1.红黑树
红黑树其实就是一种数据结构,设计它的目的就是为了高效地进行增删改查,
性能极其之高,仅通过几十次查询就能从百亿级的数据中查找到数据
而链表从百亿数据中找数据它就要查百亿次,百亿次的查找数据库是不能忍受的
它应用的地方很多,比如说java中的HashMap和TreeMap。还有就是linux也经常使用到。由于节点之间地址不连续,所以红黑树只适于存在内存的数据,不适合磁盘
所以该数据结构在面试的时候是一个常问问题
红黑树性质约束:
1.结点是红色或黑色
2.根结点是黑色
3.从根节点到叶子节点,不会出现两个连续的红色节点
4.对于任意一结点,其到叶子结点的每条路径上的黑色结点数相同
5.每个叶子结点是黑色null结点
红黑树底层是自平衡的二叉查找树(左节点小于根节点,右节点大于根结点),
我们在对红黑树进行插入和删除等操作时,对树做了修改,那么可能会违背红黑树的性质。
为了继续保持红黑树的性质约束,可以通过对结点进行重新着色(新插入的结点默认红色 )
以及对树进行相关的旋转操作来达到对红黑树进行插入或删除结点等操作后,继续保持它的性质和相对的平衡。
树的旋转,分为左旋
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-lfbmYCjR-1635320637881)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%8720200329163151-693b7880f7ee4f6fb6a1c40d859ce472.gif)]
和右旋
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jPD42ZVO-1635320637897)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%8720200329163141-5f49dab4302340baa54d2c691902a0af.gif)]
手撕红黑树相关问题
1.为什么要用红黑树?
使用红黑树能使节点的查找,插入,删除等操作时间复杂度最大为O(logn),极大地提高性能。
如果不使用红黑树,插入一个有序列表,会形成一个链表,完全丧失二叉查找树的优势,以致O(n)的时间复杂度。
2.插入操作实现原理
分为三种情况
(1)要插入的结点没有父结点
这种情况比较简单,直接这个结点为黑色根结点
(2)要插入结点的父节点是黑色
这种情况插入后对照红黑树性质 发现完全符合 所以直接将结点插入到黑色父结点后即可
(3)要插入结点的父结点是红色
很明显出现两个连续红色结点,这种情况相对复杂,此时调整又要分情况说,我们分别举例说明
1.叔叔结点是红色
例如下面要插入结点21
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LUkdZ7AI-1635320637898)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329155808-266f7f3adaa84221ab10bcc1f67368b7.png)]
发现叔叔结点27是红色
第一步 把21结点的父结点22变成黑色
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-f3LiOqHx-1635320637901)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329160636-8068d390add5447abf05dc3111827b83.png)]
变色后发现该条路径上黑色节点多余其他路径,继续调整
第二步 把22结点的父结点变为红色
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0nk39Zmn-1635320637902)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329161031-f206d985d79a40d89e236298689ce8c6.png)]
发现节点25和节点27是两个连续的红色结点,继续调整 但是这是不能往上走,会出现死胡同,因此往下编27的颜色
第三步 把结点27变为黑色
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-brtKswsi-1635320637904)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329161435-1f3e670f947d40e4931a7d28a931a4b5.png)]
这时结点17和结点25是两个连续的红色,继续调整
第四步 把结点17和结点8同时变为黑色
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XK2lqPXV-1635320637906)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329161704-45801b1a09fe42fdb546dc6bc38125ec.png)]
此时再对照一下那5条规则,发现完全符合。
2.叔叔结点是黑色
这时又要分情况
(1)新插入节点为父节点的左孩子
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-IsKct1Wi-1635320637908)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329162937-e9f4396509fb42efabb6c82b3d225f83.png)]
(2)新插入节点为父节点的右孩子
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HAoGyiO8-1635320637914)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329163002-30200864d5724db2b041e108bdaa5acd.png)]
按照第一遍的思路,我们对这两种情况执行同样的操作,最终也能保证红黑树的5条特征。
3.删除结点操作实现原理
删除结点分为3种情况
(1) 要删除的结点是叶子结点
这种情况如果是根结点或结点是红色,直接删除即可
如果叶子节点是黑色的,那么就需要进行调整,调整的步骤和插入时调整的步骤一样。
(2) 要删除的结点有一个子结点
先直接让它的子节点接上它的父结点 如果该子结点是红色,就可以不做调整
如果是黑色 调整的步骤和插入时调整的步骤一样。
(3) 要删除的结点有两个子结点
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WmJRMtJX-1635320637918)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2020/3/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20200329165150-1188a6aa51e14d5990298b945935af6a.png)]
若节点13之前是叶子节点,那就和第一种情况一样了,如果节点13是红色的,可以直接删除,
如果节点13是黑色的,那么就需要进行调整,此时的节点13就是叶子节点。调整的步骤和插入时调整的步骤一样。
若节点13之前还有子节点,那就和第二种情况一样了。那就继续替换和判断。
以上呢就是删除的情况,最后一种情况是修改,这种情况是查找和插入的结合体,也就是先找到要修改的元素,
修改完值之后,继续进行调整即可
实现的完整Java代码
结点
package RBTree;
import java.util.Objects;
public class RBTreeNode {
private final boolean RED = false;
private final boolean BLACK = true;
private int key;
private boolean color;
private RBTreeNode left;
private RBTreeNode right;
private RBTreeNode parent;
public RBTreeNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.color = RED;
}
public int getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public boolean getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(boolean color) {
this.color = color;
}
public RBTreeNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(RBTreeNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public RBTreeNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(RBTreeNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
public RBTreeNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(RBTreeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RBTreeNode{" +
",key=" + key +
", color=" + color +
'}';
}
}
树
package RBTree;
public class RBTree {
RBTreeNode root;
private final boolean RED = false;
private final boolean BLACK = true;
public RBTreeNode query(int key) {
RBTreeNode tmp = root;
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.getKey() == key)
return tmp;
else if (tmp.getKey() > key)
tmp = tmp.getLeft();
else
tmp = tmp.getRight();
}
return null;
}
public void insert(int key) {
RBTreeNode node = new RBTreeNode(key);
if (root == null) {
root = node;
node.setColor(BLACK);
return;
}
RBTreeNode parent = root;
RBTreeNode son = null;
if (key <= parent.getKey()) {
son = parent.getLeft();
} else {
son = parent.getRight();
}
//find the position
while (son != null) {
parent = son;
if (key <= parent.getKey()) {
son = parent.getLeft();
} else {
son = parent.getRight();
}
}
if (key <= parent.getKey()) {
parent.setLeft(node);
} else {
parent.setRight(node);
}
node.setParent(parent);
//fix up
insertFix(node);
}
private void insertFix(RBTreeNode node) {
RBTreeNode father, grandFather;
while ((father = node.getParent()) != null && father.getColor() == RED) {
grandFather = father.getParent();
if (grandFather.getLeft() == father) { //F为G左儿子的情况,如之前的分析
RBTreeNode uncle = grandFather.getRight();
if (uncle != null && uncle.getColor() == RED) {
setBlack(father);
setBlack(uncle);
setRed(grandFather);
node = grandFather;
continue;
}
if (node == father.getRight()) {
leftRotate(father);
RBTreeNode tmp = node;
node = father;
father = tmp;
}
setBlack(father);
setRed(grandFather);
rightRotate(grandFather);
} else { //F为G的右儿子的情况,对称操作
RBTreeNode uncle = grandFather.getLeft();
if (uncle != null && uncle.getColor() == RED) {
setBlack(father);
setBlack(uncle);
setRed(grandFather);
node = grandFather;
continue;
}
if (node == father.getLeft()) {
rightRotate(father);
RBTreeNode tmp = node;
node = father;
father = tmp;
}
setBlack(father);
setRed(grandFather);
leftRotate(grandFather);
}
}
setBlack(root);
}
public void delete(int key) {
delete(query(key));
}
private void delete(RBTreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return;
if (node.getLeft() != null && node.getRight() != null) {
RBTreeNode replaceNode = node;
RBTreeNode tmp = node.getRight();
while (tmp != null) {
replaceNode = tmp;
tmp = tmp.getLeft();
}
int t = replaceNode.getKey();
replaceNode.setKey(node.getKey());
node.setKey(t);
delete(replaceNode);
return;
}
RBTreeNode replaceNode = null;
if (node.getLeft() != null)
replaceNode = node.getLeft();
else
replaceNode = node.getRight();
RBTreeNode parent = node.getParent();
if (parent == null) {
root = replaceNode;
if (replaceNode != null)
replaceNode.setParent(null);
} else {
if (replaceNode != null)
replaceNode.setParent(parent);
if (parent.getLeft() == node)
parent.setLeft(replaceNode);
else {
parent.setRight(replaceNode);
}
}
if (node.getColor() == BLACK)
removeFix(parent, replaceNode);
}
//多余的颜色在node里
private void removeFix(RBTreeNode father, RBTreeNode node) {
while ((node == null || node.getColor() == BLACK) && node != root) {
if (father.getLeft() == node) { //S为P的左儿子的情况,如之前的分析
RBTreeNode brother = father.getRight();
if (brother != null && brother.getColor() == RED) {
setRed(father);
setBlack(brother);
leftRotate(father);
brother = father.getRight();
}
if (brother == null || (isBlack(brother.getLeft()) && isBlack(brother.getRight()))) {
setRed(brother);
node = father;
father = node.getParent();
continue;
}
if (isRed(brother.getLeft())) {
setBlack(brother.getLeft());
setRed(brother);
rightRotate(brother);
brother = brother.getParent();
}
brother.setColor(father.getColor());
setBlack(father);
setBlack(brother.getRight());
leftRotate(father);
node = root;//跳出循环
} else { //S为P的右儿子的情况,对称操作
RBTreeNode brother = father.getLeft();
if (brother != null && brother.getColor() == RED) {
setRed(father);
setBlack(brother);
rightRotate(father);
brother = father.getLeft();
}
if (brother == null || (isBlack(brother.getLeft()) && isBlack(brother.getRight()))) {
setRed(brother);
node = father;
father = node.getParent();
continue;
}
if (isRed(brother.getRight())) {
setBlack(brother.getRight());
setRed(brother);
leftRotate(brother);
brother = brother.getParent();
}
brother.setColor(father.getColor());
setBlack(father);
setBlack(brother.getLeft());
rightRotate(father);
node = root;//跳出循环
}
}
if (node != null)
node.setColor(BLACK);
}
private boolean isBlack(RBTreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return true;
return node.getColor() == BLACK;
}
private boolean isRed(RBTreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return false;
return node.getColor() == RED;
}
private void leftRotate(RBTreeNode node) {
RBTreeNode right = node.getRight();
RBTreeNode parent = node.getParent();
if (parent == null) {
root = right;
right.setParent(null);
} else {
if (parent.getLeft() != null && parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(right);
} else {
parent.setRight(right);
}
right.setParent(parent);
}
node.setParent(right);
node.setRight(right.getLeft());
if (right.getLeft() != null) {
right.getLeft().setParent(node);
}
right.setLeft(node);
}
private void rightRotate(RBTreeNode node) {
RBTreeNode left = node.getLeft();
RBTreeNode parent = node.getParent();
if (parent == null) {
root = left;
left.setParent(null);
} else {
if (parent.getLeft() != null && parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(left);
} else {
parent.setRight(left);
}
left.setParent(parent);
}
node.setParent(left);
node.setLeft(left.getRight());
if (left.getRight() != null) {
left.getRight().setParent(node);
}
left.setRight(node);
}
private void setBlack(RBTreeNode node) {
node.setColor(BLACK);
}
private void setRed(RBTreeNode node) {
node.setColor(RED);
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(root);
}
private void inOrder(RBTreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.getLeft());
System.out.println(node);
inOrder(node.getRight());
}
}
HashTable(哈希表也叫散列表)底层的put方法使用Synchronized保证线程安全,是一种非常重要的数据结构,与HashMap相似的键值对
但是不可以接受null,应用场景很多。
HashMap的数组称为哈希桶 每个桶包含四个字段
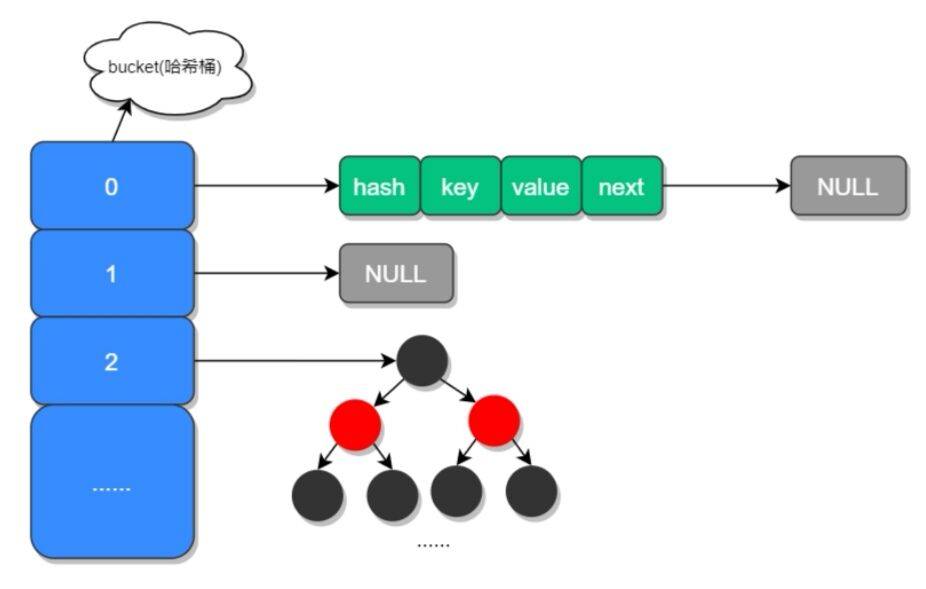
Java7是先扩容再插入新值,头插法,结构是数组+链表,hash采用取模运算
Java8是先插入后扩容,尾插法,结构是数组+链表+红黑树,hash采用高位与运算。
Java7的头插法在并发插入数据时可能会形成环,接下来的get查询方法就会死循环(就是指针在两个节点之间互相引用)
Java8采用尾插法解决了死循环问题。
HashMap是线程不安全的,他的put方法在线程并发时可能会丢失数据
put方法的执行过程
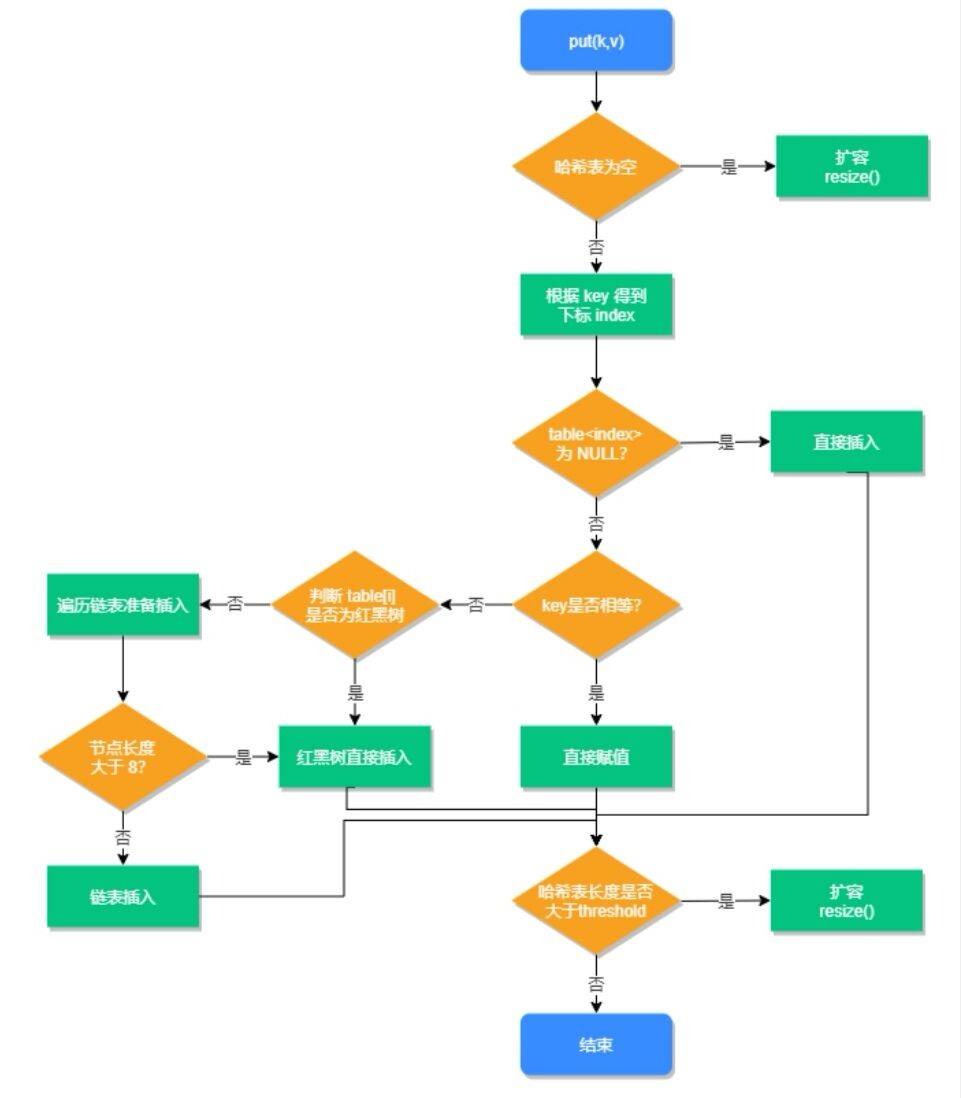
HashMap有四种构造方法,它的无参构造函数 默认初始容量为16,默认负载因子为0.75 ,即容量达到12(阈值16*0.75)时便扩容一倍,
java7扩容后是重新对元素取模哈希,Java8是通过高位与运算来确定元素是否要移动 结果为0表示不移动 极大地提高了性能, 容量始终是2的幂次倍。
默认0.75的负载因子较为合适,负载因子为0.5太低,临时阈值明显会很小,这样会造成分配内存的浪费,也不满足了哈希表均匀分布的情况。
如果负载因子达到了1的情况,也就是Entry数组存满了才发生扩容,会出现大量的哈希冲突的情况,出现链表过长,因此造成get查询数据的效率。
Java8使用一个Node数组取代了JDK7的Entry数组来存储数据,这个Node可能是链表结构,也可能是红黑树结构,红黑树极大地提高了性能;
如果插入的元素key的hashcode值相同,那么这些key也会被定位到Node数组的同一个格子里,如果不超过8个使用链表存储;
超过8个,会调用treeifyBin函数,将链表转换为红黑树。那么即使所有key的hashcode完全相同,由于红黑树的特点,
查找某个特定元素,也只需要O(logn)的开销。 红节点的子节点一定是黑色 ,一个节点到null的所有路径中的黑节点数目相同
新插入的节点为红色 保持红黑树的结构会进行颜色变换和旋转
深入理解红黑树可以看我另一篇博文
深度优先搜索算法
(英语:Depth-First-Search,DFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。当节点v的所在边都己被探寻过,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。这一过程一直进行到已发现从源节点可达的所有节点为止。如果还存在未被发现的节点,则选择其中一个作为源节点并重复以上过程,整个进程反复进行直到所有节点都被访问为止。属于盲目搜索。
深度优先搜索是图论中的经典算法,利用深度优先搜索算法可以产生目标图的相应拓扑排序表,利用拓扑排序表可以方便的解决很多相关的图论问题,如最大路径问题等等。
简单说:就是一头扎到底的玩法。我们选择一条支路,尽可能不断地深入,如果遇到死路就往回退,回退过程中如果遇到没探索过的支路,就进入该支路继续深入
因发明「深度优先搜索算法」,约翰 · 霍普克洛夫特与罗伯特 · 塔扬在1986年共同获得计算机领域的最高奖:图灵奖。
嘻嘻 配一张与约翰 · 霍普克洛夫特爷爷的合照
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4gCQP1hA-1635320711817)(http://huangxiaohua.top/upload/2019/11/1569426896197-5cbc219744734d06b6d277bff480febb.jpeg)]
1. 合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠,他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
递归实现的Java代码
public class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if(t1==null)
return t2;
if(t2==null)
return t1;
t1.val+=t2.val;
t1.right=mergeTrees(t1.right,t2.right);
t1.left=mergeTrees(t1.left,t2.left);
return t1;
}
}
2.根据中序,后序遍历数组还原二叉树
public class Solution6 {
int inIndex;
int postIndex;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
inIndex=inorder.length-1;
postIndex=postorder.length-1;
return helper(inorder,postorder,(long)Integer.MAX_VALUE+1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] inorder, int[] postorder, long stop){
if(postIndex<0){
return null;
}
if(inorder[inIndex]==stop){
inIndex--;
return null;
}
int val=postorder[postIndex--];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(val);
root.right=helper(inorder,postorder,val);
root.left=helper(inorder,postorder,stop);
return root;
}
}
根据后序遍历的特点,知最后为根结点,连续将后序遍历的后面元素按顺序依次转成树的右节点,
直到该结点的值等于中序遍历数组的最后一个元素才返回null,
根据中序 前序遍历数组还原二叉树
也是同理相反,连续将前序遍历数组按顺序写到树的左结点,直到该结点的值等于中序遍历数组的第一个元素才返回null
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder.length==0 || inorder.length==0) {
return null;
}
//根据前序数组的第一个元素,就可以确定根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
for(int i=0;i<preorder.length;++i) {
//用preorder[0]去中序数组中查找对应的元素
if(preorder[0]==inorder[i]) {
//将前序数组分成左右两半,再将中序数组分成左右两半
//之后递归的处理前序数组的左边部分和中序数组的左边部分
//递归处理前序数组右边部分和中序数组右边部分
int[] pre_left = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1,i+1);
int[] pre_right = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,i+1,preorder.length);
int[] in_left = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,i);
int[] in_right = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,i+1,inorder.length);
root.left = buildTree(pre_left,in_left);
root.right = buildTree(pre_right,in_right);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
}
3.有序链表转换为二叉搜索树
给定一个单链表,其中的元素按升序排序,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
/**
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
/**
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
else if(head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode p = pre.next;
ListNode q = p.next;
//找到链表的中点p
while(q!=null && q.next!=null){
pre = pre.next;
p = pre.next;
q = q.next.next;
}
pre.next = null;//将中点左边的链表分开
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(p.val);
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
root.right = sortedListToBST(p.next);
return root;
}
}
快慢指针找到链表的中间结点,该结点为根结点 循环这个操作
4.路径总和2
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> inner = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return list;
sum -= root.val;
inner.add(root.val); // 入列表
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
if (sum == 0){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(inner)); // 记得拷贝一份
}
}
if (root.left != null) pathSum(root.left, sum);
if (root.right != null) pathSum(root.right, sum);
inner.remove(inner.size()-1); //从列表中删除
return list;
}
}
岛屿最大面积
给定一个包含了一些 0 和 1的非空二维数组 grid , 一个 岛屿 是由四个方向 (水平或垂直) 的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合。你可以假设二维矩阵的四个边缘都被水包围着。找到给定的二维数组中最大的岛屿面积。(如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为0。
public class Solution13 {
int X,Y;
// 用于向四周访问
int[] xarr = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int[] yarr = {0, 0, -1, 1};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
// 获取X和Y
X = grid.length;
Y = grid[0].length;
int ans = 0;
// 遍历整个数组
for (int i = 0; i < X; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < Y; j++) {
// 出现了陆地则进行深搜
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
int sum = dfs(grid, i, j);
// 选出最大的面积
if (sum > ans) {
ans = sum;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public int dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j) {
int sum = 1; // 能进入该方法,岛屿面积默认为1
grid[i][j] = 0; // 访问了,则将该陆地变为海洋
// 向四周访问
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + xarr[k];
int y = j + yarr[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < X && y >= 0 && y < Y && grid[x][y] == 1) {
sum += dfs(grid, x, y);
}
}
return sum;
}
}







 本文深入探讨了红黑树的性质、插入删除操作及其实现原理,展示了如何保持红黑树的平衡。此外,还介绍了哈希表的实现,特别是Java中的HashMap和TreeMap,讨论了它们的插入、删除和查找操作。最后,文章提到了深度优先搜索算法及其在二叉树问题中的应用。
本文深入探讨了红黑树的性质、插入删除操作及其实现原理,展示了如何保持红黑树的平衡。此外,还介绍了哈希表的实现,特别是Java中的HashMap和TreeMap,讨论了它们的插入、删除和查找操作。最后,文章提到了深度优先搜索算法及其在二叉树问题中的应用。
















 951
951

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








