为PHP版本常见问题
错误提示
Deprecated: Methods with the same name as their class will not be constructors in a future version of PHP; StringReader has a deprecated constructor in D:\phpstudy_pro\WWW\project\includes\php-gettext\streams.php on line 48
Deprecated: Methods with the same name as their class will not be constructors in a future version of PHP; gettext_reader has a deprecated constructor in D:\phpstudy_pro\WWW\project\includes\php-gettext\gettext.php on line 36
错误分析
这些警告信息表明您正在使用的代码中有一些类构造函数的定义方式在PHP的未来版本中将不再被支持。具体来说,这些警告指的是类的方法名称与类名相同,并且它们被当作构造函数使用,这在PHP 7.x中已经被弃用,并在PHP 8.x中完全移除。
代码修改
初始代码
以streams.php为例
<?php
class StreamReader
{
// should return a string [FIXME: perhaps return array of bytes?]
function read($bytes)
{
return false;
}
// should return new position
function seekto($position)
{
return false;
}
// returns current position
function currentpos()
{
return false;
}
// returns length of entire stream (limit for seekto()s)
function length()
{
return false;
}
};
class StringReader
{
var $_pos;
var $_str;
function StringReader($str = '')
{
$this->_str = $str;
$this->_pos = 0;
}
function read($bytes)
{
$data = substr($this->_str, $this->_pos, $bytes);
$this->_pos += $bytes;
if (strlen($this->_str) < $this->_pos)
$this->_pos = strlen($this->_str);
return $data;
}
function seekto($pos)
{
$this->_pos = $pos;
if (strlen($this->_str) < $this->_pos)
$this->_pos = strlen($this->_str);
return $this->_pos;
}
function currentpos()
{
return $this->_pos;
}
function length()
{
return strlen($this->_str);
}
};
class FileReader
{
var $_pos;
var $_fd;
var $_length;
function FileReader($filename)
{
if (file_exists($filename)) {
$this->_length = filesize($filename);
$this->_pos = 0;
$this->_fd = fopen($filename, 'rb');
if (!$this->_fd) {
$this->error = 3; // Cannot read file, probably permissions
return false;
}
} else {
$this->error = 2; // File doesn't exist
return false;
}
}
function read($bytes)
{
if ($bytes) {
fseek($this->_fd, $this->_pos);
// PHP 5.1.1 does not read more than 8192 bytes in one fread()
// the discussions at PHP Bugs suggest it's the intended behaviour
$data = '';
while ($bytes > 0) {
$chunk = fread($this->_fd, $bytes);
$data .= $chunk;
$bytes -= strlen($chunk);
}
$this->_pos = ftell($this->_fd);
return $data;
} else return '';
}
function seekto($pos)
{
fseek($this->_fd, $pos);
$this->_pos = ftell($this->_fd);
return $this->_pos;
}
function currentpos()
{
return $this->_pos;
}
function length()
{
return $this->_length;
}
function close()
{
fclose($this->_fd);
}
};
// Preloads entire file in memory first, then creates a StringReader
// over it (it assumes knowledge of StringReader internals)
class CachedFileReader extends StringReader
{
function CachedFileReader($filename)
{
if (file_exists($filename)) {
$length = filesize($filename);
$fd = fopen($filename, 'rb');
if (!$fd) {
$this->error = 3; // Cannot read file, probably permissions
return false;
}
$this->_str = fread($fd, $length);
fclose($fd);
} else {
$this->error = 2; // File doesn't exist
return false;
}
}
};
问题分析
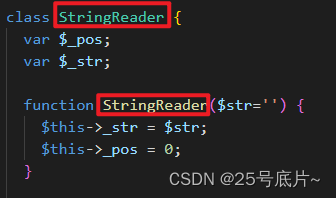
如上图:类名与方法名一致,故导致问题出现 ,需要将构造函数的命名从类名更改为__construct()
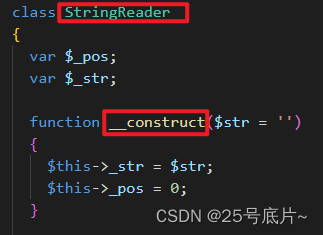
修改后代码
<?php
// Simple class to wrap file streams, string streams, etc.
// seek is essential, and it should be byte stream
class StreamReader
{
// should return a string [FIXME: perhaps return array of bytes?]
function read($bytes)
{
return false;
}
// should return new position
function seekto($position)
{
return false;
}
// returns current position
function currentpos()
{
return false;
}
// returns length of entire stream (limit for seekto()s)
function length()
{
return false;
}
};
class StringReader
{
var $_pos;
var $_str;
function __construct($str = '')
{
$this->_str = $str;
$this->_pos = 0;
}
function read($bytes)
{
$data = substr($this->_str, $this->_pos, $bytes);
$this->_pos += $bytes;
if (strlen($this->_str) < $this->_pos)
$this->_pos = strlen($this->_str);
return $data;
}
function seekto($pos)
{
$this->_pos = $pos;
if (strlen($this->_str) < $this->_pos)
$this->_pos = strlen($this->_str);
return $this->_pos;
}
function currentpos()
{
return $this->_pos;
}
function length()
{
return strlen($this->_str);
}
};
class FileReader
{
var $_pos;
var $_fd;
var $_length;
function __construct($filename)
{
if (file_exists($filename)) {
$this->_length = filesize($filename);
$this->_pos = 0;
$this->_fd = fopen($filename, 'rb');
if (!$this->_fd) {
$this->error = 3; // Cannot read file, probably permissions
return false;
}
} else {
$this->error = 2; // File doesn't exist
return false;
}
}
function read($bytes)
{
if ($bytes) {
fseek($this->_fd, $this->_pos);
// PHP 5.1.1 does not read more than 8192 bytes in one fread()
// the discussions at PHP Bugs suggest it's the intended behaviour
$data = '';
while ($bytes > 0) {
$chunk = fread($this->_fd, $bytes);
$data .= $chunk;
$bytes -= strlen($chunk);
}
$this->_pos = ftell($this->_fd);
return $data;
} else return '';
}
function seekto($pos)
{
fseek($this->_fd, $pos);
$this->_pos = ftell($this->_fd);
return $this->_pos;
}
function currentpos()
{
return $this->_pos;
}
function length()
{
return $this->_length;
}
function close()
{
fclose($this->_fd);
}
};
// Preloads entire file in memory first, then creates a StringReader
// over it (it assumes knowledge of StringReader internals)
class CachedFileReader extends StringReader
{
function __construct($filename)
{
if (file_exists($filename)) {
$length = filesize($filename);
$fd = fopen($filename, 'rb');
if (!$fd) {
$this->error = 3; // Cannot read file, probably permissions
return false;
}
$this->_str = fread($fd, $length);
fclose($fd);
} else {
$this->error = 2; // File doesn't exist
return false;
}
}
};























 513
513

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










