这周日的白天没什么事可做,花一天的时间做下新生第二轮考核里边的简单搜索专题,复习一下基础的bfs和dfs,练练手,前几天也做几道贪心练下思维(最近思维题做得比较少,脑子有点短路了…)。
简单搜索:
A - Red and Black (HDU - 1312)

这道题是要我们找跟’@’同属一个连通块的’.’个数,所以直接搜索找符合条件的数量就可以了,统计过的标记下即可(水题)。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
int n, m, s[25][25], vis[25][25], a[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, b[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
char u[25][25];
int bfs(int p, int q){
if(vis[p][q]) return 0;
vis[p][q] = 1;
int ans = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int x = p + a[i], y = q + b[i];
if(u[x][y] == '.' && x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m){
ans += bfs(x, y);
vis[x][y] = 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int p, q;
while(cin >> m >> n){
if(m == 0 && n == 0) break;
memset(s, 0, sizeof s);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin >> u[i][j];
if(u[i][j] == '@'){
p = i, q = j;
}
}
}
cout << bfs(p, q) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B - Knight Moves (HDU - 1372)

这道题是8 * 8的棋盘上的两个点,找到从一个点到另一个点的最短操作次数,每次操作只能进行象棋里“马”能走的操作,典型的宽搜(水题)。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
char w[5], v[5];
int s, vis[10][10];
int a[8] = {1, 1, 2, 2, -1, -1, -2, -2}, b[8] = {2, -2, 1, -1, 2, -2, 1, -1};
struct node{
int x, y, s;
};
int bfs(){
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
queue<node> q;
node p;
p.x = w[0] - 'a', p.y = w[1] - '1', p.s = 0;
vis[p.x][p.y] = 1;
int ex = v[0] - 'a', ey = v[1] - '1';
if(p.x == ex && p.y == ey) return p.s;
q.push(p);
while(!q.empty()){
node u = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
node t;
t.x = u.x + a[i], t.y = u.y + b[i];
if(t.x == ex && t.y == ey) return u.s + 1;
if(t.x >= 0 && t.y >= 0 && t.x < 8 && t.y < 8 && vis[t.x][t.y] == 0){
t.s = u.s + 1;
vis[t.x][t.y] = 1;
q.push(t);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while(~scanf("%s%s", w, v)){
printf("To get from %s to %s takes %d knight moves.\n", w, v, bfs());
}
return 0;
}
C - Oil Deposits (HDU - 1241)

找总共有多少个连通块,斜着也算是一个连通块,直接搜索,满足题意的坐标且已被搜索过的点要变成’*’,最后把不同连通块的个数累加在一起即可。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
char u[105][105];
int n, m, a[8] = {0, 0, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1}, b[8] = {-1, 1, -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 1};
void bfs(int p, int q){
u[p][q] = '*';
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
int x = p + a[i], y = q + b[i];
if(x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m && u[x][y] == '@') bfs(x, y);
}
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while(cin >> n >> m){
int ans = 0;
if(n == 0 && m == 0) break;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin >> u[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(u[i][j] == '@'){
bfs(i, j);
ans++;
}
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
D - Rescue (HDU - 1242)

其实这道题我走了弯路,用dfs做比用bfs做简单,因为dfs只要一直搜索,然后记录到达目的坐标的最小值即可。而bfs要用优先队列做,因为每遇到’x’,走一步的代价是2,所以从一个点到另一点扩充的时候,如果是普通的队列,早入队的节点中s(操作的代价)不一定比晚入队的节点中s(操作的代价)少,所以要维护一个优先队列,才能保证最后返回的是两个点之间操作的最小代价。因为是多组输入,所以在处理每组数据调用bfs函数的时候要把优先队列的元素(上一组数据得到的)都弹出。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
int n, m, sx, sy, ex, ey, ans, vis[205][205], a[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1}, b[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
char u[205][205];
struct node{
int x, y, s;
};
priority_queue<node> q;
bool operator<(const node a, const node b){
return a.s > b.s;
}
int bfs(int x, int y){
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
node p;
p.x = x, p.y = y, p.s = 0;
q.push(p);
while(!q.empty()){
node t = q.top();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
node v;
v.x = t.x + a[i], v.y = t.y + b[i], v.s = t.s + 1;
if(v.x == ex && v.y == ey) return v.s;
if(v.x >= 0 && v.y >= 0 && v.x < n && v.y < m && (u[v.x][v.y] == '.' || u[v.x][v.y] == 'x') && vis[v.x][v.y] == 0){
if(u[v.x][v.y] == 'x') v.s++;
q.push(v);
vis[v.x][v.y] = 1;
}
}
}
return INF;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while(cin >> n >> m){
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin >> u[i][j];
if(u[i][j] == 'r') sx = i, sy = j;
else if(u[i][j] == 'a') ex = i, ey = j;
}
}
debug(sx, sy);
debug(ex, ey);
ans = bfs(sx, sy);
if(ans == INF) cout << "Poor ANGEL has to stay in the prison all his life.\n";
else cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
E - 迷宫问题 (POJ - 3984)

这道题也是经典的搜索版题,要注意确定到达某个点的最短操作次数的时候,把它前面的点记录下来,最后递归输出这些点的坐标即可。
具体的实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
int u[5][5], prex[5][5], prey[5][5], ans[5][5], a[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, b[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int n = 5, m = 5
void bfs(int p, int q){
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int x = p + a[i], y = q + b[i];
if(x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m && u[x][y] == 0){
if((ans[p][q] + 1) < ans[x][y]){
ans[x][y] = ans[p][q] + 1;
prex[x][y] = p, prey[x][y] = q;
bfs(x, y);
}
}
}
return;
}
void print(int x, int y){
if(x == 0 && y == 0){
cout << "(0, 0)\n";
return;
}
print(prex[x][y], prey[x][y]);
cout << "(" << x << "," << " " << y << ")\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){
cin >> u[i][j];
}
}
memset(ans, INF, sizeof ans);
ans[0][0] = 0;
bfs(0, 0);
print(4, 4);
return 0;
}
F - 棋盘问题 (POJ - 1321)
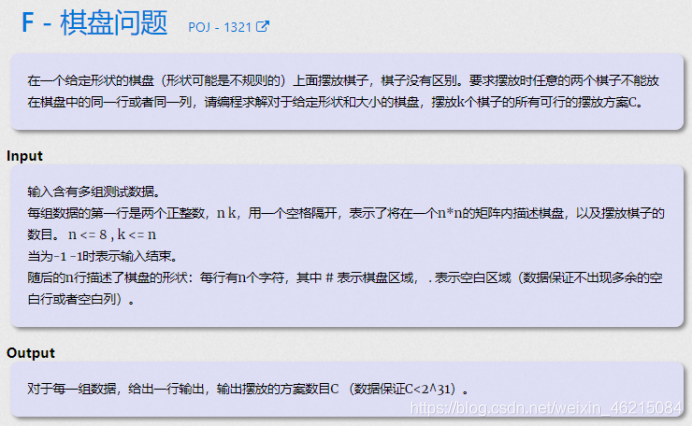
直接深搜记录前i行哪些列有棋子,如果把所有棋子都摆好了,则可行方案数加一,之后回溯,注意每次dfs的时候,要传入参数,表示前r行已经排好了,接下来将从第r + 1行开始放棋子。
具体的实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
int n, k, ans;
char u[10][10];
int y[10];
void dfs(int t, int r){
if(t == k){
ans++;
return;
}
for(int i = r + 1; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(u[i][j] == '#' && !y[j]){
y[j]++, t++;
dfs(t, i);
y[j]--, t--;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while(cin >> n >> k){
ans = 0;
if(n == -1) break;
memset(y, 0, sizeof y);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
cin >> u[i][j];
}
}
dfs(0, -1);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
G - Find The Multiple (POJ - 1426)

这道题需要用到dfs来解决,而且这道题的测试数据得到的倍数的位数恰好不超过20,正好符合long long的数据范围,所以直接定一个long long类型的整数记录数据即可,若m是n的倍数,则直接返回并输出m。调用dfs函数时,如果遇到m是n的倍数,要把标记为1,题目要求只要一个倍数即可,所以dfs函数中当标记为1时,不断return。
具体的实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
int n, flag;
void dfs(LL m, int n, int s){
if(flag ||s == 20) return;
if(m % n == 0){
flag = 1;
cout << m << endl;
return;
}
dfs(m * 10 + 1, n, s + 1);
dfs(m * 10, n, s + 1);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while(cin >> n){
if(n == 0) break;
flag = 0;
dfs(1, n, 1);
}
return 0;
}
H - 统计问题 (HDU - 2563)

没啥好讲的,直接递推…
具体的实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
int dp[25];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
dp[1] = 3;
dp[2] = 7;
for(int i = 3; i <= 20; i++){
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] * 2 + dp[i - 2];
}
int t, n;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n;
cout << dp[n] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
I - LETTERS (POJ - 1154)

这道题用dfs做,重点是记录到达某个点的时候,前面经过的点里的字母有什么,所以要用一个vis数组保存以A ~ Z为下标的字母是否已经走过了,每次更新经过字母数量的最大值,直到“无路可走”就回溯。
具体的实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
char o[25][25];
int ans, vis[30], u[25][25], a[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, b[4] = {1 , -1, 0, 0};
int n, m;
void dfs(int p, int q, int s){
ans = max(ans, s);
vis[u[p][q]]++;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int x = p + a[i], y = q + b[i];
if(x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m && !vis[u[x][y]]){
dfs(x, y, s + 1);
vis[u[x][y]]--;
}
}
}
int main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while(cin >> n >> m){
ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin >> o[i][j];
u[i][j] = o[i][j] - 'A';
debug(o[i][j]);
}
}
dfs(0, 0, 1);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
J - N皇后问题 (HDU - 2553)

经典的dfs算法,主要是用加减法表示两个棋子是否在同一个对角线上…
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
int n, ans, cnt,flag, s[15], u[15];
void dfs(int cnt){
if(cnt == n){
ans++;
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
u[cnt] = i;
flag = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < cnt; j++){
if(i == u[j] || u[cnt] + cnt == u[j] + j || u[cnt] - cnt == u[j] - j){
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
if(flag) dfs(cnt + 1);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
n = i;
ans = 0;
dfs(0);
s[i] = ans;
debug(i, s[i]);
}
while(cin >> n){
if(!n) break;
cout << s[n] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
贪心:
AcWing 905. 区间选点

经典的区间选点问题,每个区间按照右端点从小到大进行排序,先选第一个区间的右端点为第一个点,不断遍历后面的区间,如果遇到某个区间的左端点在这个点的右边,则再选这个区间的右端点为新的点,这样循环下去即得最终答案。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
struct node{
int l, r;
bool operator < (const node & A) const{
return r < A.r;
}
}u[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> u[i].l >> u[i].r;
}
sort(u, u + n);
int ans = 0, ed = -2e9;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(u[i].l > ed){
ans++;
ed = u[i].r;
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
AcWing 908. 最大不相交区间数量

这道题的代码跟上道题一模一样,上一道题选的点所在的区间就是这道题所选的区间。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
struct node{
int l, r;
bool operator < (const node & A) const{
return r < A.r;
}
}u[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> u[i].l >> u[i].r;
}
sort(u, u + n);
int ans = 0, ed = -2e9;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(u[i].l > ed){
ans++;
ed = u[i].r;
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
AcWing 906. 区间分组

贪心决策:从前往后枚举每个区间,判断此区间能否将其放到现有的组中,如果一个区间的左端点比最小组的右端点要小,u[i].l <= c.top(),就开一个新组c.push(u[i].r);
如果一个区间的左端点比最小组的右端点要大,则放在该组,c.pop(), c.push(u[i].r);
每组去除右端点最小的区间,只保留一个右端点较大的区间,这样c有多少区间,就有多少组。(c是一个小根堆,维护的是每个组所有区间最右端点的最小值)
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
struct node{
int l, r;
bool operator < (const node & A) const{
return l < A.l;
}
}u[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
u[i] = {l, r};
}
sort(u, u + n);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > c;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(c.empty() || c.top() >= u[i].l) c.push(u[i].r);
else{
c.pop();
c.push(u[i].r);
}
}
cout << c.size();
return 0;
}
AcWing 907. 区间覆盖


具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
struct node{
int l, r;
bool operator < (const node & A) const{
return l < A.l;
}
}u[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
int st, ed;
cin >> st >> ed;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
u[i] = {l, r};
}
sort(u, u + n);
int flag = 0, ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int r = -2e9, j = i;
while(j < n && u[j].l <= st){
r = max(r, u[j].r);
j++;
}
if(r == -2e9) break;
ans++;
if(r >= ed){
flag = 1;
break;
}
st = r;
j = i - 1;
}
if(!flag) cout << "-1";
else cout << ans;
return 0;
}
AcWing 148. 合并果子

经典哈夫曼树的模型,每次合并重量最小的两堆果子即可。
时间复杂度:使用小根堆维护所有果子,每次弹出堆顶的两堆果子,并将其合并,合并之后将两堆重量之和再次插入小根堆中。每次操作会将果子的堆数减一,一共操作n - 1次即可将所有果子合并成1堆。每次操作涉及到2次堆的删除操作和1次堆的插入操作,计算量是O(logn),因此总时间复杂度是O(nlogn)。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
int ans;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> u;
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int x;
cin >> x;
u.push(x);
}
while(u.size() > 1){
int a = u.top();
u.pop();
int b = u.top();
u.pop();
u.push(a + b);
ans += a + b;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
AcWing 913. 排队打水.

水题…
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
int a[N];
LL ans;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ans += a[i] * (n - i - 1);
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
AcWing 104. 货仓选址

把货仓建在中位数的位置,它能保证左右有对应的两点到这个位置的距离和最小,是这两个点的局部最优解,所有点两两一组都有局部最优解,合起来就是全局最优解,所以货仓建在中位数的位置能保证总距离和最小。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 100005;
int a[N];
LL ans;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >>a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ans += abs(a[i] - a[n / 2]);
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
AcWing 125. 耍杂技的牛



具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
const int N = 50005;
struct node{
int w, s;
bool operator < (const node & A) const{
return w + s < A.w + A.s;
}
}u[50005];
LL ans = -2e9, sum;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int w, s;
cin >> w >> s;
u[i].w = w;
u[i].s = s;
}
sort(u, u + n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ans = max(ans, sum - u[i].s);
sum += u[i].w;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








