();//12 20
int i,max,min;
//最大公约数(肯定小于或等于两个数中最小的那个数)
//1.获取两个数中的较小值
min = (num1 > num2)? num2 : num1;
//2.遍历
for(i = min;i > 0;i--){//因为要找最大的,所以从 min 开始,倒着往回找(<--),找到的符合条件的第一个数就是最大的.
if(num1 % i == 0 && num2 % i ==0){
break;//一旦在循环中找到那个值,就跳出循环
}
}
System.out.println("最大公约数为:" + i);
//最小公倍数(肯定大于或等于两个中最大的那个数)
//1.获取两个数中较大值
max = (num1 > num2)? num1 : num2;
//2.遍历
for(i = max;i < num1 * num2;i++){//因为要找最小的,所以从 max 开始,顺着往后找(-->).找到符合条件的第一个数就是最小的.
if(i % num1 == 0 && i % num2 == 0){//不要写成 max % num1....
break;
}
}
System.out.println("最小公倍数为:" + i);
}
}
例4:
3.输出所有的水仙花数,所谓水仙花数是指一个3位数,其各个位上数
字立方和等于其本身。例如:153=1*1*1+3*3*3+5*5*5
class num {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
int ge,shi,bai;
for(i = 100;i < 1000;i++){
bai = i / 100;
shi = i / 10 % 10;
ge = i % 10;
if(i == ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai *bai){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
while循环
①
while(②){
③;
④;
}
执行过程:①②③④②③④…②(直到不满足②就跳出)
说明:
1.写while循环千万小心不要丢了迭代条件。一旦丢了,就可能导致死循环!
2.我们写程序,要避免出现死循环。
3.for循环和while循环是可以相互转换的!
区别:for循环和while循环的初始化条件部分的作用域(作用范围)不同。
详细说明区别:区别就在于 ①。for循环 初始化条件 (i) 定义在循环里,出了 for循环就失效了。而 while 的 初始化条件 (i) 定义在 while循环外面,在while循环外仍可以调用。
例:使用while循环遍历100以内的所有偶数
int i = 1;
while(i <= 100){
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
}
i++;
}
//出了while循环以后,仍可以调用 i.
System.out.println(i);/*输出:101(执行到100后,i++ 变成101,
再回去判断条件(i <= 100)不满足,结束循环,输出i就是101)*/
do-while 循环
①
do{
③;
④;
}while(②);
执行过程:①③④②③④…②(直到不满足②就跳出)
说明:
1.do-while循环至少会执行一次循环体!
2.开发中,使用for和while更多一些。较少使用do-while
例:使用do-while循环遍历100以内的偶数
int num = 1;
do{
if(num % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(num);
}
num++;
}while(num <= 100);
一个程序说明while 和 do-while 的区别
int number1 = 10;
while(number1 > 10){
System.out.println("hello:while");
number1--;
}
int number2 = 10;
do{
System.out.println("hello:do-while");
number2--;
}while(number2 > 10);
输出结果:

练习:
从键盘读入个数不确定的整数,并判断读入的正数和负数的个数,输入为0时结束程序。
说明:
最简单无限循环(不是死循环)格式: while(true) , for(;;),无限循环存在的原因是并不知道循环多少次,需要根据循环体内部某些条件,来控制循环的结束。
import java.util.Scanner;
class number {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入数字:");
int positiveNumber = 0;//记录正数的个数
int negativeNumber = 0;//记录负数的个数
while(true){//也可以写 for(;;)
int number =scan.nextInt();
//判断number的正负情况
if(number > 0){
positiveNumber++;
}else if(number < 0){
negativeNumber++;
}else{
break;//输入0就结束
}
}
System.out.println("输入的正数个数为:" + positiveNumber);
System.out.println("输入的正数个数为:" + negativeNumber);
说明:
1.不在循环条件部分限制次数的结构:for(;;)while(true)
2.结束循环有几种方式?
方式一:循坏条件部分返回false
方式二:在循环体中,执行break
嵌套循环
嵌套循环的使用
1.嵌套循环:将一个循环结构A声明在另一个循环结构B的循环体中,就构成了嵌套循环。
2.外层循环:循环结构B.内层循环:循环结构A。
3.说明
内层循环结构遍历一遍,只相当于外层循环循环体执行了一次。
假设外层循环需要执行m次,内层循环需要执行n次。此时内层循环的循环体一共执行了m*n次。
请输出:

int i,j;
for(i = 1;i < 6;i++){//i控制行数
for(j = 1;j < 7;j++){//j控制列数
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
技巧:外层循环控制行数,内层循环控制列数
请输出:
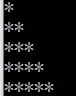
int i,j;
for(i = 1;i <= 5;i++){
for(j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
请输出:

自己写的版本:
int i,j;
for(i = 4;i >= 1;i--){
for(j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
老师写的版本
规律分析:
/* i(行号) j(*的个数) 规律:i + j = 5 换句话说:j = 5 - i;
**** 1 4
*** 2 3
** 3 2
* 4 1
*/
int i,j;
for(i = 1;i <= 4;i++){
for(j = 1;j <= 5 - i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
请输出:

把上面两种情况代码拼在一起就行了。
int i,j;
for(i = 1;i < 6;i++){
for(j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
for(i = 4;i >= 1;i--){
for(j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
请输出:

int i,j,k;
for(i = 1;i < 6;i++){
for(k = 1; k <= 5 - i;k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for(i = 1;i <= 4;i++){
for(k = 1;k <=i;k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(j = 1;j <= 5 - i;j++){
System.out.print("*");
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
嵌套循环应用一:
输出九九乘法口诀表
int i,j;
for(i = 1;i < 10;i++){
for(j = 1;j <=i;j++){
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + (i * j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
例:输出100以内的所有质数。
质数:也叫 素数。只能被 1 和它本身整除。即 从 2 开始,到这个数-1结束,都不能被这个数本身整除。
int i,j;
boolean isFlag = true;//标示 i 是否被 j 除尽,一旦除尽,修改其值
for(i = 2;i <= 100;i++){//遍历100以内的自然数。因为最小的质数是 2。所以从 2 开始。
for(j = 2;j < i;j++){//j:被 i 去除
if(i % j ==0){// i 被 j 除尽
isFlag =false;
}
}
if(isFlag == true){
System.out.println(i);
}
//重置isFlag
isFlag = true;
/*如果不重置,当外层循环 i = 4 时,进到内层循环,会将 isFlag 修改为
false,那么 4 后面进来的数,就算没有除尽,是一个质数 isFlag也会是 false.所以重置
这一步很关键*/
}
注意,将 boolean isFlag = true;换个位置,还可以不重置。如以下这种情况,也是可以的。但这种不如前面那种内存变量加载的少。(个人更喜欢第一种)
int i,j;
for(i = 2;i <= 100;i++){
boolean isFlag = true;
for(j = 2;j < i;j++){
if(i % j ==0){
isFlag =false;
}
}
if(isFlag == true){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
优化版本
int i,j;
boolean isFlag = true;//标示 i 是否被 j 除尽,一旦除尽,修改其值
for(i = 2;i <= 100;i++){//遍历100以内的自然数。因为最小的质数是 2。所以从 2 开始。
//优化二:除到这个数开根号即可(记得这种情况要带等号)
for(j = 2;j <=Math.sqrt(i);j++){//j:被 i 去除
if(i % j ==0){// i 被 j 除尽
isFlag = false;
/*如果不重置,当外层循环 i = 4时,
进到内层循环,会将 isFlag 修改为
false,那么 4 后面进来的数,就算没有除尽,
是一个质数 isFlag也会是 false.所以重置这
一步很关键*/
break;//优化一
}
}
if(isFlag == true){
System.out.println(i);
}
//重置isFlag
isFlag = true;
/*如果不重置,当外层循环 i = 4 时,进到内层循环,会将 isFlag 修改为
false,那么 4 后面进来的数,就算没有除尽,是一个质数 isFlag也会是 false.所以重置这一步很关键*/
}
怎么看执行一个程序的耗时?
需要一个方法:
//获取当前时间距离1970-01-01 00:00:00的毫秒数
long star = System.currentTimeMillis();//写在程序开始的地方
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//写在程序结束的地方
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - star));//然后通过做差得出运行时间
将程序改为 输出 100000 以内的质数。
优化前:

只优化一:

同时优化一,二

特殊关键字(break,continue)break
break:
使用范围:switch-case/循环结构中
循环中使用的作用(不同点):结束当前循环
相同点:关键字后不能声明执行语句
特别注意:跳出包裹次关键字最近的一层循环
continue:
使用范围:循环结构中
循环中使用的作用(不同点):结束当次循环
相同点:关键字后不能声明执行语句
特别注意:跳出包裹次关键字最近的一层循环的当前那一次,接着执行下一次
例:
int i;
for(i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
if(i % 4 == 0){
//break;//输出:123
continue;//输出:123567910(没有4和8)
}
System.out.print(i);
}
带标签的 break,continue
int i,j;
lable:for(i = 1;i <= 4;i++){
for(j = 1;j <= 10;j++){
if(j % 4 == 0){
//break lable;//结束指定标识的一层循环结构
//输出:123
continue lable;//结束指定标识的一层循环的当次循环
//输出:123123123123//是不会换行的,因为直接结束了外层循环,执行不到
//输出换行的语句
}
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
用 带标签的continue 来输出质数
int i,j;
long star = System.currentTimeMillis();
label:for(i = 2;i <= 100000;i++){
for(j = 2;j <= Math.sqrt(i);j++){
if(i % j ==0){
continue label;
}
}
System.out.println(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - star));
耗时:

每日一考
一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为"完数"。例如6=1+2+3。编程找出1000以内的所有完数。(因子:除去这个数本身的其它约数)
int factor = 0;
int i,j;
for(i =1;i <= 1000;i++){
for(j = 1;j <= i/2;j++){
if(i % j == 0){
factor += j;
}
}
if(i == factor){
System.out.println(i);
}
//重置factor 这一步很重要!!!
factor = 0;
}







 本文围绕Java编程展开,详细介绍了分支结构(if-else、switch-case)和循环结构(for、while、do-while)的使用方法、注意事项,并给出大量实例,如成绩奖励判断、彩票游戏等。还讲解了特殊关键字(break、continue)的作用,以及嵌套循环的应用。
本文围绕Java编程展开,详细介绍了分支结构(if-else、switch-case)和循环结构(for、while、do-while)的使用方法、注意事项,并给出大量实例,如成绩奖励判断、彩票游戏等。还讲解了特殊关键字(break、continue)的作用,以及嵌套循环的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








