注解的使用
引入外部的properties文件
首先创建配置文件
创建beans6.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="druid" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/maclu"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试
@Test
public void Tses15(){
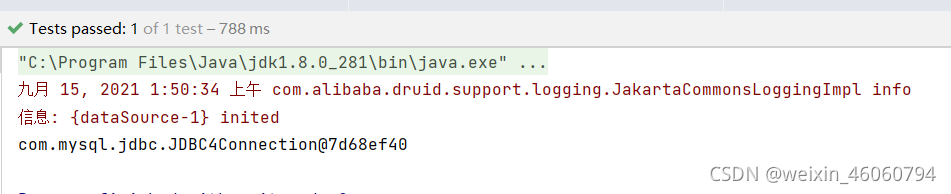
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans6.xml");
DruidDataSource druid = context.getBean("druid", DruidDataSource.class);
DruidPooledConnection connection = null;
try {
connection = druid.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果
或者先添加druid的pom依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
创建beans7.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="druid" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
结果
依赖注入
1)Spring配置文件引入context约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.3.xsd">
</beans>
2)Spring配置文件中开启注解扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.3.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cqucc" />
</beans>
在classpath中的扫描组件:component-scan,他能够在classpath中自动扫描,自动检查和实例化具有特定注解的组件。
特定组件包括
- @Component :组件通用注解,标识一个受Spring管理的组件
- @Controller :常用于对表现标注
- @Service:常用于对服务层(业务层)标注
- @Repository:常用于对持久层标注
@Component、@Controller、@Service和@Repository功能一样,可以互换,我们使用不同注解主要为了区分被注解的类处在不同的业务层,使逻辑更加清晰。
它们使用方法:
(1)标注在类上
(2)@Component("name")等于@Component(value="user")
(3)@Component相当于@Component("className")
3)案例
Users类
package com.cqucc.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Users {
private Integer userid;
private String usernama;
private String password;
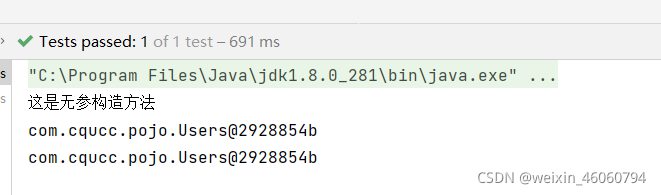
public Users (){
System.out.println("这是无参构造方法");
}
public Users(Integer userid, String usernama, String password) {
System.out.println("这是有参构造方法");
this.userid = userid;
this.usernama = usernama;
this.password = password;
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getUsernama() {
return usernama;
}
public void setUsernama(String usernama) {
this.usernama = usernama;
}
public Integer getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(Integer userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Users{" +
"userid=" + userid +
", usernama='" + usernama + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
编写测试类:
@Test
public void Tses(){
ApplicationContext act = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans8.xml");
Users users = act.getBean(Users.class);
Users users2 = act.getBean("users",Users.class);
System.out.println(users);
System.out.println(users2);
}
测试结果
注:在注解中value属性值可以省略不写,
@Test
public void Tses17(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans8.xml");
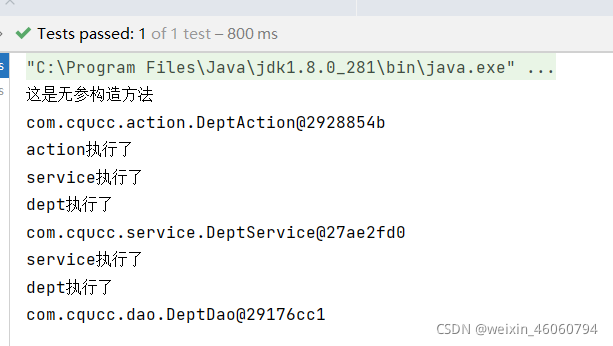
DeptAction deptAction = context.getBean(DeptAction.class);
System.out.println(deptAction);
deptAction.show();
DeptService deptService = context.getBean(DeptService.class);
System.out.println(deptService);
deptService.show();
DeptDao deptDao = context.getBean(DeptDao.class);
System.out.println(deptDao);
}
,首字母小写
4)属性注入
4.1@Autowired
自动注入的方式进行注入,默认根据类的名称来进行装配
DeptDao类
package com.cqucc.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class DeptDao {
public void show(){
System.out.println("dept执行了");
}
}
DeptService 类
package com.cqucc.service;
import com.cqucc.dao.DeptDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptDao deptDao;
public void show(){
System.out.println("service执行了");
deptDao.show();
}
}
DeptAction 类
package com.cqucc.action;
import com.cqucc.service.DeptService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class DeptAction {
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
public void show(){
System.out.println("action执行了");
deptService.show();
}
}
测试类
@Test
public void Tses17(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans8.xml");
DeptAction deptAction = context.getBean(DeptAction.class);
System.out.println(deptAction);
deptAction.show();
DeptService deptService = context.getBean(DeptService.class);
System.out.println(deptService);
deptService.show();
DeptDao deptDao = context.getBean(DeptDao.class);
System.out.println(deptDao);
}
测试结果
@Autowired注意事项:
默认情况下,所有使用@Autowired注解的属性都需要被设置。当Spring找不到匹配的bean装配属性时,会抛出异常。
如去掉DeptAction 类中的的@Autowired时
package com.cqucc.action;
import com.cqucc.service.DeptService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class DeptAction {
private DeptService deptService;
public void show(){
System.out.println("action执行了");
deptService.show();
}
}
//测试方法
@Test
public void Tses17(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans8.xml");
DeptAction deptAction = context.getBean(DeptAction.class);
System.out.println(deptAction);
deptAction.show();
}
测试结果
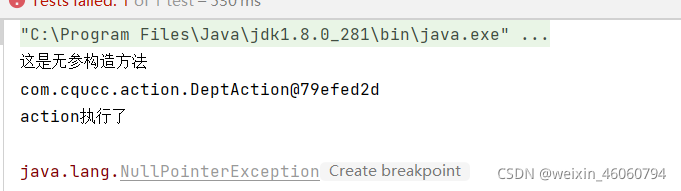
4.2 @Qualifier
@Autowired是按照类型进行匹配,如果当前@Autowired标注的依赖在容器中只能找到一个实例一致对应的话,那还好。可是,要是能够同时找到多个或者同一类型的对象实例,那该怎么办?可以使用@Qualifier对依赖注入的条件做进一步限定。如下
定义接口
package com.cqucc.dao;
public interface DeptDaoInter {
public void show();
}
实现接口的两个类
package com.cqucc.dao.Impl;
import com.cqucc.dao.DeptDaoInter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class DeptDao implements DeptDaoInter {
public void show(){
System.out.println("dept执行了");
}
}
package com.cqucc.dao.Impl;
import com.cqucc.dao.DeptDaoInter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class DeptDao1 implements DeptDaoInter {
public void show(){
System.out.println("dept1执行了");
}
}
测试类
@Test
public void test18(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans9.xml");
DeptService deptService = context.getBean(DeptService.class);
System.out.println(deptService);
}
结果:
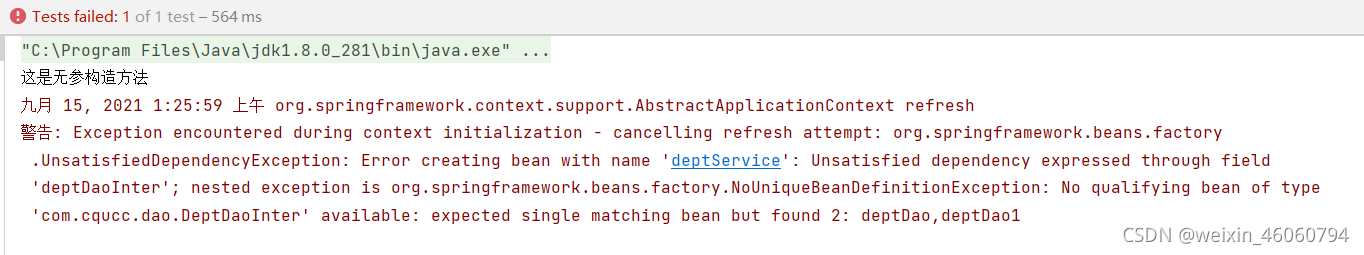
当添加 @Qualifier("deptDao1")后
package com.cqucc.service;
import com.cqucc.dao.DeptDaoInter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("deptDao1")
private DeptDaoInter deptDaoInter;
public void show(){
System.out.println("service执行了");
deptDaoInter.show();
}
}
测试结果
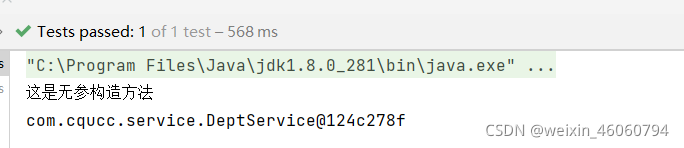
4.3 @Resource
@Resource(name = "deptDao1")相当于@Autowired+@Qualifier("name")
package com.cqucc.service;
import com.cqucc.dao.DeptDaoInter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class DeptService {
// @Autowired
// @Qualifier("deptDao1")
@Resource(name = "deptDao1")
private DeptDaoInter deptDaoInter;
public void show(){
System.out.println("service执行了");
deptDaoInter.show();
}
}
测试结果
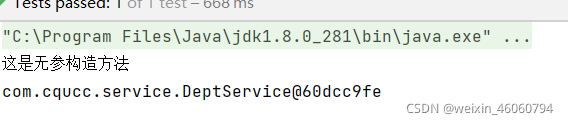
5)包含(不包含)组件
<context:component-scan>提供了两个子标签
- <context:include-filter>
- <context:exclude-filter>
在说明这两个子标签前,先说一下<context:component-scan>有一个use-default-filters属性,该属性默认为true,这就意味着会扫描指定包下的全部的标有Spring注解的类,并注册成bean。也就是@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Reposity等。所以如果仅仅是在配置文件中这么写
<context:component-scan base-package="com.*"/>
use-default-filter此时为true那么会对base-package包或者子包下的所有的进行java类进行扫描,并把匹配的java类注册成bean。
可以发现这种扫描的粒度有点太大,如果你只想扫描指定包下面的Controller,该怎么办?此时子标签<context:incluce-filter>就起到了勇武之地。如下所示
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cqucc" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
这样就会只扫描base-package包或者子包下所有@Controller下的java类,并注册成bean。
去访问除了@Controller以为的类会包下面的错误
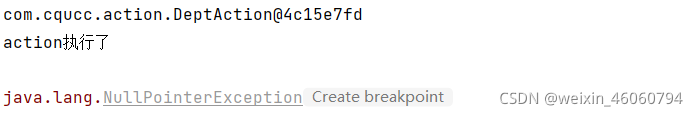
如果不想扫描指定包下面的Controller时,需要使用<context:exclude-filter>标签
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cqucc">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
去访问@Controller以为的类会包下面的错误
6)无配置注解
@Configuration用于定义配置类,可替换xml配置文件,被注解的类内部包含有一个或多个被@Bean注解的方法,这些方法将会被AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext类进行扫描,并用于构建bean定义,初始化Spring容器。
注意:@Configuration注解的配置类有如下要求:
@Configuration不可以是final类型;
@Configuration不可以是匿名类;
嵌套的configuration必须是静态类。
如下:
package com.cqucc.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.cqucc"})
public class SpringConfig {
public SpringConfig(){
System.out.println("容器启动初始化...");
}
}
测试类
@Test
public void test20(){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
DeptAction action = context.getBean(DeptAction.class);
System.out.println(action);
action.show();
}
结果
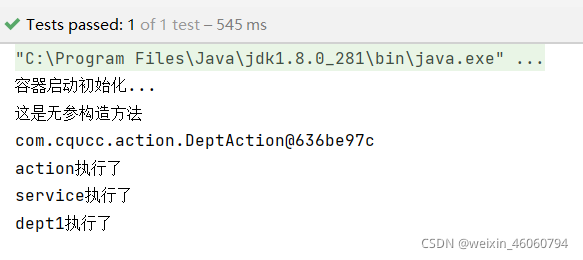























 1891
1891

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








