1.数据输入
1.1 操作步骤
1. 导入Scanner:import java.util.Scanner; // 必须写在类的声明之前。
2. Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
3. 如果要获取整数:int a = sc.nextInt();
4. 如果要获取浮点型:double d = sc.nextDouble();
5. 当整个程序的输入结束后 需要sc.close();
2.流程控制
2.1 顺序结构
按照代码的先后顺序,依次执行;
2.2 分支结构
2.2.1 if单分支结构
if(关系表达式){
语句体;
}
首先计算关系表达式的值
为true则执行语句体
为false则不执行语句体(跳过)
2.2.2 if - else 双分支结构
if(关系表达式){
语句体1;
}else{
语句体2;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ifDemo{
/*需求:任意给出一个整数,请用程序实现判断该整数是奇数还是偶数,
并在控制台输出该整数是奇数还是偶数。
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(String.in);
System.out.pringln("请输入你要判断的整数:");
// 获取一个整数
int number = sc.nextInt();
// 对输入的整数进行判断 与2进行求余运算
if(number % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(number + "为偶数");
}
else if(number % 2 == 1){
System.out.println(number + "为奇数");
}
}
}
2.2.3 if - else if 多分支结构
if(关系表达式1){
语句体1;
}else if(关系表达式2){
语句体2;
}
.
.
.
else{
语句体n+1;
}
2.2.4 分支嵌套
import java.util.Scanner;
class IfDemo2
{
/*
需求:小明快要期末考试了,小明爸爸对他说,会根据他不同的考试成绩,
送他不同的礼物,假如你可以控制小明的得分,请用程序实现小明到底该获得什么样的礼物,
并在控制台输出
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(String.in);
System.out.println("请输入小明的考试成绩:");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if(score >= 0 && score <= 100){
if(score >= 95 && score <= 100){
System.out.println("奖励自行车一辆");
}else if(score >= 90 && score <= 94){
System.out.println("奖励游乐园玩一次");
}else if(score >= 80 && score <= 89){
System.out.println("奖励变形金刚玩具一个");
}else{
System.out.println("奖励胖揍一顿");
}
}
sc.close();
}
}
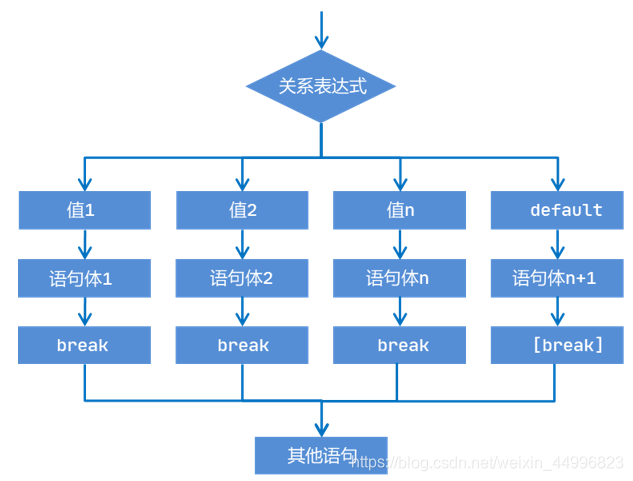
2.2.5 switch语句格式
Switch(表达式) //表达式的类型:byte short int char 枚举 String ( jdk7开始 )
{
case 值1:
语句1;
break;
。
。
。
default:
语句n+1;
break;
}
2.2.6 Switch执行流程:
1. 首先计算表达式的值。
2. 依次和case后面的值进行比较,如果有对应的值,就会执行相应的语句,再执行过程中,遇到break就会结束
3. 如果所有的case后面的值和表达式的值都不匹配,就会执行default里面的语句体,然后结束程序。
注意事项:
1. switch的表达式类型:byte short int char (这是jdk1.5)还可以是枚举,jdk7引入了String
2. 在每一个case及default后面要加上break,否则会出现case穿透;
3. default可以出现在任意位置,但一般写在末尾;
import java.util.Scanner;
class SwitchDome1
{
/*
需求:一年有12个月,分属于春夏秋冬4个季节,键盘录入一个月份,请用程序实现判断该月份属于哪个季节,并输出。
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("请输入你要判断的月份:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(String.in);
int month = sc.nextInt();
switch(month){
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println(month + "月份是春季");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
System.out.println(month + "月份是夏季");
break;
case 9:
case 10:
case 11:
System.out.println(month + "月份是秋季");
break;
case 12:
case 1:
case 2:
System.out.println(month + "月份是冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("无效输入");
break;
}
}
}
// 字符串switch
String str == "audi";
switch (str){
case "audi":
System.out.println("我买了台奥迪");
break;
case "benz":
System.out.println("我买了台奔驰");
break;
default:
System.out.println("比亚迪,挺好!");
}
if和switch的区别:
if:适用于对一定范围的数据的判断。
switch:适用于对有穷数据,而且数据是可以列举有限的判断。
2.3 循环结构
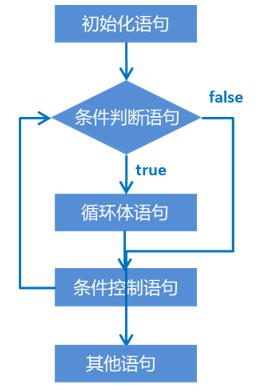
2.3.1 for循环语句
循环结构组成:
初始化语句:
条件判断语句:
循环体语句:
条件控制语句:
2.3.2 for 循环语句格式
for(初始化语句;条件判断语句;条件控制语句)
{
循环体语句;
}
执行流程:
1. 执行初始化语句
2. 执行条件判断语句,看其结果是true还是false
false:循环结束
true:继续执行
3. 执行循环体语句
4. 执行条件控制语句
5. 回到2.继续
//输出数据
class ForDemo1
{
/*
需求:在控制台输出1-5和5-1的数据
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
for(int i = 5; i >= 1; i--){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
// 求和
class ForDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 定义一个变量来保存和
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++){
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
class ForDemo3
{
// 求1--100之间所有的偶数的和
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int sum = 0 ;
for(int i = 1 ; i <=100; i++){
if( i % 2 == 0){
sum += i;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
class ForDemo4
{
/*
案例:水仙花
什么是“水仙花数”?
水仙花数是一个三位数
111 222 333 370 371 520 999
水仙花数的个位、十位、百位的数字立方和等于原数
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 100 ; i < 1000 ; i++){
int ge = i % 10 ;
int bai = i / 100;
int shi = i /10 %10;
int sum = ge * ge * ge + shi * shi *shi + bai * bai *bai;
if(i == sum){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
class ForDemo4
{
/*
案例:统计水仙花数的个数
什么是“水仙花数”?
水仙花数是一个三位数
111 222 333 370 371 520 999
水仙花数的个位、十位、百位的数字立方和等于原数
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 100 ; i < 1000 ; i++){
int ge = i % 10 ;
int bai = i / 100;
int shi = i /10 %10;
int sum = ge * ge * ge + shi * shi *shi + bai * bai *bai;
if(i == sum){
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
2.3.3 while循环语句格式
初始化语句;
while(条件判断语句){
循环语句;
条件控制语句;
}
class WhileDemo
{
/*
需求:世界最高山峰是珠穆朗玛峰(8844.43米=8844430毫米),
假如我有一张足够大的纸,它的厚度是0.1毫米。
请问,我折叠多少次,可以折成珠穆朗玛峰的高度?
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int number = 0;
double paper = 0.1;//单位为毫米
int zf = 8844430;//单位为毫米
while(paper <= zf){
paper = paper * 2;
number++;
}
System.out.println(number);
}
}
2.3.4 do…while循环语句格式
初始化语句;
do{
循环体语句;
}while(条件判断语句);
2.3.5 三者区别
for的初始化语句在循环体内,
while的初始化语句在结构体外,循环结束后仍可以使用初始化语句
while和do ... while区别在于判断语句的先后判断
// while和do...while的区别
int j = 0;
while (j < 0)
{
System.out.println(j);
j++;
}
int x = 0;
do
{
System.out.println(x);
x++;
}
while (x <= 0);
2.3.6 死循环
while (true){
System.out.println("**************");
}
for ( ;true; )
{
System.out.println("---------");
}
2.3.7 循环嵌套
在控制台上输出九九乘法表;
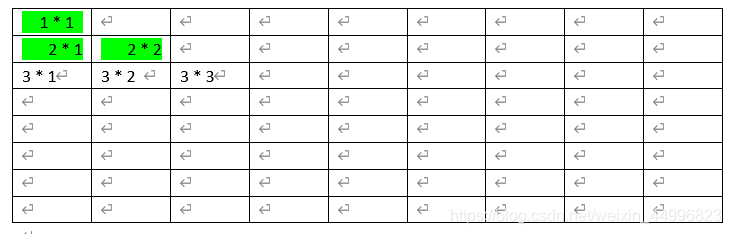
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 1;i <= 9 ; i++){ // 外循环控制行 外循环循环一次,内循环循环多次
for (int j = 1 ; j <= i ; j++){ // 内循环控制列
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + i * j + "\t");
// System.out.println("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class ForForDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 模拟始终的分 针走动60次 时针走动一次
for(int hour = 0 ; hour < 24 ; hour++){
for(int min = 0; min<60 ; min++){
System.out.println("当前时间为:" + hour +"时" + min +"分");
}
}
}
}
3. 跳转控制语句
3.1 概述
continue
break
当没有其他控制的时候,break 和 continue 只能控制离他最近的循环
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 查找1-100之间的整数,第一个可以同时被 23 整除
/*
for (int i = 1;i <= 100 ;i++ ){
if ( i % 23 == 0 ){
System.out.println(i);
break; //终止当前循环,后续循环都将不再执行
}
}
*/
// 查找1-5之间的整数,第一个可以同时被 3 整除
for (int i = 1;i <= 5 ;i++ ){
if ( i % 3 == 0 ){
continue; // 结束本次循环,继续下次循环;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
// break 和 continue 之后不能有语句,因为执行不到
}
}
3.2 跳转标记(仅作了解)
class BreakDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 查找1--5之间的整数中 第一个能被3整除的数
out:for( int i = 1 ; i <= 5; i++){
for(int j = 1 ; j < 10; j++){
if( j == 3 ){
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++");
continue out;
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
}
}
}
}
不推荐使用





 本文详细介绍了Java编程语言的基础知识,包括数据输入方法、流程控制结构(如if-else、switch-case)、循环结构(for、while、do-while)以及跳转控制语句(break、continue)。通过多个实例演示了如何运用这些基本概念解决实际问题。
本文详细介绍了Java编程语言的基础知识,包括数据输入方法、流程控制结构(如if-else、switch-case)、循环结构(for、while、do-while)以及跳转控制语句(break、continue)。通过多个实例演示了如何运用这些基本概念解决实际问题。
















 1135
1135

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








