单输出感知机 梯度计算
"""
单一输出 单层感知机
"""
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random.normal([1, 3])
w = tf.ones([3, 1])
b = tf.ones([1])
y = tf.constant([1])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w, b])
y_prob = tf.sigmoid(x @ w + b)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(y, y_prob))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w, b])
print("求导梯度结果 w:\n", grads[0].numpy())
print("求导梯度结果 b:\n", grads[1].numpy())

多输出感知机 梯度计算
"""
多输出的单层感知机 梯度计算
"""
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random.normal([2, 4])
w = tf.random.normal([4, 3])
b = tf.zeros([3])
y = tf.constant([2, 0])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w, b])
y_prob = tf.nn.softmax(x @ w + b, axis=1)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(tf.one_hot(y,depth=3), y_prob))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w, b])
print("求导梯度结果 w:\n", grads[0].numpy())
print("求导梯度结果 b:\n", grads[1].numpy())
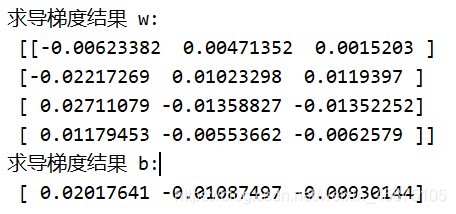







 本文介绍了使用TensorFlow实现单输出及多输出感知机的梯度计算过程。通过具体实例展示了如何利用GradientTape进行梯度追踪,并计算损失函数关于权重w和偏置b的梯度。
本文介绍了使用TensorFlow实现单输出及多输出感知机的梯度计算过程。通过具体实例展示了如何利用GradientTape进行梯度追踪,并计算损失函数关于权重w和偏置b的梯度。


















 341
341

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










