注解的优势:
虽然XML可以提高阅读性,但是如果XML中的文件较多,也会使XML文件变得臃肿,故还需要进行简化
什么是注解:
注解的主要作用:对我们的程序进行标注和解释。
注释和注解的区别:
注释:给程序员看的
注解:给编译器看的(让虚拟机看到程序中的注解,注解代表程序的一些特殊功能)
自定义注解
自定义注解格式:
public @interface 注解名称 {
}
示例:
package aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML;
public @interface Anno1 {
//定义一个基本类型的属性
int a () default 23;
//定义一个String类型的属性
public String name () ;
//定义一个Class类型的属性
public Class clazz() default Anno2.class;
//定义一个注解类型的属性
public Anno2 anno() default @Anno2;
//定义一个枚举类型的属性
public Season season() default Season.SPRING;
//以上类型的一维数组
public int[] arr() default {1,2,3,4,5};
//枚举数组
public Season[] seasons() default {Season.SPRING,Season.SUMMER};
}
//在使用时注解里的属性没有指定默认值会报错,需要手动给上
@Anno1(name = "dz666")
public class AnnoDemo {
}
注:在使用注解的时候如果注解里面的属性没有指定默认值//那么我们就需要手动给出注解属性的设置值。
但是存在特殊属性value:如果所有属性都有默认值,但value未给默认值,可以省略 value= ,直接给其赋值。(示例:@Anno1(value = "dz666")可以写成 - >
@Anno1("dz666"))
自定义注解小练习:
( 自 定 义 一 个 注 解 (@Test),用 于 指 定 类 上,如 果 某 一 个 类 的 方 法 上 使 用 了 该 注 解 , 就 执 行 该 方 法 )
UserTest
package aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML.ZidingYi;
public class UserTest {
public void show(){
System.out.println("UserTest...show");
}
@Test
public void method(){
System.out.println("UserTest...method");
}
@Test
public void function(){
System.out.println("UserTest...function");
}
}
Test
package aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML.ZidingYi;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Test {
}
AnnoDemo
package aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML.ZidingYi;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AnnoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.通过反射获取到UserTest类的字节码文件对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML.ZidingYi.UserTest");
//通过反射获取到这个类里所有的方法
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
UserTest usertest = (UserTest) clazz.newInstance();
//遍历数组,得到每一个对象
for (Method method : methods) {
//method依次表示每个方法对象
//通过查阅得知
//isAnnotationPresent (Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass)
//括号内的参数:注解的字节码文件(.class)
//返回值:布尔类型,true-存在 false-不存在
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Test.class)){
method.invoke(usertest);
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
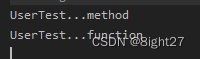
元注解
描述注解的注解
@Target: 指定了注解能在哪里使用
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) //指定注解的使用位置(成员变量,类,方法)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //指定该注解的存活时间
@Inherited //指定该注解可以被继承
public @interface Anno {
}
@Retention: 可以理解为保留时间(生命周期)
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) //指定注解的使用位置(成员变量,类,方法)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //指定该注解的存活时间
@Inherited //指定该注解可以被继承
public @interface Anno {
}
@Inherited: 表示修饰的白定义注解可以被子类继承
Anno:
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) //指定注解的使用位置(成员变量,类,方法)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //指定该注解的存活时间
@Inherited //指定该注解可以被继承
public @interface Anno {
}
Person
@Anno
public class Person {
}
Student
public class Student extends Person {
public void show(){
System.out.println("student...show...");
}
}
StudentDemo
package aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML.YuanZhuJie;
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取到Student类的字节码文件对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("aResumeitheima.Day_16.XML.YuanZhuJie.Student");
//查询注解是否被继承
boolean result = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Anno.class);
System.out.println(result);
}
}























 1613
1613

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








