1、设计程序A和程序B,程序B每隔100ms向有名管道写入一个随机整数(值为0~100),程序A循环读取并打印有名管道数据,当连续出现3个50以上的数据时打印提示信息并暂停程序B,延时5s后继续启动程序B,然后继续读取数据。
有名管道通信;随机数产生
rand(): 它返回的最大值是RAND_MAX
srand ((int) time()); // 产生一个随机的随机数生成种子
i = (int)(100 * rand() /RAND_MAX); — >0 – 100
i=rand()%100; //取模
有名管道通信:
1)创建FIFO文件
#define FIFO_FILE_NAME “/tmp/my_fifo”
在B程序中:
mkfifo (FIFO_FILE_NAME, 0777); // 创建了一个管道文件,由最高权限
2)打开:读打开或者写打开
int fd;
fd = open(FIFO_FILE_NAME, O_WRONLY);//写打开
i = getpid(); //B的进程号 --发给A
write (fd, &i, sizeof(int));
while (1){
//i = (int)(100 * rand() /RAND_MAX);//随机写随机数
i=rand()%100;
write (fd, &i, sizeof(int));
sleep (1);//定时一百毫秒 延时1
}
A:读-----怎么写的信息怎么读
int fd;
fd = open(FIFO_FILE_NAME, O_RDONLY);
int B_pid;
read (fd, &B_pid, sizeof(int));
int i;
int k=0;
while (1){
read (fd, &i, sizeof(int));
if (i > 50) //判断得到的数是不是大于50,大于五十k+1
k ++;
else
k =0;
if (k >= 3){
kill (B_pid, SIGSTOP); // 当输入大于等于3次50时,暂停b的传输,停五秒在继续
sleep (5);
kill (B_pid, SIGCONT);
}
}
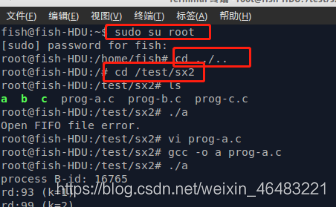
程序A代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define FIFO_FILE "/tmp/myfofo"
int main (void)
{
int fd;
int pid=0;
fd = open (FIFO_FILE, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1){
printf("Open FIFO file error.\n");
exit(-1);
}
if(read (fd, &pid, sizeof(int)) == -1){
printf ("Read error.\n");
exit(-2);
}
printf("process B-id: %d\n",pid);
int j=0, k=0;
while (1){
if (read (fd, &j, sizeof(int)) == -1)
exit(-1);
if(j>50)
k++;
else
k=0;
printf ("rd:%d (k=%d)\n", j, k);
if (k >= 3){
printf ("pause 5s.\n");
kill (pid, SIGSTOP);
k = 0;
}
}
close (fd);
return 0;
}
程序B代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<time.h>
#define FIFO_FILE "/tmp/myfofo"
int main(void){
int fd;
int res;
srand((int)time(0));
if(access(FIFO_FILE,F_OK)==-1){
printf("Create the fifo pipe.\n");
res=mkfifo(FIFO_FILE,0777);
if(res!=0){
fprintf(stderr,"Could not create fifo %s\n",FIFO_FILE);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
fd=open(FIFO_FILE,O_WRONLY);
if(fd==-1){
printf("Open FIFO file error.\n");
exit(-1);
}
int i,kk;
i=getpid();
printf("Current•pid:%d\n",i);
if(write(fd,&i,sizeof(int))==-1){
printf("Read error.\n");
exit(-2);
}
i=0;
while(1){
kk=(int)(100.0*rand()/RAND_MAX);
write(fd,&kk,sizeof(kk));
printf("rand:%-3d(times=%d)\n",kk,i++);
if(i==-1){
printf("write error.\n");
exit(-1);
}
sleep(1);
}
close(fd);
printf("Ene write.\n");
return 0;
}
**2、用alarm定时信号,设计一个程序C,每隔5s生成5个随机字符(‘a’~’z’),当用户看到这5个随机字符后,若对照输入正确,则成功次数加1,错误则次数清零,每次回车后显示成功次数。
rand(): 它返回的最大值是RAND_MAX
srand ((int) time()); // 产生一个随机的随机数生成种子
i = (int)(26 * rand() /RAND_MAX); — >0 – 100
‘a’ + i —> ‘a’ ‘z’ //i=0 a ; =25 z
等输入:5s

重新打开终端 进入管理员模式 cd跳转到sx2文件夹
Vi编辑 -----编译-----运行。
root@fish-HDU:/test/sx2# vi prog-c.c
root@fish-HDU:/test/sx2# gcc -o c prog-c.c
root@fish-HDU:/test/sx2# ./c

代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
int pid;
int succ_times=0;
void sig_handler(int num )
{
printf("\ntimeover, Input <Enter> to continue ...\n");
succ_times=0;
}
int main()
{
int i;
char bufa[10], bufb[10];
pid = getpid ();
srand ((int)time(0));
signal(SIGALRM,sig_handler);
alarm (5);
while(1)
{
printf ( "Enter what you see in 5s: \n\n ");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
bufa[i] ='a'+(int)(26.0*rand()/RAND_MAX);
printf ("%c ",bufa[i]);
}
printf ("\n\n Enter: ");
bufa[i] = '\0';
fgets (bufb, 5, stdin);
bufb[i] = '\0' ;
if (bufb[0] =='0')
break;
if (strcmp(bufa, bufb) == 0)
succ_times++;
else
succ_times = 0;
printf("continue successed times = %d.\n", succ_times);
alarm (5);
}
printf ("Test end.\n" );
}







 本文介绍了如何设计两个程序A和B,程序B通过有名管道每100ms向管道写入0~100的随机整数,程序A读取并打印,当连续3次出现50以上数值时暂停B,5s后恢复。同时,展示了程序C如何利用alarm定时信号,每5s生成5个随机字母,用户输入正确则成功次数+1,错误则清零。
本文介绍了如何设计两个程序A和B,程序B通过有名管道每100ms向管道写入0~100的随机整数,程序A读取并打印,当连续3次出现50以上数值时暂停B,5s后恢复。同时,展示了程序C如何利用alarm定时信号,每5s生成5个随机字母,用户输入正确则成功次数+1,错误则清零。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








