- 传统vue是单向数据流。如果是兄弟组件之间传值兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力
- 我们经常会采用父子组件通过正向/逆向传值来对数据进行传递。以上的这些模式非常脆弱,通常会导致无法维护的代码。
- vuex只能用于单个页面中不同组件(例如兄弟组件)的数据流通。
1.安装
npm install vuex --save
配置vuex文件创建在src中创建store文件夹–>与store.js
2.main.js引入
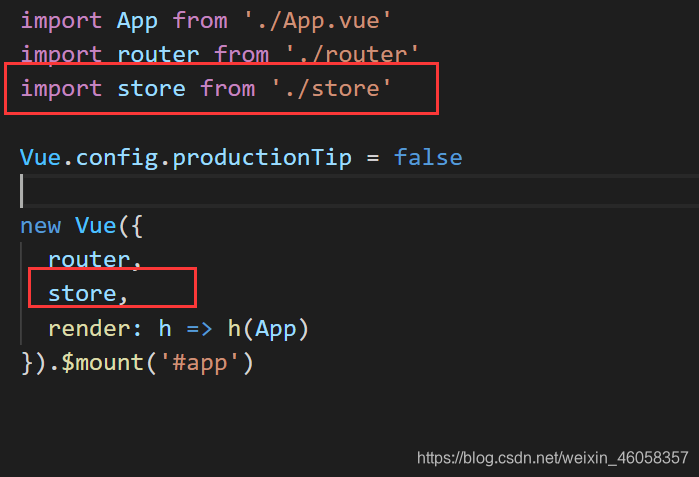
4.创建store/index.js实例
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
5.vuex-- State数据源-储存
(1)书写数据,vuex中的数据源state,我们需要保存的数据就保存在这里
state: { //存数据
arr: [
{ id: 1, name: "小哈", age: 184 },
{ id: 11, name: "小白", age: 181 },
{ id: 12, name: "小在", age: 187},
{ id: 13, name: "小的", age: 186 },
{ id: 4, name: "小给", age: 181 },
{ id: 17, name: "小后", age: 180 },
]
},
(2)使用数据源
<template>
<div>
{{$store.state.arr[1].name}} <!--1.可以使用$store.state.xx调用,在页面中使用-->
{{obj}} <!--2.计算属性调用this. $store. state.xxx,在js中使用-->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed:{
obj(){
return this.$store.state.arr[1]
}
}
}
</script>
6.vuex-- Mutations–修改
(1)写入
mutations: { //修改数据 stateYaxu就是state中的数据
add(stateYaxu){
stateYaxu.arr[1].name="小黑" //修改小白为小黑
}
},
(2)使用
<template>
<div>
<button @click="fun()">点我修改vuex种存储的数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
fun(){
this.$store.commit("add")
}
},
}
</script>
payload也能传
mutations: { //修改数据 stateYaxu就是state中的数据
// add(stateYaxu){
// stateYaxu.arr[1].name="小黑"
// }
add(stateYaxu,payload){
stateYaxu.arr[1].name=payload
}
},
<template>
<div>
<button @click="fun()">点我修改vuex种存储的数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
// fun(){
// this.$store.commit("add")
// }
fun(){
this.$store.commit("add",1111) //**111即为修改后的值**
}
}
}
</script>
vuex–Mutations问题
- vuex中页面刷新数据丢失问题
- 使用vue进行开发的过程中,状态管理工具-般使用vuex进行管理。但是修改后的vuex数据存储在内存中,所以当前页面刷新数据会产生丢失现象
- 使用H5特性本地存储
在使用页面写入,保证刷新页面的时候VUEX中修改后的数据不丢失
created () {
//在页面加载时读取localStorage里的状态信息
if (localStorage.getItem("data") ) {
//replaceState替换数据 Object.assign合并对象
this.$store.replaceState(Object.assign({}, this.$store.state,JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("data"))))
}
//在页面刷新时将vuex里的信息保存到localStorage里
window.addEventListener("beforeunload",()=>{
localStorage.setItem("data",JSON.stringify(this.$store.state))
})
},
7.vuex–Actions–异步操作
(1)异步封装请求(看不懂封装点击这里),并用函数obj包住,方便传输
actions: {
obj() {
vuexAxios().then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
}
},

(2)使用页面接收
语句: this.$store.dispatch(“xxx”)
<template>
<div>
VUEX的一个异步请求
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
created() {
//调用vuex中的actions的异步请求
this.$store.dispatch("obj")
},
}
</script>
3.把actions请求来的数据给state



存入state中
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import {vuexAxios} from '@/api/indexVuex.js'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: { //存数据
arr: [
{ id: 1, name: "小哈", age: 184 },
{ id: 11, name: "小白", age: 181 },
],
yaxu:{}
},
mutations: { //修改数据 stateYaxu就是state中的数据
// add(stateYaxu){
// stateYaxu.arr[1].name="小黑"
// }
add(stateYaxu,payload){
stateYaxu.arr[1].name=payload
},
mudd(storeVuex,payload){
storeVuex.yaxu=payload //3.写入storeVuex,payload,用state接收
}
},
actions: {
obj(storeVuex) { //1.storeVuex形参随便起名
vuexAxios().then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data)
storeVuex.commit("mudd",res.data) // 2.调用mutations中的方法
})
}
},
modules: {
}
})
4.在需要的页面调用即可
<h1>{{$store.state.yaxu.name}}</h1>
<h1>{{$store.state.yaxu.honm}}</h1>

8.vuex–Getters属性
- getters相当于之前组件中学习的计算属性,getters属性主要是对于state中数据的一种过滤
- 使用场景:在项目开发中,有时候希望对state中的某个属性在多个组件中展示出不同状态
(1)写入
//vuex中的计算属性
getters: {
newname(state) { //state(形参,随便起名)就是存储的数据库
return '<<' + state.arr[1].age + ">>"
}
},
(2)使用–与使用state相同在组件中的"计算属性"当中使用this. $store.getters.xxx来进行调用
{{$store.getters.newname}}
特性
- getters 可以对State进行计算操作,它就是Store的计算属性
- 虽然在组件内也可以做计算属性,但是getters 可以在多组件之间复用
- 如果一个状态只在一个组件内使用一次或者使用了多次但是展示的形 态相同,是可以不用getters
9.vuex–Mutations kw54-50
- 在Vue中State使用是单一状态树结构,应该的所有的状态都放在state里面
如果项目比较复杂,那state是-一个很大的对象,store对象也将对变得非常大,难于管理。 - module:可以让每一个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、 action、getters,使得结构非常清晰,方便管理。
(1)写入
a.创建文件容纳模块(在store中创建modelew文件,再创建tabbarModule.js)
export let modulesVue=({
state: {
test:"我和我的祖国"
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
b.在vuex中引入模块
import { modulesVue } from './module/tabbarModule.js'
modules: {
modulesVue
}
(2)使用
使用数据: $store.state.模块名 .xxx
修改数据:和没有modules的时候一样。
{{$store.state.modulesVue.test}}
未完待续
扩展
切割函数,不用$store.state.CinemaList类似这样嵌套这么深,看着难受
import {mapState} from 'vuex' //1.引入 mapState是vuex提供的切割函数
state=mapState getters=mapGetters mutations=mapMutations actions=mapActions
// mapState([""]), //2.在computed计算属性中传入数组 mapGetters用法一致
//mapMutations([""]) //3.方法的话要在methods传入 mapActions用法一致
...mapState(["CinemaList"]), //3.展开后就可以用CinemaList替换$store.state.CinemaList
...mapMutations("tabbarModule",["hide","show"]) //tabbarModule里面有hide和show两种方法,调用的话即为:hide(),show()
示例
修改前 var newarr = this.$store.state.CinemaList.map(
(item) => item.districtName
);
修改后 var newarr = this.CinemaList.map(
(item) => item.districtName
);
用上面的方法的话,用module就要有点修改
(1)namespaced:true, //开启命名空间
export let modulesVue=({
namespaced:true, //开启命名空间
state: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
getters:{
},
modules: {
}
})
(2)解构写法:解构的地方输入"tabbarModule",大意是从tabbarModule命名空间中找到isTabberShow,这样就好了
computed: {
//从tabbarModule命名空间中找到isTabberShow
...mapState("tabbarModule",["isTabberShow"])
},
扩展(2)普通写法:大意是从cinmeaModule命名空间中找到getCinemeAction
this.$store.dispatch("cinmeaModule/getCinemeAction")
xixi-7-24-2
























 284
284

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








