MapReduce运行机制和join算法
MapTask运行机制详解以及Map任务的并行度
在mapTask当中,一个文件的切片大小使用默认值是128M,就是跟我们一个block块对应大小一样
MapTask运行的整个过程
1、TextInputFormat读取数据
2、调用map逻辑,默认是一个切片(就是一个block块)对应一个mapTask
3、数据写入到环形缓冲区,默认环形缓冲区的大小是100M,换型缓冲区其实就是一个数组
4、数据一直往环形缓冲区当中写,数据在环形缓冲区当中实现分区,排序,规约,分组等
5、等到数据写到环形缓冲区的80%的时候,启动溢写线程,将内存当中80M的数据,溢写到磁盘上面去
6、等到maptask完成之后,磁盘上面可能存在很多的小文件,这些小文件已经做好了局部排序,分区,规约等步骤,再把这些小文件合并成一个大的文件
7、等待reduce阶段来拉取这个文件


mapTask的一些基础设置配置(mapred-site.xml当中):
设置一:设置环型缓冲区的内存值大小(默认设置如下)
mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb 100
设置二:设置溢写百分比(默认设置如下)
mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent 0.80
设置三:设置溢写数据目录(默认设置)
mapreduce.cluster.local.dir ${hadoop.tmp.dir}/mapred/local
设置四:设置一次最多合并多少个溢写文件(默认设置如下)
mapreduce.task.io.sort.factor 10
ReduceTask 工作机制以及reduceTask的并行度
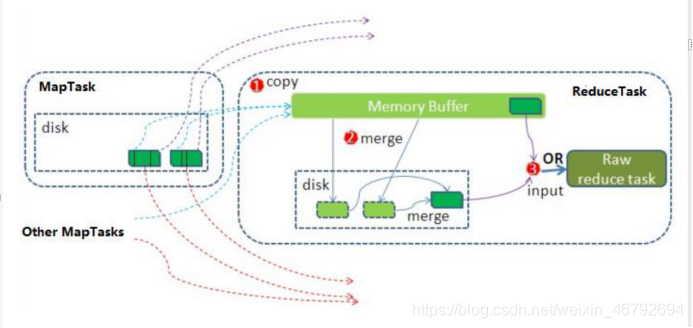
ReduceTask的运行的整个过程
1、启动线程到mapTask那里去拷贝数据,拉取属于每一个reducetask自己内部的数据
2、数据的合并,拉取过来的数据进行合并,合并的过程,有可能在内存当中,有可能在磁盘当中,有可能在内存和磁盘当中,合并的时候同时要进行分组操作
3、调用reduce逻辑
4、数据输出
shuffle阶段数据的压缩机制
hadoop支持的压缩算法

各种压缩算法对应使用的java类

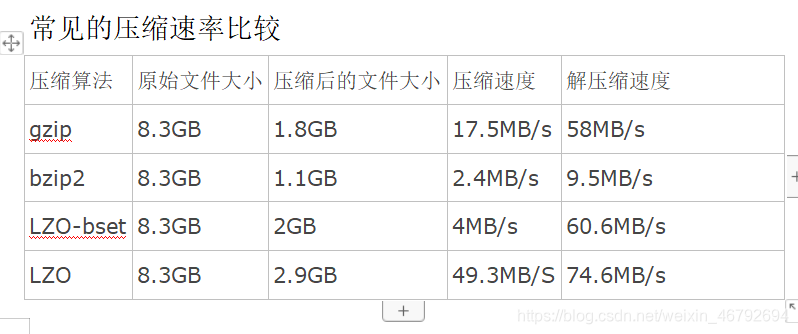
snappy比以上方式都要快
方式一:在代码中进行设置压缩
设置我们的map阶段的压缩
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress","true");
configuration.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec","org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec");
设置我们的reduce阶段的压缩
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress","true");
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type","RECORD");
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec","org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec");
方式二:配置全局的MapReduce压缩
我们可以修改mapred-site.xml配置文件,然后重启集群,以便对所有的mapreduce任务进行压缩
map输出数据进行压缩
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.output.compress</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec</value>
</property>
reduce输出数据进行压缩
<property> <name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property> <name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type</name>
<value>RECORD</value>
</property>
<property> <name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec</value> </property>
所有节点都要修改mapred-site.xml,修改完成之后记得重启集群
使用hadoop的snappy压缩来对我们的数据进行压缩
reduce端join算法实现

2、实现机制:
通过将关联的条件作为map输出的key,将两表满足join条件的数据并携带数据所来源的文件信息,发往同一个reduce task,在reduce中进行数据的串联
第一步:定义我们的OrderBean
public class OrderJoinBean implements Writable {
private String id;
private String date;
private String pid;
private String amount;
private String name;
private String categoryId;
private String price;
@Override
public String toString() {
return id+"\t"+date+"\t"+pid+"\t"+amount+"\t"+name+"\t"+categoryId+"\t"+price;
}
public OrderJoinBean() {
}
public OrderJoinBean(String id, String date, String pid, String amount, String name, String categoryId, String price) {
this.id = id;
this.date = date;
this.pid = pid;
this.amount = amount;
this.name = name;
this.categoryId = categoryId;
this.price = price;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(String pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
public String getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(String amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCategoryId() {
return categoryId;
}
public void setCategoryId(String categoryId) {
this.categoryId = categoryId;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(id+"");
out.writeUTF(date+"");
out.writeUTF(pid+"");
out.writeUTF(amount+"");
out.writeUTF(name+"");
out.writeUTF(categoryId+"");
out.writeUTF(price+"");
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.id = in.readUTF();
this.date = in.readUTF();
this.pid = in.readUTF();
this.amount = in.readUTF();
this.name = in.readUTF();
this.categoryId = in.readUTF();
this.price = in.readUTF();
}
}
第二步:定义我们的map类
public class OrderJoinMap extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,OrderJoinBean> {
private OrderJoinBean orderJoinBean = new OrderJoinBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//通过获取文件名来区分两个不同的文件
String[] split = value.toString().split(",");
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
String name = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
System.out.println("获取文件名为"+name);
if(name.contains("orders")){
//订单数据
orderJoinBean.setId(split[0]);
orderJoinBean.setDate(split[1]);
orderJoinBean.setPid(split[2]);
orderJoinBean.setAmount(split[3]);
context.write(new Text(split[2]),orderJoinBean);
}else{
//商品数据
orderJoinBean.setName(split[1]);
orderJoinBean.setCategoryId(split[2]);
orderJoinBean.setPrice(split[3]);
context.write(new Text(split[0]),orderJoinBean);
}
}
}
第三步:自定义reduce类
public class OrderJoinReduce extends Reducer<Text,OrderJoinBean,OrderJoinBean,NullWritable> {
private OrderJoinBean orderJoinBean;
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<OrderJoinBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
orderJoinBean = new OrderJoinBean();
for (OrderJoinBean value : values) {
System.out.println(value.getId());
//相同的key的对象都发送到了这里,在这里将数据拼接完整
if(null !=value.getId() && !value.getId().equals("null") ){
orderJoinBean.setId(value.getId());
orderJoinBean.setDate(value.getDate());
orderJoinBean.setPid(value.getPid());
orderJoinBean.setAmount(value.getAmount());
}else{
orderJoinBean.setName(value.getName());
orderJoinBean.setCategoryId(value.getCategoryId());
orderJoinBean.setPrice(value.getPrice());
}
}
context.write(orderJoinBean,NullWritable.get());
}
}
map端join算法实现
第一步:定义mapJoin
public class JoinMap extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,Text> {
HashMap<String,String> b_tab = new HashMap<String, String>();
String line = null;
/*
map端的初始化方法当中获取我们的缓存文件,一次性加载到map当中来
*/
@Override
public void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//这种方式获取所有的缓存文件
// URI[] cacheFiles1 = DistributedCache.getCacheFiles(context.getConfiguration());
Path[] localCacheFiles = DistributedCache.getLocalCacheFiles(context.getConfiguration());
URI[] cacheFiles = DistributedCache.getCacheFiles(context.getConfiguration());
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(cacheFiles[0], context.getConfiguration());
FSDataInputStream open = fileSystem.open(new Path(cacheFiles[0]));
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(open));
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
String[] split = line.split(",");
b_tab.put(split[0],split[1]+"\t"+split[2]+"\t"+split[3]);
}
fileSystem.close();
IOUtils.closeStream(bufferedReader);
}
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//这里读的是这个map task所负责的那一个切片数据(在hdfs上)
String[] fields = value.toString().split(",");
String orderId = fields[0];
String date = fields[1];
String pdId = fields[2];
String amount = fields[3];
//获取map当中的商品详细信息
String productInfo = b_tab.get(pdId);
context.write(new Text(orderId), new Text(date + "\t" + productInfo+"\t"+amount));
}
}
第二步:定义程序运行main方法
public class MapSideJoin extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = super.getConf();
//注意,这里的缓存文件的添加,只能将缓存文件放到hdfs文件系统当中,放到本地加载不到
DistributedCache.addCacheFile(new URI("hdfs://192.168.52.100:8020/cachefile/pdts.txt"),conf);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, MapSideJoin.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(MapSideJoin.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("file:///F:\\map端join\\map_join_iput"));
job.setMapperClass(JoinMap.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("file:///F:\\map端join\\map_join_output")) ;
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return b?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ToolRunner.run(configuration,new MapSideJoin(),args);
}
}























 289
289

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








