一、 MySQL的数据类型 1.字段类型
数值类型:
int 整型
long 长整型
bigint 整型包括负数
float 单精度
double 双精度
decimal 小数 跟钱有关
字符串
char 字符 0-255 长度 zuoshaoxxxxxxx 255 自动补齐
varchar 字符串 变长 zuoshao
text 文本
日期:
date 日期 YYYY-MM-DD 在代码块中以‘%Y-%m-%d’进行输出
time 时间 HH:mm:SS
datetime 年月日时分秒 YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:SS
timestamp 年月日时分秒【时间戳】 YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:SS
二、对数据库进行操作
create database gh; 创建数据库
show databases ;查看整个数据库
use gh;//使用数据库
三、创建表
创建表内容
create table student(
id int(11) not null auto_increment[该字段是该属性是自增长的],
name varchar(255),
age int (10),
create_user varchar(255),
create_time timestamp not null default current_timestamp[该字段表明该表的创建时间],
update_user varchar(255)[该字段表示更新人员名称],
update_time timestamp not null default current_timestamp on current_timestamp[该字段表明该表的更新时间],
primary key(id));
对表进行操作
1.查看表
show table 【表名】;2.插入数据
insert into gh.student(name, age)values (“zhangshi”,21);3.查看数据
select *;//查看所有的内容
select name from gh.student;//只查看表中名字4.更新数据
update gh.student set age=20 where name=”zhangshi”;5.删除数据
delect from gh.student
where name=”zhanshi”;四、其他用法 1.条件过滤 where
select * from gh.student where age>(</=)20;
select * from gh.student where age=20 and name=”zhangshi”;
select * from gh.student where age=20 or name=”zahngshi”;
select * from gh.student where age in(10,20,30);
select * from gh.student where age not in (10,20,52);
2.排序 order by
select * from gh.student order by age asc;//正序
select *from gh.student order by age desc;//倒序
3.模糊查询 like
select * from gh.student where name like ‘z%’;
select *from gh.student where name like ’__n%’;(_占位符,该代码表达名字中第三个是n的)
4. 合并表
首先建表
create table a(id int(10),name varchar(255));
create table b(id int(10),name varchar(255));
合并
select *from a union select * from b;(去重)
select *from a union all select * from b;(不去重)
5. 过滤 null
select *from gh.studen name is null;//查找数据库gh中student表中名字是空的信息
数据清洗 etl
脏数据 -》规范的数据
函数:ifnull coalesce
select id,name,age
,ifnull(create_user,”--”)as etl_create_user create_user(该表创建的人员名称)
,create_time create_time(该表创建的时间)
from gh.student;
6. 聚合函数 聚合函数:多行数据 按照一定的规律【聚合函数】聚合到一行 1.group by 分组
select avg(age) from student;
select name,,avg(age) asavg_age from student group by name;(求每个名字的平均年龄 有相同名字时可以使用)
select ‘wenjian’ as name_1,//定一个常量名name_1
avg(age) as avg_age from student
where name like “%wenjian%” group by name_1;(该代码将名字含有wenjian的分为一组求年龄的平均值)
2.聚合之后不能使用where 要使用having
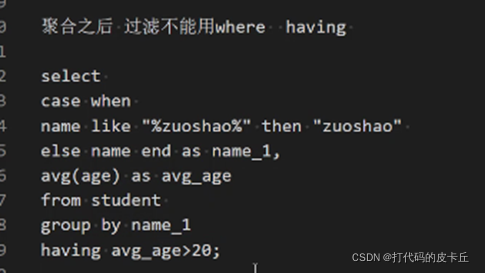
3.子查询:模板

案例:查询平均年龄大于20的并且名字中含有wenjin字段的学生信息
select name_1,avg_age
from
(
select
case when
name like "%wenjian%" then"wenjian"
else name end as name_1,
avg(age) as avg_agefrom student
group by name_1
)as tmp
where avg_age>20;4.多表联查
内连接 inner join (join)
案例:
select a.id,a.name,a.adress,b.age
from a1 as a join b1 as b
on a.id =b.id and a,name =b.name; //在两个表中查找左连接 left join
以左表为主 是全的 右边能连接上就链接上连接不上那么null来填充
select a.id,a.name,a.adress,b.age
from a1 as a left join b1 as b
on a.id =b.id and a,name =b.name;右连接 right
以右表为主 是全的 左边能连接上就链接上连接不上那么null来填充
select a.id,a.name,a.adress,b.age
from a1 as a right join b1 as b
on a.id =b.id and a,name =b.name;全连接 full outer join(MySQL不支持 但是可以使用 union / union all)
全连接都为主 数据是全的
左表来匹配 匹配不上 null
右表来匹配 匹配不上 null








 本文介绍了MySQL的主要数据类型,包括数值类型(如int、float、double、decimal)、字符串(char、varchar、text)、日期时间类型(date、time、datetime、timestamp)。接着,概述了对数据库的操作,如创建数据库、使用数据库。还详细讲解了如何创建表、插入数据、查看与更新数据、删除数据等基本操作。最后,提到了一些高级查询技巧,如条件过滤(where)、排序(order by)、模糊查询(like)、表的合并以及聚合函数(group by)和子查询的应用。
本文介绍了MySQL的主要数据类型,包括数值类型(如int、float、double、decimal)、字符串(char、varchar、text)、日期时间类型(date、time、datetime、timestamp)。接着,概述了对数据库的操作,如创建数据库、使用数据库。还详细讲解了如何创建表、插入数据、查看与更新数据、删除数据等基本操作。最后,提到了一些高级查询技巧,如条件过滤(where)、排序(order by)、模糊查询(like)、表的合并以及聚合函数(group by)和子查询的应用。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








