#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char*ps;
public:
String(char*p = " "):ps(new char[strlen(p)+1])
{
strcpy(ps, p);
}
~String()
{
delete[] ps;
ps = NULL;
}
String(const String&ref):ps(new char[strlen(ref.ps)+1])
{
strcpy(ps, ref.ps);
}
String &operator=(const String&ref)
{
if (this->ps != NULL)
{
delete[]ps;
ps = NULL;
}
this->ps = new char[strlen(ref.ps) + 1];
strcpy(this->ps, ref.ps);
return *this;
}
String &operator+=(const String&ref)
{
String a;
a.ps = new char[strlen(this->ps) + strlen(ref.ps) + 1];
strcpy(a.ps, this->ps);
strcat(a.ps, ref.ps);
this->ps = new char[strlen(a.ps) + 1];
strcpy(this->ps, a.ps);
return *this;
}
String operator+(const String&ref)const
{
String a;
a.ps= a.ps = new char[strlen(this->ps) + strlen(ref.ps) + 1];
strcpy(a.ps, this->ps);
strcat(a.ps, ref.ps);
return a;
}
bool operator==(const String&ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator!=(const String&ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) == 0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
bool operator<(const String&ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) < 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator>(const String&ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) >0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator<=(const String&ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) <= 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const String&ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) >=0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
char operator[](const int i)const
{
return this->ps[i];
}
void show()
{
cout << ps << endl;
}
};
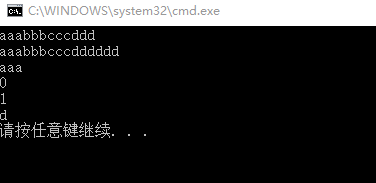
int main(){String s1("aaa");
String s2("bbb");
String s3("ccc");
String s4("ddd");
String s5;
s5 = s1 + s2 + s3 + s4;
s5.show();
s5 += s4;
s5.show();
s5 = s1;
s5.show();
if (s4 == s1)
{
cout << 1 <<endl;
}
else
{
cout << 0 << endl;
}
if (s4 != s1)
{
cout << 1 << endl;
}
else
{
cout << 0 << endl;
}
cout << s4[2] << endl;
return 0;
}
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








