引言
1.对于AOP编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现,Spring就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程。然后,AspectJ也实现了AOP的功能。并且实现的更加简单、方便,并且还支持注解式开发。所以,spring又将AspectJ的对于AOP的实现也引入到了自己的框架中。
2.在Spring中使用AOP开发的时候,一般使用AspectJ的实现方式。
3.AspectJ是一个优秀的面向切面的框架,它扩展了java语言,提供了强大的切面实现,它是Eclipse的一个开源项目。
2.AspectJ的通知类型
AspectJ中常用的通知有五种类型:
1.前置通知@Before
2.后置通知@AfterReturning
3.环绕通知@Arround
4.异常通知@After Throwing
5.最终通知@After
3.AspectJ的切入点表达式



3.准备AspectJ的开发环境
1.加入Maven依赖
```xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.bjpowernode</groupId>
<artifactId>ch06-aop-aspectj</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--aspectj依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2.引入AspectJ依赖

4.AspectJ基于注解的AOP实现
实现步骤
a.定义业务接口和实现类
public interface SomeService {
void doSome(String name,Integer age);
}
//目标类 厂家
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome(String name,Integer age) {
//给doSome方法增加一个功能,在doSome()执行之前, 输出方法的执行时间
System.out.println("====目标方法doSome()====");
}
public void doOther(String name,Integer age) {
//给doSome方法增加一个功能,在doSome()执行之前, 输出方法的执行时间
System.out.println("====目标方法doSome()====");
}
}
b.定义切面类
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Aspect : 是aspectj框架中的注解。
* 作用:表示当前类是切面类。
* 切面类:是用来给业务方法增加功能的类,在这个类中有切面的功能代码
* 位置:在类定义的上面
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 定义方法,方法是实现切面功能的。
* 方法的定义要求:
* 1.公共方法 public
* 2.方法没有返回值
* 3.方法名称自定义
* 4.方法可以有参数,也可以没有参数。
* 如果有参数,参数不是自定义的,有几个特殊参数类型可以使用。
*/
/**
* @Before: 前置通知注解
* 属性:value ,是切入点表达式,表示切面的功能执行的位置。
* 位置:在方法的上面
* 特点:
* 1.在目标方法之前先执行的
* 2.不会改变目标方法的执行结果
* 3.不会影响目标方法的执行。
*/
@Before(value = "" +
"execution(" +
"public void com.bjpowernode.ba01.SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))" +
"")
public void myBefore(){
//就是你目标类要增加的功能代码
System.out.println("前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}
/*@Before(value = "execution(void com.bjpowernode.ba01.SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(){
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("1=====前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}*/
/* @Before(value = "execution(void *..SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(){
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("2=====前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}*/
/*@Before(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void myBefore(){
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("3=====前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}*/
/*@Before(value = "execution(* do*(..))")
public void myBefore2(){
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("4=====前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}*/
/*@Before(value = "execution(* com.bjpowernode.ba01.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void myBefore2(){
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("2=====前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}*/
/**
* 指定通知方法中的参数 : JoinPoint
* JoinPoint:业务方法,要加入切面功能的业务方法
* 作用是:可以在通知方法中获取方法执行时的信息, 例如方法名称,方法的实参。
* 如果你的切面功能中需要用到方法的信息,就加入JoinPoint.
* 这个JoinPoint参数的值是由框架赋予, 必须是第一个位置的参数
*/
@Before(value = "execution(void *..SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(JoinPoint jp){ //下面就是切面要执行的功能
//获取方法的完整定义
System.out.println("方法的签名(定义)="+jp.getSignature());
System.out.println("方法的名称="+jp.getSignature().getName());
//获取方法的实参
Object args [] = jp.getArgs();
for (Object arg:args){
System.out.println("参数="+arg);
}
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("2=====前置通知, 切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+ new Date());
}
}
c. 声明目标对和目标类对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--把对象交给spring容器,由spring容器统一创建,管理对象-->
<!--声明目标对象-->
<bean id="someService" class="com.bjpowernode.ba01.SomeServiceImpl" />
<!--声明切面类对象-->
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.bjpowernode.ba01.MyAspect" />
<!--声明自动代理生成器:使用aspectj框架内部的功能,创建目标对象的代理对象。
创建代理对象是在内存中实现的, 修改目标对象的内存中的结构。 创建为代理对象
所以目标对象就是被修改后的代理对象.
aspectj-autoproxy:会把spring容器中的所有的目标对象,一次性都生成代理对象。
-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<!--
有接口也想用cjlib实现动态代理:
如果你期望目标类有接口,使用cglib代理
proxy-target-class="true":告诉框架,要使用cglib动态代理
-->
<!-- <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>-->
</beans>
d.测试类中使用目标对象的id(测试前置通知@Before)
import com.bjpowernode.ba01.SomeService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest01 {
@Test
public void test01(){
String config="applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService) ctx.getBean("someService");
//com.sun.proxy.$Proxy8 :jdk动态代理
//com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
System.out.println("proxy:"+proxy.getClass().getName());
//通过代理的对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
proxy.doSome("lisi",20);
}
}
5.@Before前置通知-参数JoinPoint

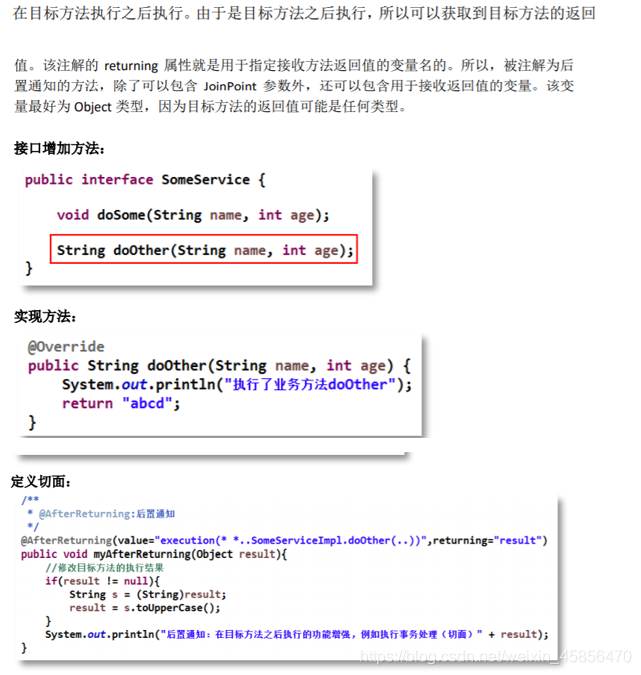
6.@AfterReturning后置通知-returning属性
7.@Around环绕通知- ProceedingJoinPoint 参数


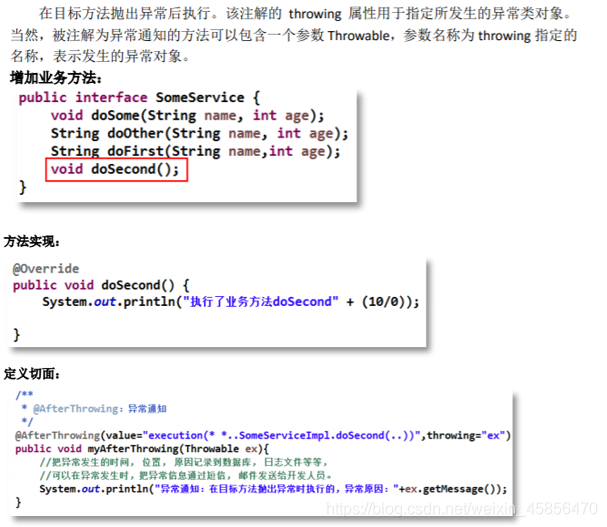
8.AfterThrowing异常通知-throwing属性
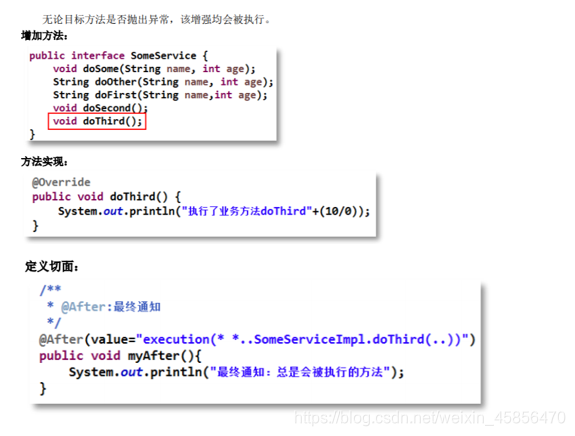
9.@After最终通知
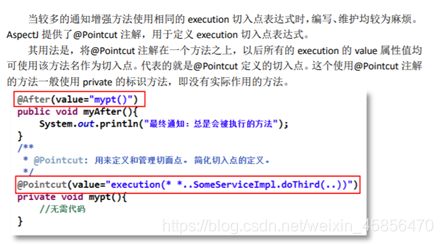
10.@Pointcut定义切入点





 本文介绍了AspectJ如何实现AOP,相较于Spring的AOP,AspectJ更简单且支持注解开发。AspectJ提供了五种通知类型:前置、后置、环绕、异常和最终通知。同时,文章详细阐述了AspectJ的切入点表达式、开发环境配置以及基于注解的AOP实现步骤,包括定义接口、切面类、目标对象和测试。最后,讲解了各种通知类型的使用,如@Before、@AfterReturning、@Around等。
本文介绍了AspectJ如何实现AOP,相较于Spring的AOP,AspectJ更简单且支持注解开发。AspectJ提供了五种通知类型:前置、后置、环绕、异常和最终通知。同时,文章详细阐述了AspectJ的切入点表达式、开发环境配置以及基于注解的AOP实现步骤,包括定义接口、切面类、目标对象和测试。最后,讲解了各种通知类型的使用,如@Before、@AfterReturning、@Around等。
















 4769
4769

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








