subqueries
案例一
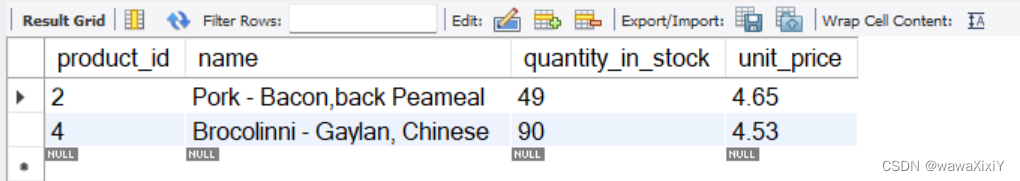
找到比lettuce生菜(id=3)更贵的product
select
*
FROM products
where unit_price > (
select unit_price
from products
where product_id = 3)
案例二
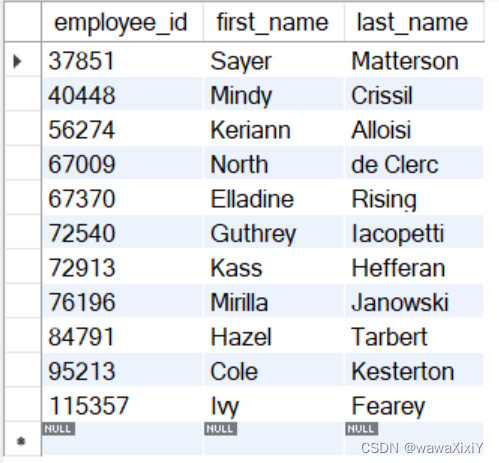
在SQL_hr 中, 找到employees 中谁赚的钱比平均工资高
select
e.employee_id,
e.first_name,
e.last_name
FROM employees e
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from employees)
IN operator
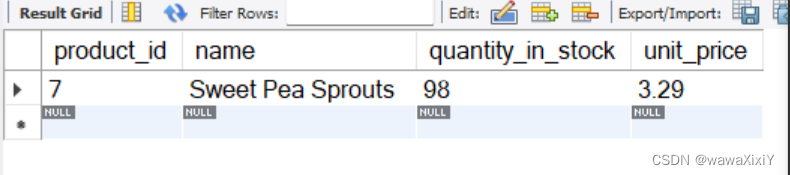
case 1: Find the product that u never been orderd?
select *
from products
where product_id not in(
select
distinct product_id
from order_items)
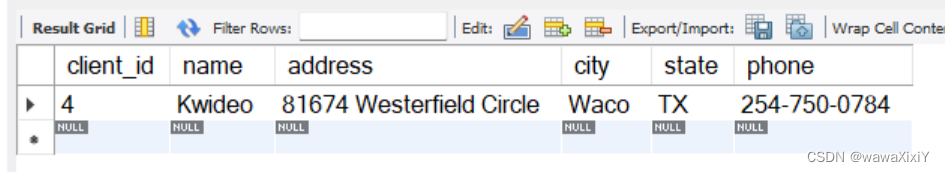
case 2 : find clients without invoices
select *
from clients
where client_id not in(
select
distinct client_id
from invoices)
Subqueries VS Join
case1: 仍然是找到clients 没有invoices的 (但是要使用left join 了)
select *
from clients
left join invoices
using (client_id)
where invoice_id is null

练习
Find customers who have ordered lettuce (id=3), select customer_id, first_name, last_name
方法1:子查询和表连接
select
c.customer_id,
c.first_name,
c.last_name
from customers c
where customer_id in (
select o.customer_id
from orders o
join order_items oi
using(order_id)
where oi.product_id = 3)
方法2: 全部子查询
讲解:写的时候,要想着把三个表连接起来。分别是customers, orders, order_item,
customers和orders 通过customer_id 连接, 然后再通过order_id 将orders和order_items ;连接起来,再将order_items 中的product=3的条件给挑选出来。
select c.customer_id,
c.first_name,
c.last_name
from customers c
where customer_id in (
select o.customer_id
from orders o
where o.order_id in (
select DISTINCT oi.order_id
from order_items oi
where product_id = 3))
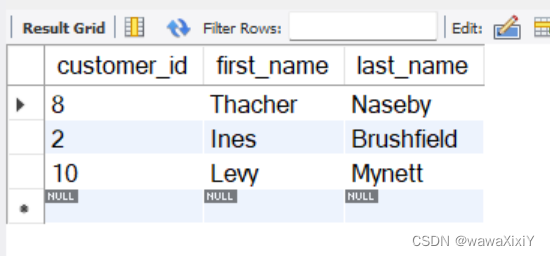
方法3 : 将三个表全部连接成一个表
select distinct
c.customer_id,
c.first_name,
c.last_name
from customers c
join orders o using(customer_id)
join order_items oi using(order_id)
where oi.product_id = 3
The ALL Keyword
select invoices larger than all invoices of client 3 查询出所有 比client为3的大的invoice。
尝试:
select
invoice_id
FROM invoices
where invoice_total > (
select
invoice_total
from invoices
where client_id = 3)
报错:Error Code: 1242. Subquery returns more than 1 row ,
子循环中存在多条查询,
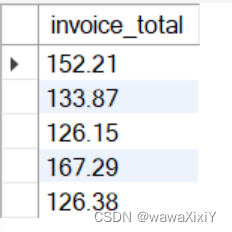
正确答案:
1:使用 SELECT MAX() 语句
select
*
FROM invoices
where invoice_total > (
select max(
invoice_total)
from invoices
where client_id = 3)
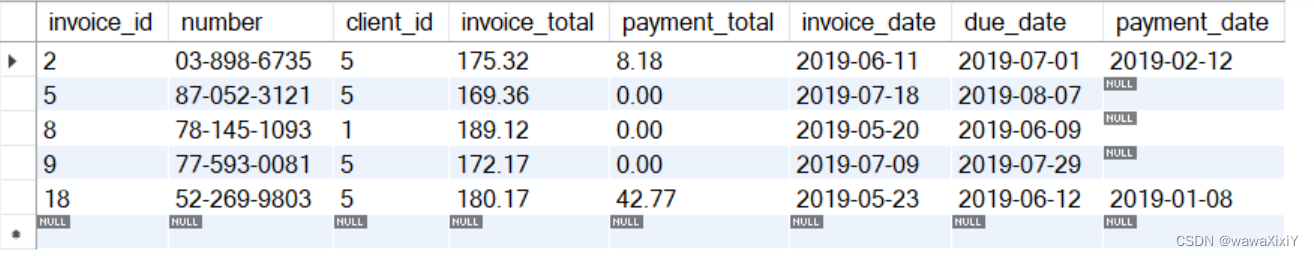
2:使用 where invoice_total > ALL ( )
select *
from invoices
where invoice_total > ALL (
select invoice_total
from invoices
where client_id = 3)
The ANY keyword
案例1:select 至少有两张 invoices 的客户信息
思路: 先在clients中选择出拥有两张及以上 invoices 的 client_id .
注意:count(*) 是聚合函数 ,要用group by , 和 having
select
client_id,
count(*)
from invoices
group by client_id
having count(*) >=2
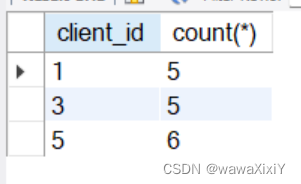
再从clients表中挑选出所有信息。 因为上述搜索存在两列,作为子查询,多列会报错,这里将select count(*)这列删去,只留下client_id这一列。
下列两种方法都是有效的。
IN 和 '= ANY' 是等效操作
select *
from clients
where client_id in(
select client_id
from invoices
group by client_id
HAVING count(*) > 1)
select *
from clients
where client_id = ANY
(
select client_id
from invoices
group by client_id
HAVING count(*) > 1)
Correlated subqueries | 相关子查询
选出 sql_hr.employees 里那些工资超过他所在办公室平均工资(而不是整体平均工资)的员工
就是员工和他所在部门的平均工资相比
两种方式如下: 在employee表上 创建一个虚拟的employee表。 我的理解是,外层每一个员工,和内层查询做比较,内层是计算相同部门员工的平均工资的。外层的员工和内层员工id 一样时进行比较
select *
from employees e
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from employees
where e.office_id = office_id
)
select *
from employees e
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from employees e2
group by office_id
having e.office_id = e2.office_id
)
练习
在 sql_invoicing 库 invoices 表中,找出高于每位顾客平均发票金额的发票. (每个client 可能有多个invoice,所以需要对每个client 求出他们的invoice平均值)。
三种方法:
select *
from invoices i
where invoice_total > (
select avg(invoice_total)
from invoices i2
where i.client_id = i2.client_id)
select *
from invoices i
where invoice_total > (
select avg(invoice_total)
from invoices i2
group by client_id
having i.client_id = i2.client_id)
-- 第三个运功了创建新表,然后筛选条件。最原始的方法。
主表连接了一个创建的新表(计算每个client的invoice平均值),
最后用主表中每一个client 和 虚拟虚拟表的平均值对比 ,得到答案
SELECT i.*
FROM invoices i
JOIN (
SELECT i2.client_id, AVG(i2.invoice_total) AS avg_invoice_total
FROM invoices i2
GROUP BY i2.client_id
) AS avg_table
ON i.client_id = avg_table.client_id
WHERE i.invoice_total > avg_table.avg_invoice_total;
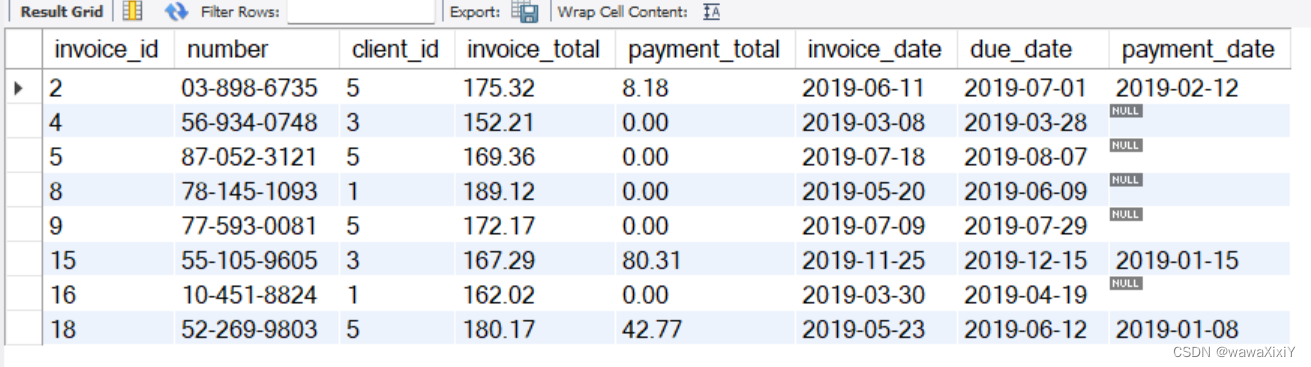
EXISTS operator
找出有过发票记录的客户
下方是三种方法:
1. 第一种是使用IN
2. 第二种是使用表连接的方法
3. 第三种是使用了exists()
SELECT *
FROM clients
WHERE client_id IN (
SELECT DISTINCT client_id
FROM invoices)
select distinct client_id, name, address, city, state, phone
from clients c
join invoices i
using(client_id)
select *
from clients c
where EXISTS(
select client_id
from invoices i
where c.client_id = i.client_id)
EXISTS() , 并不会返回一个具体的值,只会返回一个指令,告诉在子查询中是否存在符合搜索条件的行。如果存在,就会返回TRUE 给exists, 就会在结果中添加这个记录。
练习
在sql_store 中,找到那些从来没有被ordered的products
select *
from products p
where not exists (
select product_id
from order_items oi
where p.product_id = oi.product_id)
select *
from products p
where product_id not in(
select distinct product_id
from order_items oi
)
select *
from products p
left join order_items oi
using(product_id)
where oi.product_id is null
select 子句中的子查询
查询出下列表格
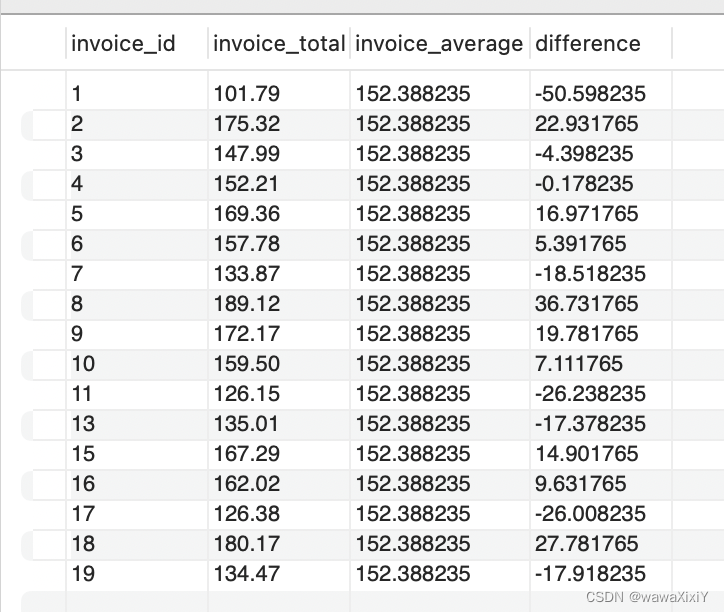
SELECT
invoice_id, invoice_total,
(SELECT AVG(invoice_total) from invoices) as invoice_average,
(select(invoice_total - invoice_average) )as difference
FROM
invoices
select(select()) 会对每一行都进行处理
select(select())可对as 后的别名进行处理
练习
完成下列查询(需要链接clients和invoices两表)
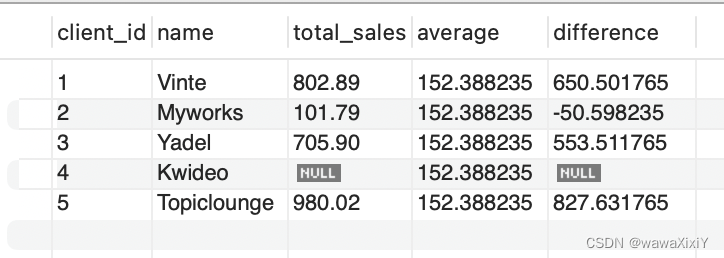
SELECT
c.client_id,
c.name,
(SELECT
SUM(invoice_total)
FROM
invoices i
WHERE
i.client_id = c.client_id) AS total_sales,
(SELECT
AVG(invoice_total)
FROM
invoices) AS average,
(SELECT total_sales - average)
FROM
clients c
针对第三列total_sales, 先把invoice_total进行求和,然后使用相关子查询,可以理解为创建一个虚拟表,和真实的表比较找出client_id是一样的用户 进行求和。
注意: (select )可以对别名进行操作
FROM字句中的子查询
案例
将上一节练习里的查询结果当作来源表,查询其中 total_sales 非空的记录
USE sql_invoicing;
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT
client_id,
name,
(SELECT SUM(invoice_total) FROM invoices WHERE client_id = c.client_id) AS total_sales,
(SELECT AVG(invoice_total) FROM invoices) AS average,
(SELECT total_sales - average) AS difference
FROM clients c
) AS sales_summury
/* 在FROM中使用子查询,即使用 “派生表” 时,
必须给派生表取个别名(不管用不用),这是硬性要求,不写会报错:
Error Code: 1248. Every derived table(派生表、导出表)
must have its own alias */
WHERE total_sales IS NOT NULL
复杂的子查询再嵌套进 FROM 里会让整个查询看起来过于复杂,上面这个最好是将子查询结果储存为叫 sales_summury 的视图,然后再直接使用该视图作为来源表,之后会讲。




















 425
425

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








