一、resize()
void test7()
{
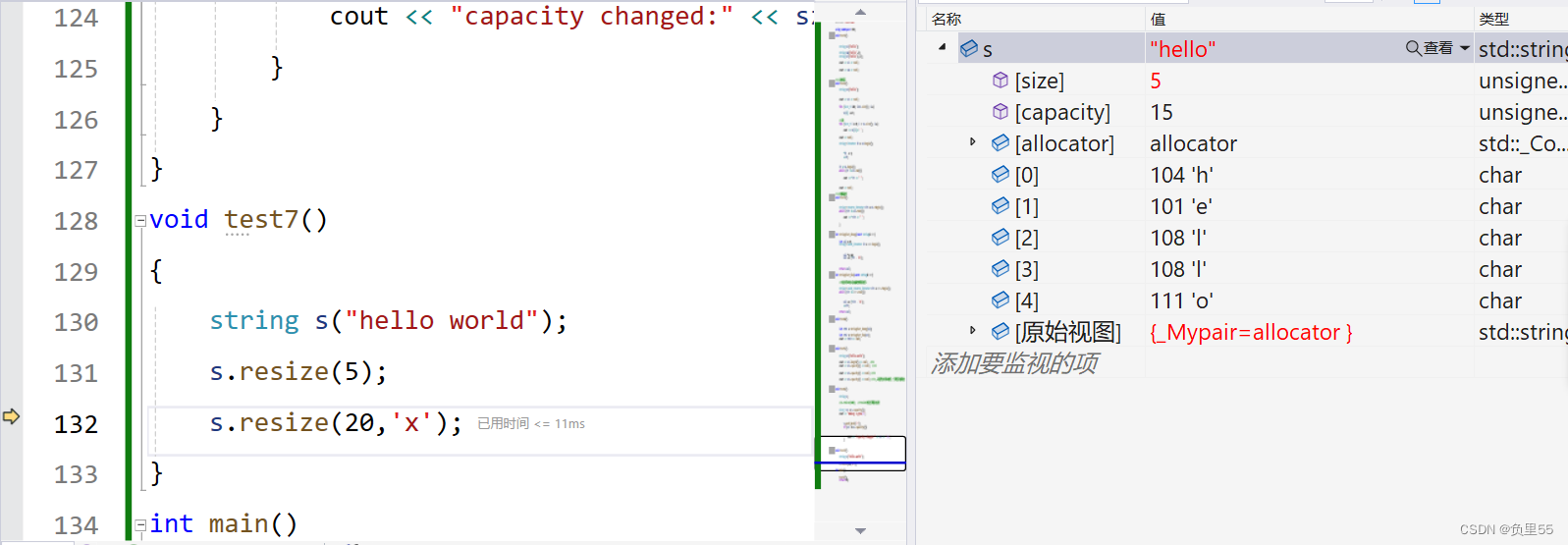
string s("hello world");
s.resize(5); //改变长度
s.resize(20,'x'); //改变空间大小
}
int main()
{
test7();
return 0;
}

二、string常用函数接口
1.打印
2.+=、push_back、append
3.迭代器,读写;s.begin()、s.end()、s.rbegin()、s.rend()
4. s.size()、s.length()、s.capacity()
5.s.reserve(100)、s.resize(100,'x')
6.s.insert(0,"x")、s.insert(s.begin(),"x")
7.s.erase(2,3)
8.s.substr(2,3) //从下标为2开始,往后打印3个
9.< >,比较的是字符的ascii码
10.getline(cin,s1),遇到换行结束;cin>>s1,遇到换行或空格结束
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//1.常规用法
void test1()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello");
string s3(s2); //拷贝构造
string s4("hello",2); //he,打印前两个
string s5("hello",1,2); //el,从第二个开始打印
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << s5 << endl;
}
//2.读和写
void test2()
{
string s1("hello");
s1 += ' ';
s1 += "world";
cout << s1 << endl;
//写
for (size_t i=0; i<s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i] += 1;
}
//读
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i]<<' ';
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器 写
string::iterator it = s1.begin(); //可将it看作指针
while (it != s1.end()) //end指向‘o’后面的位置
{
*it -= 1;
++it;
}
//迭代器 读
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
//3.倒着遍历
void test3()
{
string s1("hello");
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
whi







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1141
1141

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








